概述
- 属于行为型模式
- 将算法与其作用的对象隔离开
- 动机:由于需求的变化,某些类层次结构中常常需要增加新的行为(方法),如果直接在基类中做这样的更改,将会给子类带来很繁重的负担,甚至破坏原有设计
- 如何在不更改类层次结构的前提下,在运行时根据需要透明地为类层次结构上的各个类动态添加新的操作,从而避免上述问题?
- 能预料到加操作,但不知道要加多少,加什么样的操作
- 在Visitor1, Visitor2中添加操作,实现扩展
- 虚函数:找运行时类型,多态对象
- 定义:表示一个作用域某对象结构(Element/ElementA/ElementB)中的各元素的操作,使得可以在不改变(稳定)各元素的类的前提下定义(扩展)作用于这些元素的新操作(变化)
- 符合开闭原则
- 写Visitor时必须知道Element有几个子类,这就要求Element的子类个数确定(缺点)
- 如果Element类的层次结构不能稳定,则不能用Visitor模式
- Visitor模式通过双重分发(double dispatch),来实现在不更改(不添加新的操作-编译时)Element类层次结构的前提下,在运行时透明地为类层次结构添加新的操作(支持变化)
- 双重分发:Visitor模式中间包括了两个多态分发(注意其中的多态机制):第一个为accept方法的多态辨析,第二个为visitElementX方法的多态辨析
- Visitor模式的最大缺点在于扩展类层次结构(增添新的Element子类),会导致Visitor类的改变,因此Visitor模式适用于“Element类层次结构稳定,而其中的操作却经常面临频繁改动”
- 前提条件太严格,导致实际开发中用的很少
- 重载(overload):方法名称相同,参数不同,调用时根据参数区分执行哪个方法,如多个构造函数(早绑定,编译时)
- 覆写(override):重写一个方法,如实现接口,子类覆盖父类方法(晚绑定,运行时,多态)
- 双分发(double dispatch):在重载时使用动态绑定
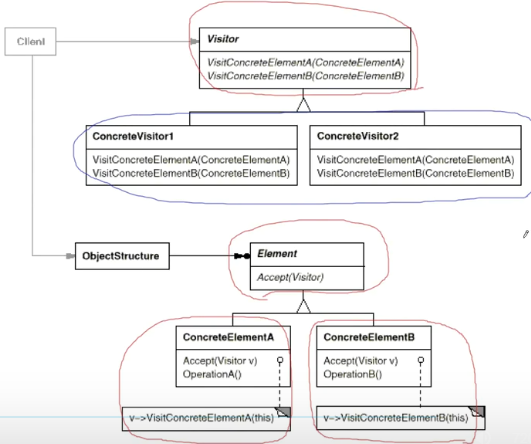
结构
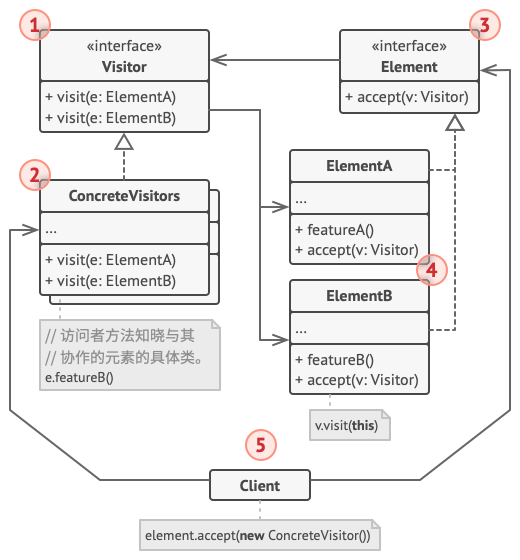
- 访问者接口:声明以对象结构的具体元素为参数的访问者方法
- 具体访问者:为不同的具体元素类实现想用行为的几个不同版本
- 元素接口:声明了一个方法来接收访问者,该方法必须有一个参数被声明为访问者接口类型
- 具体元素:实现接收方法,该方法可根据当前元素类将其调用重定向到相应访问者的方法
- 客户端:作为集合或其他复杂对象的代表,通过抽象接口与集合中的对象进行交互
示例1
Visitor1.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Visitor; 5 6 class Element 7 { 8 public: 9 virtual void Func1() = 0; 10 11 virtual void Func2(int data)=0; 12 virtual void Func3(int data)=0; 13 //... 14 15 virtual ~Element(){} 16 }; 17 18 class ElementA : public Element 19 { 20 public: 21 void Func1() override{ 22 //... 23 } 24 25 void Func2(int data) override{ 26 //... 27 } 28 29 }; 30 31 class ElementB : public Element 32 { 33 public: 34 void Func1() override{ 35 //*** 36 } 37 38 void Func2(int data) override { 39 //*** 40 } 41 42 };
Visitor2.cpp

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Visitor; 5 6 class Element 7 { 8 public: 9 virtual void accept(Visitor& visitor) = 0; //第一次多态辨析 10 11 virtual ~Element(){} 12 }; 13 14 class ElementA : public Element 15 { 16 public: 17 void accept(Visitor &visitor) override { 18 visitor.visitElementA(*this); 19 } 20 21 }; 22 23 class ElementB : public Element 24 { 25 public: 26 void accept(Visitor &visitor) override { 27 visitor.visitElementB(*this); //第二次多态辨析 28 } 29 30 }; 31 32 class Visitor{ 33 public: 34 virtual void visitElementA(ElementA& element) = 0; 35 virtual void visitElementB(ElementB& element) = 0; 36 37 virtual ~Visitor(){} 38 }; 39 40 //================================== 41 42 //扩展1 43 class Visitor1 : public Visitor{ 44 public: 45 void visitElementA(ElementA& element) override{ 46 cout << "Visitor1 is processing ElementA" << endl; 47 } 48 49 void visitElementB(ElementB& element) override{ 50 cout << "Visitor1 is processing ElementB" << endl; 51 } 52 }; 53 54 //扩展2 55 class Visitor2 : public Visitor{ 56 public: 57 void visitElementA(ElementA& element) override{ 58 cout << "Visitor2 is processing ElementA" << endl; 59 } 60 61 void visitElementB(ElementB& element) override{ 62 cout << "Visitor2 is processing ElementB" << endl; 63 } 64 }; 65 66 int main() 67 { 68 Visitor2 visitor; 69 ElementB elementB; 70 elementB.accept(visitor);// double dispatch 71 72 ElementA elementA; 73 elementA.accept(visitor); 74 75 return 0; 76 }
- 70:分发到26,再到61(给ElementB添加Visitor2操作),同理73->18->58(double dispatch 二次多态辨析)
示例2
- 通过访问者模式为几何图像层次结构添加对于XML文件导出功能的支持
- 在原有图形类中增加accept()方法
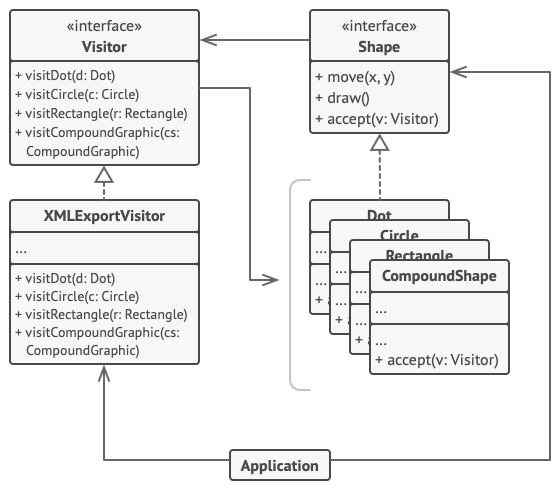

1 // 元素接口声明了一个`accept(接收)`方法,它会将访问者基础接口作为一个参 2 // 数。 3 interface Shape is 4 method move(x, y) 5 method draw() 6 method accept(v: Visitor) 7 8 // 每个具体元素类都必须以特定方式实现`accept`方法,使其能调用相应元素类的 9 // 访问者方法。 10 class Dot implements Shape is 11 // ... 12 13 // 注意我们正在调用的`visitDot(访问点)`方法与当前类的名称相匹配。 14 // 这样我们能让访问者知晓与其交互的元素类。 15 method accept(v: Visitor) is 16 v.visitDot(this) 17 18 class Circle implements Shape is 19 // ... 20 method accept(v: Visitor) is 21 v.visitCircle(this) 22 23 class Rectangle implements Shape is 24 // ... 25 method accept(v: Visitor) is 26 v.visitRectangle(this) 27 28 class CompoundShape implements Shape is 29 // ... 30 method accept(v: Visitor) is 31 v.visitCompoundShape(this) 32 33 34 // 访问者接口声明了一组与元素类对应的访问方法。访问方法的签名能让访问者准 35 // 确辨别出与其交互的元素所属的类。 36 interface Visitor is 37 method visitDot(d: Dot) 38 method visitCircle(c: Circle) 39 method visitRectangle(r: Rectangle) 40 method visitCompoundShape(cs: CompoundShape) 41 42 // 具体访问者实现了同一算法的多个版本,而且该算法能与所有具体类进行交互。 43 // 44 // 访问者模式在复杂对象结构(例如组合树)上使用时能发挥最大作用。在这种情 45 // 况下,它可以存储算法的一些中间状态,并同时在结构中的不同对象上执行访问 46 // 者方法。这可能会非常有帮助。 47 class XMLExportVisitor implements Visitor is 48 method visitDot(d: Dot) is 49 // 导出点(dot)的 ID 和中心坐标。 50 51 method visitCircle(c: Circle) is 52 // 导出圆(circle)的 ID 、中心坐标和半径。 53 54 method visitRectangle(r: Rectangle) is 55 // 导出长方形(rectangle)的 ID 、左上角坐标、宽和长。 56 57 method visitCompoundShape(cs: CompoundShape) is 58 // 导出图形(shape)的 ID 和其子项目的 ID 列表。 59 60 61 // 客户端代码可在不知晓具体类的情况下在一组元素上运行访问者操作。“接收”操 62 // 作会将调用定位到访问者对象的相应操作上。 63 class Application is 64 field allShapes: array of Shapes 65 66 method export() is 67 exportVisitor = new XMLExportVisitor() 68 69 foreach (shape in allShapes) do 70 shape.accept(exportVisitor)
示例3


1 public interface ComputerPart { 2 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor); 3 } 4 5 public class Keyboard implements ComputerPart { 6 7 @Override 8 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor) { 9 computerPartVisitor.visit(this); 10 } 11 } 12 13 public class Monitor implements ComputerPart { 14 15 @Override 16 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor) { 17 computerPartVisitor.visit(this); 18 } 19 } 20 21 public class Mouse implements ComputerPart { 22 23 @Override 24 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor) { 25 computerPartVisitor.visit(this); 26 } 27 } 28 29 public class Computer implements ComputerPart { 30 31 ComputerPart[] parts; 32 33 public Computer(){ 34 parts = new ComputerPart[] {new Mouse(), new Keyboard(), new Monitor()}; 35 } 36 37 38 @Override 39 public void accept(ComputerPartVisitor computerPartVisitor) { 40 for (int i = 0; i < parts.length; i++) { parts[i].accept(computerPartVisitor); } computerPartVisitor.visit(this); } } 41 42 public interface ComputerPartVisitor { 43 public void visit(Computer computer); 44 public void visit(Mouse mouse); 45 public void visit(Keyboard keyboard); 46 public void visit(Monitor monitor); 47 } 48 49 public class ComputerPartDisplayVisitor implements ComputerPartVisitor { 50 51 @Override 52 public void visit(Computer computer) { 53 System.out.println("Displaying Computer."); 54 } 55 56 @Override 57 public void visit(Mouse mouse) { 58 System.out.println("Displaying Mouse."); 59 } 60 61 @Override 62 public void visit(Keyboard keyboard) { 63 System.out.println("Displaying Keyboard."); 64 } 65 66 @Override 67 public void visit(Monitor monitor) { 68 System.out.println("Displaying Monitor."); 69 } 70 } 71 72 public class VisitorPatternDemo { 73 public static void main(String[] args) { 74 75 ComputerPart computer = new Computer(); 76 computer.accept(new ComputerPartDisplayVisitor()); 77 } 78 }
Displaying Mouse. Displaying Keyboard. Displaying Monitor. Displaying Computer.
参考
双分发
https://refactoringguru.cn/design-patterns/visitor-double-dispatch
