作业08-集合
1.本周学习总结
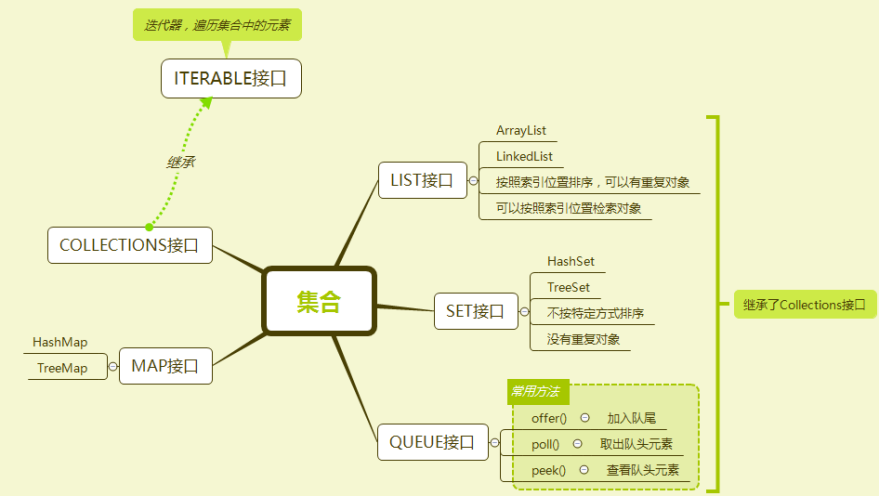
以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结集合相关内容。
2.书面作业
1. ArrayList代码分析
1.1 解释ArrayList的contains源代码
源代码如下:
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) { //遍历元素看是否存在元素“o”
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
答:由上述源代码可以看出ArrayList的contain方法是通过调用indexOf()方法判断元素在数组中的位置来确定是否存在该元素的。在indexOf()方法中,为了防止null去调用equals()方法而产生空指针异常,方法将元素分为了非null元素和null元素分别进行处理,在对象不为null时,最终调用的是Object类的equals()方法来确定其是否存在。
1.2 解释E remove(int index)源代码
答:源代码如下:
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++; //修改次数+1
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved); //System类中的一个本地方法复制
elementData[--size] = null; // 删除数组最后一个元素并修改大小
return oldValue;
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
由源代码可以看出,remove方法首先调用了rangeCheck方法来判断数组是否越界,然后再删除指定位置的元素并进行数组长度的修改。
1.3 结合1.1与1.2,回答ArrayList存储数据时需要考虑元素的具体类型吗?
答:不需要,由上面两题可以看出,数组中存放的元素的类型为Object类型,它是所有类的父类,在传入数据时都是向上转型,因此不需要考虑元素的具体类型。
1.4 分析add源代码,回答当内部数组容量不够时,怎么办?
答:源代码如下:
//将数据添加尾部的add方法
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
首先调用了ensureCapacityInternal方法判断是否要进行数组的扩容,说到容量的话,ArrayList继承于List接口,每个ArrayList实例都有一个容量,在创建对象时没有指定长度的话,初始容量会被设置为10,然后随着元素的增多而增长。当判断为需要扩容时则调用ensureExplicitCapacity实现数组的扩容。最后再修改对象数组的长度。
//在指定位置添加元素的add方法
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
这个方法其实和上一个差不多,只是多了要将插入元素位置后的剩余元素的下标进行修改的操作。
1.5 分析private void rangeCheck(int index)源代码,为什么该方法应该声明为private而不声明为public?
答:修饰为private体现了其封装性,rangeCheck方法是在remove元素时用于判断是否出现数组越界的情况,这个只需要在本类中使用,而用户只需要知道remove方法的使用,至于其内部的具体实现他们就没必要知道了。
2. HashSet原理
2.1 将元素加入HashSet(散列集)中,其存储位置如何确定?需要调用那些方法?
答:在将元素加入HashSet的时候,首先先调用hashCode方法来计算元素的哈希码的值,然后再由哈希码的值计算出元素的存储位置,如果指定的位置没有值的话,则将元素添加到哈希表中,但是如果算出的位置上已经有了一个值的话,就要调用equals方法比较该位置上的值和待加入的值,如果两个值相同则不将元素添加进哈希表,因为HashSet不会存储重复的元素,如果两个值不同就使用解决冲突的方法将元素添加到相应的哈希表的位置中。
2.2 将元素加入HashSet中的时间复杂度是多少?是O(n)吗?(n为HashSet中已有元素个数)
答:HashSet是使用哈希表实现的,其中的元素是无序的,在添加元素的时候不需要遍历,是直接通过哈希算法来计算位置来直接进行元素的添加,所以时间复杂度为O(1)。
2.3 选做:尝试分析HashSet源代码后,重新解释2.1
答:查看了HashSet的源代码后发现它居然是基于HashMap实现的,它的底层还使用了HashMap来存储元素。
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
public void clear() {
map.clear();
}
然后通过HashSet的add源码追溯到HashMap的put方法上
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
由上面的源代码可以看出,在put方法中实际上是返回了putVal方法,其基本的过程如下。
put操作的基本流程:
(1)通过hash值得到所在bucket的下标,如果为null,表示没有发生碰撞,则直接put
(2)如果发生了碰撞,则解决发生碰撞的实现方式:链表还是树。
(3)如果能够找到该key的结点,则执行更新操作,无需对modCount增1。
(4)如果没有找到该key的结点,则执行插入操作,需要对modCount增1。
(5)在执行插入操作时,如果bucket中bin的数量超过TREEIFY_THRESHOLD,则要树化。
(6)在执行插入操作之后,如果size超过了threshold,这要扩容。
3. ArrayListIntegerStack
题集jmu-Java-05-集合之ArrayListIntegerStack
3.1 比较自己写的ArrayListIntegerStack与自己在题集jmu-Java-04-面向对象2-进阶-多态、接口与内部类中的题目自定义接口ArrayIntegerStack,有什么不同?(不要出现大段代码)
//本次题集中的栈的定义
List<Integer> stack = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//上次题目中的栈的定义
Integer[] Stack;
private static int top=0;
public ArrayIntegerStack(int n){
Stack = new Integer[n];
}
通过比较可以看出,最明显的不同当然是存储形式的不同,上次的题目中使用的是数组的方法来存储栈,而这次采用的则是动态数组来进行存储。也正是由于这点的不同,导致了后面对栈的操作的方法的一些不同。
对于入栈来说,由于动态数组能够自动扩容,因此与普通数组的入栈操作相比少了判断栈满的情况。
而其他的方法,像出栈或是取栈顶元素,主要的不同都是由栈顶指针引起的,在动态数组中可以通过其size方法来获得栈顶的位置,而在普通数组中则要通过自定义一个栈顶指针top,然后根据数组的出入栈进行指针的移动来实现其功能。
3.2 结合该题简单描述接口的好处,需以3.1为例详细说明,不可泛泛而谈。
答:在这题中我们用到了接口IntegerStack,这个接口和我们上次作业中的接口一样,因此我们只要重新写一个类来实现这个接口,然后根据要求实现其中的方法即可,如果我们没有定义接口,那我们就只能重新写一个栈的类然后编写方法实现,这和使用接口比就增加了我们的代码量,由此可见,使用接口来实现便于程序的维护和拓展,也使我们代码更具有了灵活性,我们可以根据不同的工作环境来使用不同的方式来实现接口里的方法。
4. Stack and Queue
4.1 编写函数判断一个给定字符串是否是回文,一定要使用栈(请利用Java集合中已有的类),但不能使用java的Stack类(具体原因自己搜索)与数组。请粘贴你的代码,类名为Main你的学号。
import java.util.*;
class Stack2 {
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
public void push(Character item) {
stack.addLast(item);
}
public void pop() {
stack.removeLast();
}
public Character peek() {
return stack.getLast();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack.isEmpty();
}
public int size() {
return stack.size();
}
}
public class Main201621123031 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Stack2 stack = new Stack2();
boolean flag = true;
String str = sc.next();
char[] ch = str.toCharArray();
for(char e:ch){
stack.push(e);
}
for(int i=0;i<stack.size();i++){
if(ch[i]!=stack.peek()){
flag=false;
break;
}
stack.pop();
}
System.out.println(flag);
sc.close();
}
}
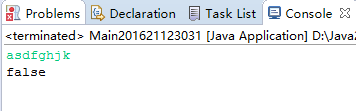
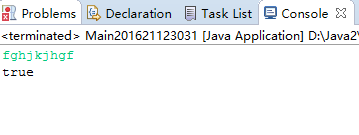
运行结果:
4.2 题集jmu-Java-05-集合之银行业务队列简单模拟(只粘贴关键代码)。请务必使用Queue接口,并说明你使用了Queue接口的哪一个实现类?
//两个队列的定义
Queue<Integer> listA = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Queue<Integer> listB = new LinkedList<Integer>();
//入队操作
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
if (a % 2 == 1)
listA.add(a);
else
listB.add(a);
}
//业务处理
while (!listA.isEmpty() && !listB.isEmpty()) {
if (!listA.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(listA.poll() + " ");
if (!listA.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(listA.poll() + " ");
}
}
Integer a = listB.poll();
if (listA.isEmpty() && listB.isEmpty())
System.out.print(a);
else
System.out.print(a + " ");
}
while (!listA.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < listA.size() - 1; i++) {
System.out.print(listA.poll() + " ");
}
System.out.print(listA.poll());
}
while (!listB.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < listB.size() - 1; i++) {
System.out.print(listB.poll() + " ");
}
System.out.print(listB.poll());
}
本题使用了LinkedList实现类,LinkedList是采用链表的形式实现的,适合队列的出队入队操作,而以数组形式实现的实现类更加适合于随机访问。
5. 统计文字中的单词数量并按单词的字母顺序排序后输出
题集jmu-Java-05-集合之5-2 统计文字中的单词数量并按单词的字母顺序排序后输出 (作业中不要出现大段代码)
5.1 实验总结
答:这题用到了TreeSet来存储数据,因为其具有排序功能且能够不添加重复的元素,然后刚开始先使用了split来分割字符串来实现数据的添加,但是这个要考虑空行或是多个空格的因素,比较不方便,所以后面直接用了next的输入方法进行输入,接着在输出前十个元素的时候,发现Set集合不像List集合,可以通过get方法获取指定位置的元素,因此只能采用foreach语句,然后添加一个计数器来实现输出指定个数的数字。
6. 选做:统计文字中的单词数量并按出现次数排序
题集jmu-Java-05-集合之5-3 统计文字中的单词数量并按出现次数排序(不要出现大段代码)
6.1 伪代码
创建HashMap对象map
循环读入文章中的单词
IF 读入单词为”!!!!!”
退出循环
ELSE
IF map中没有相应的key
添加单词到map中并设置value为1
ELSE
将key对应的value值加1
创建ArrayList对象list
实现Collections接口对map对象进行排序
输出map的长度
输出排序后list中前十个数据
6.2 实验总结
答:这题中用到了HashMap,key值为单词,value值为单词出现的次数,这题比较复杂的地方就是要使用一个能够存放Map数据ArrayList来实现Collections接口来实现相应的排序。
关键代码如下:
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(map.entrySet());
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Entry<String, Integer> o1, Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
if (o1.getValue() == o2.getValue()) {
return o1.getKey().compareTo(o2.getKey());
}
return o2.getValue() - o1.getValue();
}
});
其中Map.Entry为Map的一个内部接口,它表示Map中的一个实体(一个key-value对)。接口中有getKey(),getValue方法。使用它可以更方便我们去访问Map中的元素。
7. 选做 面向对象设计大作业-改进
7.1 使用集合类改进大作业或者简述你的面向对象设计大作业中,哪里使用到了集合类。
在系统中,存储商品信息和存储用户基本信息时都用到了ArrayList。
7.2 进一步完善图形界面(仅需出现改进的后的图形界面截图)
上周的大作业没及时交上,后面改进完一起补上了,因此就附上上一篇博客的链接。
3.码云及PTA
题目集:jmu-Java-05-集合
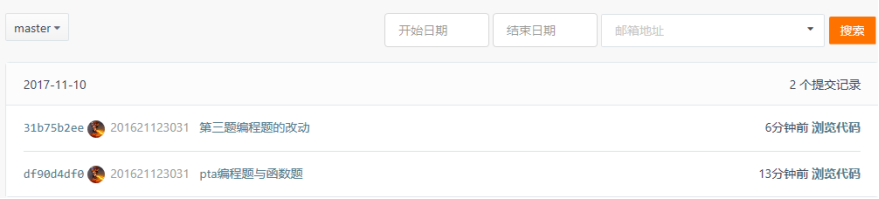
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
- 在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图
3.2 截图PTA题集完成情况图
需要有两张图(1. 排名图。2.PTA提交列表图)

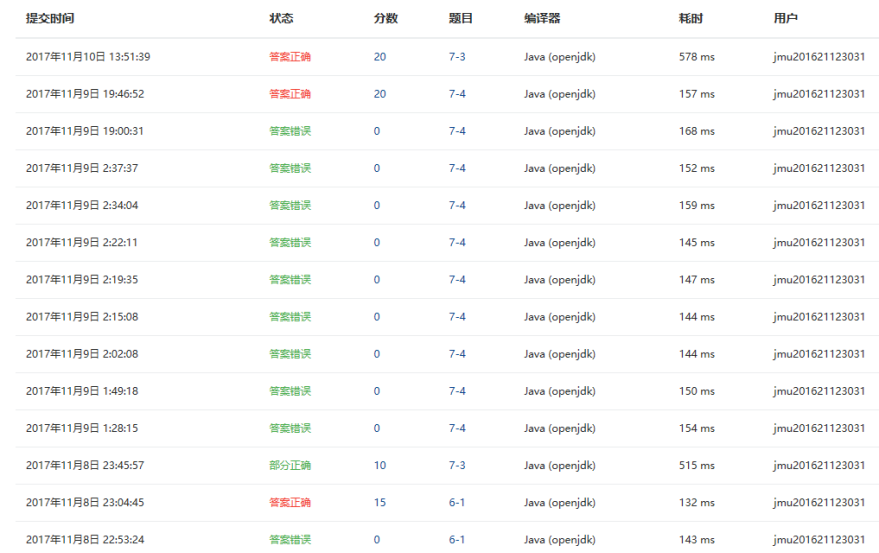

3.3 统计本周完成的代码量
需要将每周的代码统计情况融合到一张表中。

| 周次 | 总代码量 | 新增代码量 | 总文件数 | 新增文件数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 607 | 607 | 15 | 15 |
| 3 | 1642 | 1035 | 33 | 18 |
| 5 | 2044 | 402 | 42 | 9 |
| 6 | 2874 | 830 | 57 | 15 |
| 7 | 3161 | 287 | 63 | 6 |
| 8 | 4299 | 1138 | 72 | 9 |
| 9 | 4831 | 532 | 81 | 9 |