一、pwd
1.学习pwd命令
man pwd查看pwd功能

可以得知pwd功能是打印当前目录
2.研究pwd实现需要的系统调用(man -k; grep),写出伪代码
(1)man -k directory | grep 2查看是否有可用命令
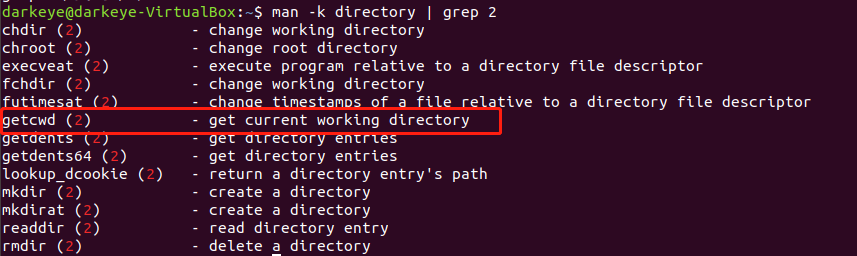
(2) 可以得知getcwd命令可以获得当前目录路径
man getcwd查看getcwd命令功能

找到所需要的头文件以及函数
#include <unistd.h>
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
(3)由刚才man -k directory | grep 2获得的相关命令中我们也可以发现chdir命令会被用到
man chdir查看chdir命令功能
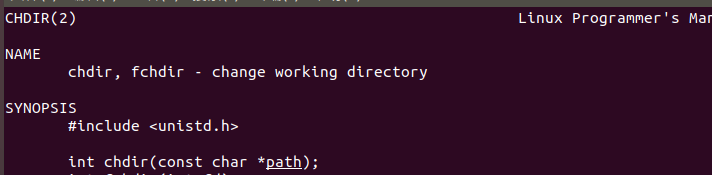
找到所需要的头文件以及函数
#include <unistd.h>
int chdir(const char *path);
(4)由刚才man -k directory | grep 2获得的相关命令中我们也可以发现readdir命令会被用到
man readdir查看readdir命令功能

找到所需要的头文件以及函数
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
伪代码
- 用“.”获取当前目录的i-node
- 用“..”获取父级目录的i-node
- 判断当前目录的i-node和父级目录的i-node是否相同
- 相同:到达根目录,输出完整路径,退出程序
- 不同:还未到根目录,切换至父级目录,返回(1)再次执行相同操作直至两个i-node相同
3.实现mypwd
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void printpath();
char *inode_to_name(int);
int getinode(char *);
//功能:打印当前目录路径
void printpath()
{
int inode,up_inode;
char *str;
inode = getinode(".");
up_inode = getinode("..");
chdir("..");
str = inode_to_name(inode);
//当当前目录的i-node与父级目录的i-node相同时,到达根目录
if(inode == up_inode) {
return;
}
//打印路径
printpath();
printf("/%s",str);
}
//功能:获取当前目录的i-node
int getinode(char *str)
{
struct stat st;
if(stat(str,&st) == -1){
perror(str);
exit(-1);
}
return st.st_ino;
}
//功能:获取当前路径
char *inode_to_name(int inode)
{
char *str;
DIR *dirp;
struct dirent *dirt;
if((dirp = opendir(".")) == NULL){
perror(".");
exit(-1);
}
while((dirt = readdir(dirp)) != NULL)
{
if(dirt->d_ino == inode){
str = (char *)malloc(strlen(dirt->d_name)*sizeof(char));
strcpy(str,dirt->d_name);
return str;
}
}
perror(".");
exit(-1);
}
//主函数
int main()
{
printpath();
putchar('
');
return 0;
}
4.测试mypwd

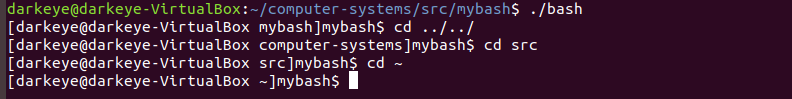
二、bash
1.有关fork(),exec(),wait()
- fork()
fork() 函数通过系统调用创建一个与原来进程几乎完全相同的进程,每个进程都启动一个从代码的同一位置开始执行的线程,父子两个进程中的线程能同时执行不同的指令要求。若调用成功返回的是两个值:父进程返回的值为子进程标志;子进程返回的值为0,不成功返回为-1。
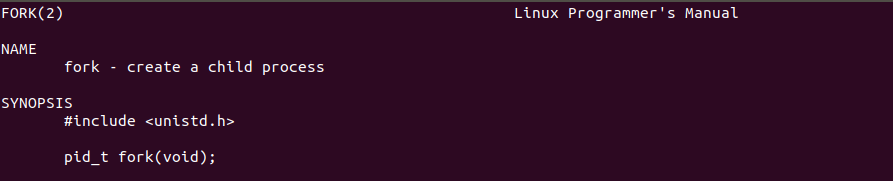
找到所需要的头文件以及函数
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t fork(void);
- exec()
系统调用 execv() 对当前进程进行替换,替换者为一个指定的可执行程序,其参数包括文件名(filename)、参数列表(argv) 以及环境变量 (envp) 。

找到所需要的头文件以及函数
#include <unistd.h>
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
- wait()
wait() 函数用于使父进程(也就是调用wait()的进程)阻塞,直到一个子进程结束或者该进程接收到了一个指定的信号为止。若该父进程没有子进程或者它的子进程已经结束,wait() 函数就会立即返回。

找到所需要的头文件以及函数
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t wait(int *status);
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int options);
2.伪代码及实现
伪代码
- 读取用户输入的指令
- 调用fork函数生成一个子进程,并将fork返回的pid值赋给父进程fpid
- 调用wait函数,传入参数NULL
- 判断fpid是否为0
- 若为0,则调用execvp函数,将用户输入的指令传进去,实现功能
- 若不为0,则提示错误,并返回(1)等待用户下一个指令
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/utsname.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define LEN 10
char* Cmd[LEN] = {0};
int count = 0;
char OLDPWD[1024] = {0};
void out_flag()
{
char flag = '$';
struct passwd *pw = getpwuid(getuid());
if(getuid() == 0)
{
flag = '#';
}
struct utsname host;
uname(&host);
char *hostname = strtok(host.nodename, ".");
char path[128] = {0};
getcwd(path, 127);//获取当前目录的绝对路径
char *p = strtok(path, "/");
char *nowdir = NULL;
while(p!= NULL)
{
nowdir = p;
p = strtok(NULL, "/");
}
if(nowdir == NULL)
{
nowdir = "/";
}
if(strcmp(nowdir, pw->pw_name) == 0)
{
nowdir = "~";
}
printf("[%s@%s %s]mybash%c ", pw->pw_name, hostname, nowdir, flag);
fflush(stdout);
}
void cut_cmd(char *cmd)
{
char *p = strtok(cmd, " ");
while(p != NULL)
{
Cmd[count++] = p;
p = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
}
int special_cmd()
{
//cd exit
if(strncmp("cd", Cmd[0], 2) == 0)
{
if(Cmd[1] == NULL || strncmp(Cmd[1], "~", 1) == 0)
{
//切换到家目录
struct passwd *pw = getpwuid(getuid());
Cmd[1] = pw->pw_dir;
}
else if(strncmp(Cmd[1], "-", 1) == 0)
{
//切换到家目录到上一次所在目录
if(strlen(OLDPWD) == 0)
{
printf("mybash: cd :: OLDPWD not set
");
return 1;
}
Cmd[1] = OLDPWD;
printf("%s
", Cmd[1]);
}
char str[1024] = {0};
getcwd(str, 1023);
chdir(Cmd[1]); // 切换路径
strcpy(OLDPWD, str);
return 1;
}
if(strncmp("exit", Cmd[0], 4) == 0)
{
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
void clear_cmd()
{
int i = 0;
for(;i < count; ++i)
{
Cmd[i] = 0;
}
count = 0;
}
void main()
{
while(1)
{
out_flag();
char cmd[128] = {0};
fgets(cmd, 128, stdin); //获取命令
cmd[strlen(cmd) - 1] = 0; //去掉最后一个回车符
if(strlen(cmd) == 0) // 判别用户的无效输入
{
continue;
}
cut_cmd(cmd); // 切割cmd
int res = special_cmd(); // 判别是否是需要集成到bash中的特殊命令
if(res == 1)
{
clear_cmd(); //清空全局的指针数组,并将count归0
continue;
}
pid_t pid = fork();
assert(pid != -1);
if(pid == 0)
{
// 用命令的可执行文件(./mypwd)替换当前进程
char path[1024] = "/home/darkeye/computer-systems/src/mybash
";
if(strstr(Cmd[0], "/") != NULL)
{
memset(path, 0, 1024);
}
strcat(path, Cmd[0]);
execv(path, Cmd);
printf("mybash: %s : command not found
", Cmd[0]);
exit(0);
}
else
{
wait(NULL);
}
clear_cmd();
}
}