We have seen that Code-First creates a database automatically in the Simple Code First Example section. Here, we will learn how EF decides the database name and server while initializing a database in code-first approach.
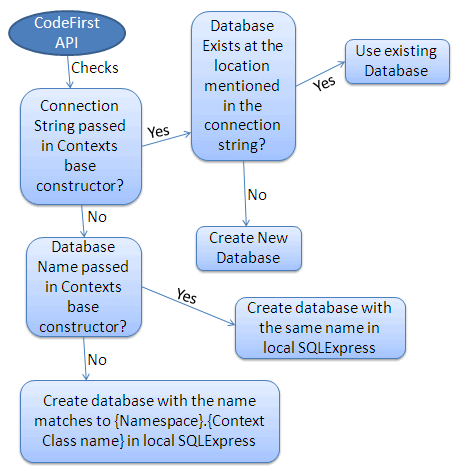
The following figure shows a database initialization workflow, based on the parameter passed in the base constructor of the context class, which is derived from DbContext:
As per the above figure, the base constructor of the context class can have the following parameter.
- No Parameter
- Database Name
- Connection String Name
No Parameter
If you do not specify the parameter in the base constructor of the context class then it creates a database in your local SQLEXPRESS server with a name that matches your {Namespace}.{Context class name}. For example, EF will create a database named SchoolDataLayer.Context for the following context class:
namespace SchoolDataLayer
{
public class Context: DbContext
{
public Context(): base()
{
}
}
}
Database Name
You can also specify the database name as a parameter in a base constructor of the context class. If you specify a database name parameter, then Code First creates a database with the name you specified in the base constructor in the local SQLEXPRESS database server. For example, Code First will create a database named MySchoolDB for the following context class.
namespace SchoolDataLayer
{
public class Context: DbContext
{
public Context(): base("MySchoolDB")
{
}
}
}
ConnectionString Name
You can also define the connection string in app.config or web.config and specify the connection string name starting with "name=" in the base constructor of the context class. Consider the following example where we pass the name=SchoolDBConnectionString parameter in the base constructor.
namespace SchoolDataLayer
{
public class Context: DbContext
{
public SchoolDBContext() : base("name=SchoolDBConnectionString")
{
}
}
}
App.config:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="SchoolDBConnectionString"
connectionString="Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=SchoolDB-ByConnectionString;Integrated Security=true"
providerName="System.Data.SqlClient"/>
</connectionStrings>
</configuration>
In the above context class, we specify a connection string name as a parameter. Please note that the connection string name should start with "name=", otherwise it will consider it as a database name. The database name in the connection string in app.config is SchoolDB-ByConnectionString. EF will create a new SchoolDB-ByConnectionString database or use the existing SchoolDB-ByConnectionString database in the local SQL Server. Make sure that you include providerName = "System.Data.SqlClient" for the SQL Server database in the connection string.