Autofac学习之三种生命周期:InstancePerLifetimeScope、SingleInstance、InstancePerDependency
InstancePerLifetimeScope:同一个Lifetime生成的对象是同一个实例
SingleInstance:单例模式,每次调用,都会使用同一个实例化的对象;每次都用同一个对象;
InstancePerDependency:默认模式,每次调用,都会重新实例化对象;每次请求都创建一个新的对象;
验证方法实现逻辑:在类的构造函数中,给属性赋值(GUID),通过判断属性值是否一致来判断 三种生命周期的效果。
先上图看结果:
1、InstancePerLifetimeScope
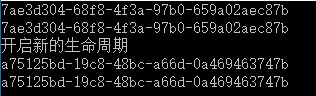
2、SingleInstance
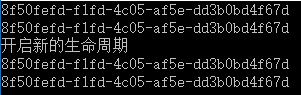
3、InstancePerDependency
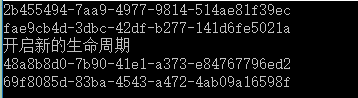
整块代码实现如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
|
using Autofac;using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Reflection;using System.Text;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace SimpleAutofacConsole{ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //IAnimal animal = new Tiger(); //animal.Show("普通new()对象"); var builder = new ContainerBuilder(); var dependencyRegistrar = new DependencyRegistrar();//(IDependencyRegistrar)Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(IDependencyRegistrar)); dependencyRegistrar.Register(builder, null); var container = builder.Build(); var animalIOC = container.Resolve<IAnimal>(); //animalIOC.Show("Autofac方式实现new()对象"); Console.WriteLine(animalIOC.Id); var animalIOC2 = container.Resolve<IAnimal>(); //animalIOC2.Show("第二次从容器中实例化"); Console.WriteLine(animalIOC2.Id); Console.WriteLine("开启新的生命周期"); ILifetimeScope inner = container.BeginLifetimeScope(); var myClass3 = inner.Resolve<IAnimal>(); Console.WriteLine(myClass3.Id); var myClass4 = inner.Resolve<IAnimal>(); Console.WriteLine(myClass4.Id); //var animalIOC = container.Resolve<Dog>(); //animalIOC.Show("Autofac方式实现new()对象"); Console.ReadLine(); } } public interface IAnimal { void Show(string name); string Id { get; set; } } public class Tiger : IAnimal { private string _Id; public string Id { get { return this._Id; } set { Id = this._Id; } } public Tiger() { _Id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(); } public void Show(string name) { Console.WriteLine("老虎说:" + name); } } public class Dog : IAnimal { public string Id { get { return Guid.NewGuid().ToString(); } set { } } public void Show(string name) { Console.WriteLine("狗狗说:" + name); } } public class DependencyRegistrar : IDependencyRegistrar { public int Order { get { return 0; } } public void Register(ContainerBuilder builder, ITypeFinder typeFinder) { // InstancePerLifetimeScope 同一个Lifetime生成的对象是同一个实例 // SingleInstance 单例模式,每次调用,都会使用同一个实例化的对象;每次都用同一个对象 // InstancePerDependency 默认模式,每次调用,都会重新实例化对象;每次请求都创建一个新的对象 builder.RegisterType<Tiger>().As<IAnimal>().InstancePerLifetimeScope(); //builder.RegisterType<Dog>().As<IAnimal>();//.PreserveExistingDefaults(); } } public interface IDependencyRegistrar { void Register(ContainerBuilder builder,ITypeFinder typeFinder); int Order { get; } } public interface ITypeFinder { IList<Assembly> GetAssemblies(); IEnumerable<Type> FindClassesOfType(Type assignTypeFrom, bool onlyConcreteClasses = true); IEnumerable<Type> FindClassesOfType(Type assignTypeFrom, IEnumerable<Assembly> assemblies, bool onlyConcreteClasses = true); IEnumerable<Type> FindClassesOfType<T>(bool onlyConcreteClasses = true); IEnumerable<Type> FindClassesOfType<T>(IEnumerable<Assembly> assemblies, bool onlyConcreteClasses = true); }} |