java.util.Scanner 是 Java5 的新特征,可以通过 Scanner 类来获取用户的输入。
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
通过 Scanner 类的 next() 与 nextLine() 方法获取输入的字符串,在读取前我们一般需要 使用 hasNext 与 hasNextLine 判断是否还有输入的数据:
首先看看next方法:
import java.util.Scanner; public class ScannerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // 从键盘接收数据 // next方式接收字符串 System.out.println("next方式接收:"); // 判断是否还有输入 if (sc.hasNext()) { String str1 = sc.next(); System.out.println("输入的数据为:" + str1); } sc.close(); } }
输出:
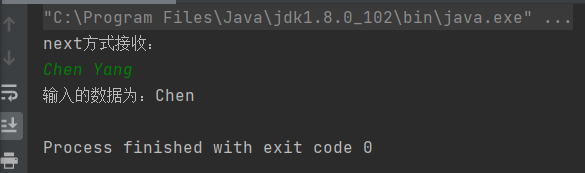
nextLine()方法:
import java.util.Scanner; public class ScannerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // 从键盘接收数据 // nextLine方式接收字符串 System.out.println("nextLine方式接收:"); // 判断是否还有输入 if (sc.hasNextLine()) { String str2 = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("输入的数据为:" + str2); } sc.close(); } }
输出:
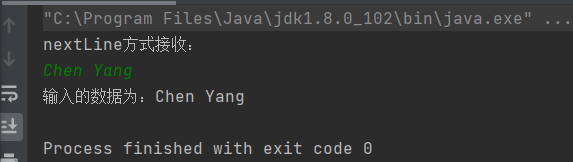
next()与nextLine()比较:
next():
1、一定要读取到有效字符后才可以结束输入。
2、对输入有效字符之前遇到的空白,next() 方法会自动将其去掉。
3、只有输入有效字符后才将其后面输入的空白作为分隔符或者结束符。
4、next() 不能得到带有空格的字符串。
nextLine():
1、以Enter为结束符,也就是说 nextLine()方法返回的是输入回车之前的所有字符。
2、可以获得空白。
参考原文:https://blog.csdn.net/Fly_as_tadpole/article/details/84203209