一、LinkedList介绍及其源码剖析
继承结构:
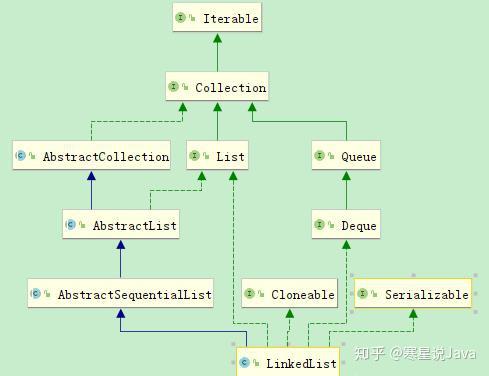
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
LinkedList 继承了AbstractSequentialList类,实现了List接口、Deque 接口、Cloneable接口、java.io.Serializable接口。
- LinkedList 实现了 List 接口,即能对它进行队列操作,提供了相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。
- LinkedList 实现了 Deque 接口,即能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用。
- LinkedList 实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),所以它能被克隆。
- LinkedList 实现java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着LinkedList支持序列化,能通过序列化进行传输。
LinkedList属性源码剖析
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { // 双向链表的节点个数 transient int size = 0; /** * Pointer to first node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) */ // 双向链表指向头节点的指针 transient Node<E> first; /** * Pointer to last node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (last.next == null && last.item != null) */ // 双向链表指向尾节点的指针 transient Node<E> last; }
从以上源码可以看出,LinkedList 的属性比较少。分别是:
- size : 双向链表的节点个数
- first: 双向链表指向头节点的指针
- last: 双向链表指向尾节点的指针
注意:first 和 last 是由引用类型Node连接的,这是它的一个内部类。
Node源码剖析
private static class Node<E> { // item表示当前存储元素 E item; // next表示当前节点的后置节点 Node<E> next; // prev表示当前节点的前置节点 Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
LinkedList 是通过双向链表实现的,而双向链表就是通过Node类来实现的,Node类中通过item变量存储当前元素,通过next变量指向当前节点的下一个节点,通过prev变量指向当前节点的上一个节点。
二、构造方法及其源码剖析
1. 无参构造方法
源码剖析
/** * Constructs an empty list. */ public LinkedList() { }
LinkedList 的无参构造就是构造一个空的list集合
2. Collection<? extends E>型构造方法
源码剖析
/** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); }
从源码中分析可得:
构造一个包含指定集合的元素的列表,按照它们由集合的迭代器返回的顺序。
三、常用方法及其源码剖析
1. add() 方法
add(E e) 方法,将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾
源码剖析
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; }
其中,调用了linkLast()方法,设置元素e为最后一个元素
/** * Links e as last element. */ void linkLast(E e) { // 获取链表的最后一个节点 final Node<E> l = last; // 创建一个新节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); // 使新的一个节点为最后一个节点 last = newNode; // 如果最后一个节点为null,则表示链表为空,则将newNode赋值给first节点 if (l == null) first = newNode; else // 否则尾节点的last指向 newNode l.next = newNode; // 元素的个数加1 size++; // 修改次数自增 modCount++; }
总结:
- 第一步,获取链表的最后一个节点
- 第二步,创建一个新节点
- 第三步,使新的一个节点为最后一个节点
- 第四步,如果最后一个节点为null,则表示链表为空,则将newNode赋值给first节点;否则尾节点的last指向 newNode
add(int index, E element) 方法,在指定位置插入元素
源码剖析
/** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any * subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { // 检查索引index的位置 checkPositionIndex(index); // 如果index==size,直接在链表的最后插入元素,相当于add(E e)方法 if (index == size) linkLast(element); else // 否则调用node方法将index位置的节点找出,接着调用linkBefore 方法 linkBefore(element, node(index)); }
总结:
首先检查索引index的位置,看下标是否越界
如果index==size,直接在链表的最后插入元素,相当于add(E e)方法
否则调用node方法将index位置的节点找出,接着调用linkBefore 方法
其中,调用checkPositionIndex()方法,检查索引index的位置
源码剖析
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) { if (!isPositionIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }
在增加元素的时候,调用了linkBefore()方法,在非null节点succ之前插入元素e
源码剖析
/** * Inserts element e before non-null Node succ. */ void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; // 指定节点的前驱 final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; // 创建新的节点,前驱节点为succ的前驱节点,后续节点为succ,则e元素就是插入在succ之前的 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); // 构建双向链表,succ的前驱节点为新的节点 succ.prev = newNode; // 如果前驱节点为null,则把newNode赋值给first if (pred == null) first = newNode; else // 构建双向列表 pred.next = newNode; // 元素的个数加 size++; // 修改次数自增 modCount++;
总结:
指定节点的前驱
创建新的节点,前驱节点为succ的前驱节点,后续节点为succ,则e元素就是插入在succ之前的
构建双向链表,succ的前驱节点为新的节点
如果前驱节点为null,则把newNode赋值给first;否则构建双向列表
2. remove() 方法
remove() 方法 删除这个列表的头(第一个元素)
源码剖析
/** * Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. * * @return the head of this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty * @since 1.5 */ public E remove() { return removeFirst(); }
其中,调用了removeFirst()方法,删除并返回第一个元素
源码剖析
/** * Removes and returns the first element from this list. * * @return the first element from this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty */ public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); }
remove(int index) 方法,删除指定位置的元素
源码剖析
/** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any * subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices). * Returns the element that was removed from the list. * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E remove(int index) { // 检查索引index的位置 checkElementIndex(index); // 调用node方法获取节点,接着调用unlink(E e)方法 return unlink(node(index)); }
总结:
检查索引index的位置
调用node方法获取节点,接着调用unlink(E e)方法
其中,调用了unlink()方法
源码剖析
/** * Unlinks non-null node x. */ E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; // 获得节点的三个属性 final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; // 进行移除该元素之后的操作 if (prev == null) { // 删除的是第一个元素 first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { // 删除的是最后一个元素 last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } // 把item置为null,让垃圾回收器回收 x.item = null; // 移除一个节点,size自减 size--; modCount++; return element; }
3. set() 方法
set(int index, E element)方法,将指定下标处的元素修改成指定值
源码剖析
/** * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the * specified element. * * @param index index of the element to replace * @param element element to be stored at the specified position * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); // 通过node(int index)找到对应下标的元素 Node<E> x = node(index); // 取出该节点的元素,供返回使用 E oldVal = x.item; // 用新元素替换旧元素 x.item = element; // 返回旧元素 return oldVal; }
总结:
先通过node(int index)找到对应下标的元素,然后修改Node中item的值。
4. get() 方法
get(int index) 返回此列表中指定位置的元素
源码剖析
public E get(int index) { // 检查索引index的位置 checkElementIndex(index); // 调用node()方法 return node(index).item; }
在此调用了node()方法
源码剖析
/** * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. */ // 这里查询使用的是先从中间分一半查找 Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); // 从前半部分进行查找 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { // 从后半部分进行查找 Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
总结:
这里查询使用的是先从中间分一半查找,根据下标是否超过链表长度的一半,来选择从前半部分开始遍历查找,还是从后半部分开始遍历查找。
如果index小于size的一半,就从首节点开始遍历,一直获取x的下一个节点
如果index大于或等于size的一半,就从尾节点开始遍历,一直获取x的上一个节点
四、双端队列操作方法的源码剖析
offerFirst(E e) 方法,将指定的元素插入到此集合列表的前面,也就是将将元素添加到首部
源码剖析
/** * Inserts the specified element at the front of this list. * * @param e the element to insert * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerFirst}) * @since 1.6 */ public boolean offerFirst(E e) { addFirst(e); return true; }
offerLast(E e)方法,将指定的元素插入到此集合列表的末尾,也就是将元素添加到尾部
源码剖析
/** * Inserts the specified element at the end of this list. * * @param e the element to insert * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast}) * @since 1.6 */ public boolean offerLast(E e) { addLast(e); return true; }
peekFirst()方法,获取此集合列表的第一个元素值
源码剖析
/** * Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * * @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} * if this list is empty * @since 1.6 */ public E peekFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; }
peekLast()方法,获取此集合列表的最后一个元素值
源码剖析
/** * Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} * if this list is empty * @since 1.6 */ public E peekLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : l.item; }
pollFirst()方法,删除此集合列表的第一个元素,如果为null,则会返回null
源码剖析
/** * Retrieves and removes the last element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} if * this list is empty * @since 1.6 */ public E pollLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l); }
push(E e)方法,将元素添加到此集合列表的首部
源码剖析
/** * Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other * words, inserts the element at the front of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}. * * @param e the element to push * @since 1.6 */ public void push(E e) { addFirst(e); }
pop()方法,删除并返回此集合列表的第一个元素,如果为null会抛出异常
源码剖析
/** * Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other * words, removes and returns the first element of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}. * * @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top * of the stack represented by this list) * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty * @since 1.6 */ //删除首部,如果为null会抛出异常 public E pop() { return removeFirst(); }
removeFirstOccurrence(Object o)方法,删除集合中元素值等于o的第一个元素值
源码剖析
/** * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this * list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list * does not contain the element, it is unchanged. * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element * @since 1.6 */ public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { return remove(o); }
注意:
removeFirstOccurrence()和remove方法是一样的,因为它的内部调用了remove方法
removeLastOccurrence(Object o)方法,删除集合中元素值等于o的最后一个元素值
源码剖析
/** * Removes the last occurrence of the specified element in this * list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list * does not contain the element, it is unchanged. * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element * @since 1.6 */ public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) { //因为LinkedList中的元素允许存在null值,所以需要进行null判断 if (o == null) { // 从最后一个节点往前开始遍历 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (x.item == null) { // 调用unlink方法删除指定节点 unlink(x); return true; } } } else { // 否则元素不为空,进行遍历 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
五、ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的区别
二者都 线程不安全,但是效率比 Vector(线程安全) 的高
- ArrayList 底层是以 数组 的形式保存数据,随机访问集合中的元素比LinkedList 快(原因是 LinkedList 要移动指针);
- LinkedList 内部以 链表 的形式保存集合里面数据,它随机访问集合中的元素性能比较慢,但是新增和删除时速度比 ArrayList 快(原因是 ArrayList 要移动数据)。