题目描述
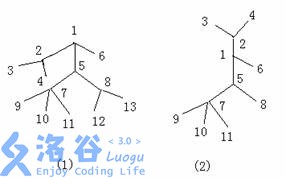
对于一棵树,我们可以将某条链和与该链相连的边抽出来,看上去就象成一个毛毛虫,点数越多,毛毛虫就越大。例如下图左边的树(图 1 )抽出一部分就变成了右边的一个毛毛虫了(图 2 )。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
在文本文件 worm.in 中第一行两个整数 N , M ,分别表示树中结点个数和树的边数。
接下来 M 行,每行两个整数 a, b 表示点 a 和点 b 有边连接( a, b ≤ N )。你可以假定没有一对相同的 (a, b) 会出现一次以上。
输出格式:
在文本文件 worm.out 中写入一个整数 , 表示最大的毛毛虫的大小。
输入输出样例
说明
40% 的数据, N ≤ 50000
100% 的数据, N ≤ 300000
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define REP(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); ++ i) #define REP(j, a, b) for(int j = (a); j <= (b); ++ j) #define PER(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); -- i) using namespace std; const int maxn=3e5+5; template <class T> inline void rd(T &ret){ char c; ret = 0; while ((c = getchar()) < '0' || c > '9'); while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){ ret = ret * 10 + (c - '0'), c = getchar(); } } struct node{int to,nx;}p[maxn<<1]; int n,m,head[maxn],a,b,tot,ans,al[maxn],dp[maxn]; void addedge(int u,int v){ p[++tot].to=v,p[tot].nx=head[u],head[u]=tot; } void dfs(int s,int fa){ for(int i=head[s];i;i=p[i].nx){ if(p[i].to!=fa)al[s]++; } for(int i=head[s];i;i=p[i].nx){ int to=p[i].to; if(to==fa)continue; dfs(to,s); ans=max(ans,dp[s]+dp[to]+1+(fa>0)); dp[s]=max(dp[s],dp[to]+al[s]); } } int main() { rd(n),rd(m); REP(i,1,m){ rd(a),rd(b); addedge(a,b),addedge(b,a); } dfs(1,0); cout<<ans<<endl; return 0; }