Watchmen are in a danger and Doctor Manhattan together with his friend Daniel Dreiberg should warn them as soon as possible. There are n watchmen on a plane, the i-th watchman is located at point (xi, yi).
They need to arrange a plan, but there are some difficulties on their way. As you know, Doctor Manhattan considers the distance between watchmen i and j to
be |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|.
Daniel, as an ordinary person, calculates the distance using the formula 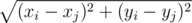 .
.
The success of the operation relies on the number of pairs (i, j) (1 ≤ i < j ≤ n), such that the distance between watchman i and watchmen j calculated by Doctor Manhattan is equal to the distance between them calculated by Daniel. You were asked to compute the number of such pairs.
The first line of the input contains the single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of watchmen.
Each of the following n lines contains two integers xi and yi (|xi|, |yi| ≤ 109).
Some positions may coincide.
Print the number of pairs of watchmen such that the distance between them calculated by Doctor Manhattan is equal to the distance calculated by Daniel.
3 1 1 7 5 1 5
2
6 0 0 0 1 0 2 -1 1 0 1 1 1
11
两种距离相等的情况就是两个点的横坐标相等或者纵坐标相等。这里分别排序一下,然后注意要减去两个点相同的情况
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 200000
struct Node
{
long long int x;long long int y;
}a[MAX+5];
long long int ans[MAX+5];
int cmp(Node a,Node b)
{
if(a.x==b.x)
return a.y<b.y;
return a.x<b.x;
}
int cmp2(Node a,Node b)
{
if(a.y==b.y)
return a.x<b.x;
return a.y<b.y;
}
int n;
long long int ans2[MAX+5];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y);
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp);
memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
int cnt=0;
int cot=0;
ans[0]=1;
ans2[0]=1;
long long int num=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
//cout<<a[i].x<<" "<<a[i-1].x<<endl;
if(a[i].x==a[i-1].x)
{
if(a[i].y==a[i-1].y)
ans2[cot]++;
else
{
cot++;
ans2[cot]=1;
}
ans[cnt]++;
}
else
{
cot++;
ans2[cot]=1;
cnt++;
ans[cnt]=1;
}
}
long long int res=0;
long long int res2=0;
for(int i=0;i<=cnt;i++)
{
res+=(ans[i]*(ans[i]-1))/2;
}
for(int i=0;i<=cot;i++)
{
res2+=(ans2[i]*(ans2[i]-1))/2;
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp2);
memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
cnt=0;
ans[0]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i].y==a[i-1].y)
{
ans[cnt]++;
}
else
{
cnt++;
ans[cnt]=1;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<=cnt;i++)
res+=(ans[i]*(ans[i]-1))/2;
printf("%lld
",res-res2);
return 0;
}