Django自带的用户认证
以前都是用Django自带的用户认证,用户名字段一对一关系对应Django--User表(其实它也是继承了abstractbaseuser)。
1 2 3 | from django.contrib.auth.models import Userclass UserInfo(models.Model): username = models.OneToOneField(User) |
为什么使用要自定义用户认证?
原生的Django--User认证只有用户名和密码字段,自定义用户认证可以根据项目的需求定制化和扩展认证系统。
比如把唯一标识改成email,或加入用户组等等。
官方说明
官方文档:
Specifying a custom User model(指定自定义用户模型)
使用Django自定义用户模型必须满足:
模型必须有一个唯一的字段,可用于识别目的。
用户给定名称为“短”的标识,用户的全名为“长”标识符。他们可以返回完全相同的值。
构建一个符合用户自定义模型的最简单的方法是继承abstractbaseuser类。abstractbaseuser提供一个用户模型的核心实现,包括密码和符号密码重置。Django自带用用户认证User也是继承了它。一些关键的实现细节:
class models.CustomUser
USERNAME_FIELD
必须有一个唯一标识--USERNAME_FIELD
1 2 3 4 | class MyUser(AbstractBaseUser): name = models.CharField(max_length=40, unique=True) ... USERNAME_FIELD = 'name' |
REQUIRED_FIELDS
创建superuser时的必须字段
1 2 3 4 5 6 | class MyUser(AbstractBaseUser): ... date_of_birth = models.DateField() height = models.FloatField() ... REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['date_of_birth', 'height'] |
abstractbaseuser提供的方法
is_active(),is_authenticated()......
自定义models(略)
settings中添加models文件名
1 | AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'app.MyUser(类名)' |
Django会去models中找这个类,所以要在原生的models.py中导入这个类。
代码实现
assetuser_models.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-from django.db import modelsfrom django.contrib.auth.models import ( BaseUserManager, AbstractBaseUser)class UserProfileManager(BaseUserManager): def create_user(self, email, name, password=None): """ Creates and saves a User with the given email, name and password. """ '''email是唯一标识,没有会报错''' if not email: raise ValueError('Users must have an email address') user = self.model( email=self.normalize_email(email), name=name, ) user.set_password(password) #检测密码合理性 user.save(using=self._db) #保存密码 return user def create_superuser(self, email, name, password): """ Creates and saves a superuser with the given email, name and password. """ user = self.create_user(email, password=password, name=name ) user.is_admin = True #比创建用户多的一个字段 user.save(using=self._db) return userclass UserProfile(AbstractBaseUser): email = models.EmailField( verbose_name='email address', max_length=255, unique=True, ) name = models.CharField(max_length=32) is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True) is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False) objects = UserProfileManager() #创建用户 USERNAME_FIELD = 'email' REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name'] def get_full_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email def get_short_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email def __str__(self): # __unicode__ on Python 2 return self.email '''django自带后台权限控制,对哪些表有查看权限等''' def has_perm(self, perm, obj=None): "Does the user have a specific permission?" # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always return True '''用户是否有权限看到app''' def has_module_perms(self, app_label): "Does the user have permissions to view the app `app_label`?" # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always return True @property def is_staff(self): "Is the user a member of staff?" # Simplest possible answer: All admins are staff return self.is_admin |
assetmodels.py
1 | from asset.user_models import UserProfile |
myCMDBsettings.py
1 | AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'asset.UserProfile' |
assetadmin.py
1 2 | from asset import modelsadmin.site.register(models.UserProfile) |
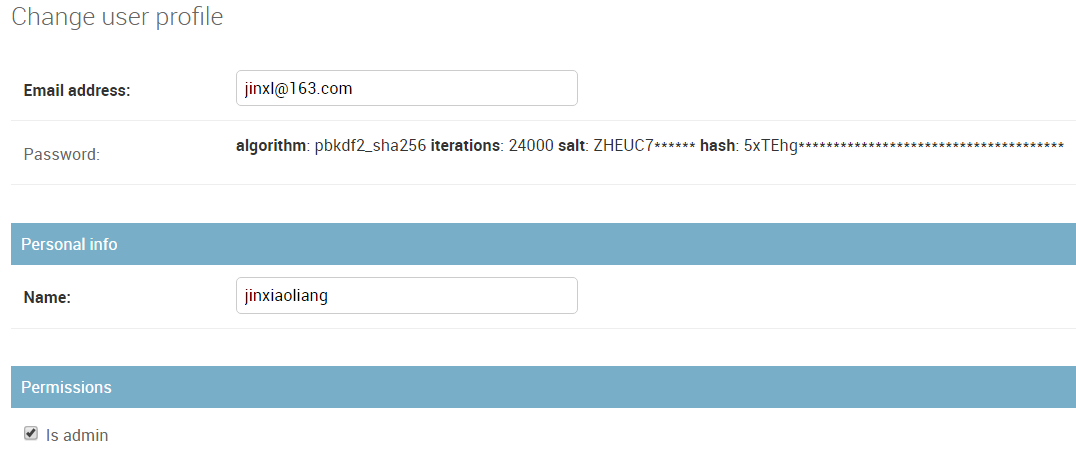
初始化数据库,登录后台。此时密码是明文显示,如果想改密码怎么办?
这时,需要自定义admin显示(官方都提供了)。
assetadmin.py
1 2 | from user_admin import UserAdminadmin.site.register(models.UserProfile,UserAdmin) |
assetuser_admin.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 | #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-from django import formsfrom django.contrib import adminfrom django.contrib.auth.models import Groupfrom django.contrib.auth.admin import UserAdmin as BaseUserAdminfrom django.contrib.auth.forms import ReadOnlyPasswordHashFieldfrom asset.models import UserProfileclass UserCreationForm(forms.ModelForm): """A form for creating new users. Includes all the required fields, plus a repeated password.""" password1 = forms.CharField(label='Password', widget=forms.PasswordInput) password2 = forms.CharField(label='Password confirmation', widget=forms.PasswordInput) class Meta: model = UserProfile fields = ('email', 'name') def clean_password2(self): # Check that the two password entries match password1 = self.cleaned_data.get("password1") password2 = self.cleaned_data.get("password2") if password1 and password2 and password1 != password2: raise forms.ValidationError("Passwords don't match") return password2 def save(self, commit=True): # Save the provided password in hashed format user = super(UserCreationForm, self).save(commit=False) user.set_password(self.cleaned_data["password1"]) if commit: user.save() return userclass UserChangeForm(forms.ModelForm): """A form for updating users. Includes all the fields on the user, but replaces the password field with admin's password hash display field. """ password = ReadOnlyPasswordHashField() class Meta: model = UserProfile fields = ('email', 'password', 'name', 'is_active', 'is_admin') def clean_password(self): # Regardless of what the user provides, return the initial value. # This is done here, rather than on the field, because the # field does not have access to the initial value return self.initial["password"]class UserAdmin(BaseUserAdmin): # 以前是ModelAdmin # The forms to add and change user instances form = UserChangeForm add_form = UserCreationForm # The fields to be used in displaying the User model. # These override the definitions on the base UserAdmin # that reference specific fields on auth.User. list_display = ('email', 'name', 'is_admin') #这个和以前一样,显示什么 list_filter = ('is_admin',) fieldsets = ( (None, {'fields': ('email', 'password')}), ('Personal info', {'fields': ('name',)}), ('Permissions', {'fields': ('is_admin',)}), ) # add_fieldsets is not a standard ModelAdmin attribute. UserAdmin # overrides get_fieldsets to use this attribute when creating a user. add_fieldsets = ( (None, { 'classes': ('wide',), 'fields': ('email', 'name', 'password1', 'password2')} ), ) search_fields = ('email',) ordering = ('email',) filter_horizontal = ()# Now register the new UserAdmin...#admin.site.register(UserProfile, UserAdmin)# ... and, since we're not using Django's built-in permissions,# unregister the Group model from admin.admin.site.unregister(Group) #不显示系统自带的group |
后台效果