1: #include <stdio.h>
2: #include <stdlib.h>
3: #define MAX_LENGTH 9999
4: void print_array(const int a[],int size)
5: {
6: int i=0;
7: for(i=0;i<size;i++)
8: {
9: printf("%d,",a[i]);
10: }
11: printf("\n");
12: }
13:
14: /*
15: assume a[i]>0
16: */
17: void counting_sort(const int a[],int b[],int size,int maxvalue)
18: {
19: int i=0;
20: for(i=0;i<size;i++)
21: {
22: b[i]=0;
23: }
24:
25: int temp[maxvalue+1];
26: for(i=0;i<=maxvalue;i++)
27: {
28: temp[i]=0;
29: }
30:
31: for(i=0;i<size;i++)
32: {
33: temp[a[i]]+=1;
34: }
35:
36: for(i=1;i<=maxvalue;i++)
37: {
38: temp[i]=temp[i]+temp[i-1];
39: }
40:
41: for(i=size-1;i>=0;i--)
42: {
43: b[temp[a[i]]-1]=a[i];
44: temp[a[i]]=temp[a[i]]-1;
45: }
46: }
47:
48: /*
49: handle a[i] <0
50: */
51: void counting_sort2(const int a[],int b[],int size,int maxvalue)
52: {
53: int i=0;
54: int copyofa[size];
55: int min=0;
56: for(i=0;i<size;i++)
57: {
58: b[i]=0;
59: if(min>a[i])
60: {
61: min=a[i];
62: }
63: }
64:
65: int newmaxvalue=maxvalue-min;
66: for(i=0;i<size;i++)
67: {
68: copyofa[i]=a[i]-min;
69: }
70:
71: int temp[newmaxvalue+1];
72: for(i=0;i<=newmaxvalue;i++)
73: {
74: temp[i]=0;
75: }
76:
77: for(i=0;i<size;i++)
78: {
79: temp[copyofa[i]]+=1;
80: }
81:
82: for(i=1;i<=newmaxvalue;i++)
83: {
84: temp[i]=temp[i]+temp[i-1];
85: }
86:
87: for(i=size-1;i>=0;i--)
88: {
89: b[temp[copyofa[i]]-1]=copyofa[i];
90: temp[copyofa[i]]=temp[copyofa[i]]-1;
91: }
92:
93: for(i=0;i<size;i++)
94: {
95: b[i]=b[i]+min;
96: }
97: }
98:
99: void bubble_sort(const int a[],int b[],int size)
100: {
101: int i=0;
102: int j=0;
103: int temp;
104:
105: for(i=0;i<size;i++)
106: {
107: b[i]=a[i];
108: }
109:
110: for(i=0;i<size;i++)
111: {
112: for(j=i;j<size;j++)
113: {
114: if(b[j]<b[i])
115: {
116: temp=b[i];
117: b[i]=b[j];
118: b[j]=temp;
119: }
120: }
121: }
122: }
the second counting method is improved for handing negative integers.
the first is O(n+k), the second is twice: O(2n+2k).
write a test program to compare these three subroutines,
1: int a[MAX_LENGTH];
2: int b[MAX_LENGTH];
3:
4: int i=0;
5: for(i=0;i<MAX_LENGTH;i++)
6: {
7: a[i]=rand();
8: b[i]=0;
9: }
10: for(i=0;i<1000;i++)
11: {
12: bubble_sort(a,b,MAX_LENGTH);
13: counting_sort2(a,b,MAX_LENGTH,RAND_MAX);
14: counting_sort(a,b,MAX_LENGTH,RAND_MAX);
15: }
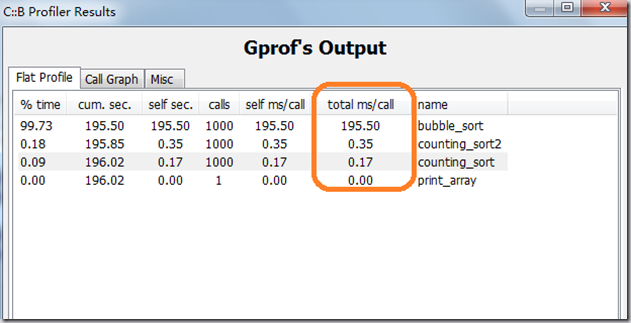
the result as follow:
we can see it’s very obvious that a O(n2) algorithm is heavy slower than O(n+k). to sort 9999 random integers it will cost 195.5ms each time sorting use bubble but only 0.17 ms by using counting method(0.35 for the second coutning sort, because its running time is O(2n+2k))