一、接收参数(postman发送)
1.form表单
@RequestParam("name") String name
会把传递过来的Form表单中的name对应到formData方法的name参数上
该注解不能接收json传参
该注解表示name字段是必须入参的,否则会报错
@RequestParam(value = "name", required = false) String name
required = false表示必须入参
@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "admin") String name
defaultValue = "admin"表示当name入参为空的时候给它一个默认值admin
/** * 测试接收form表单、URL的数据。不能接收Json数据 * */ @RequestMapping(value = "/test1", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String formData(@RequestParam("name") String name , @RequestParam("age") int age){ String result = "receive name = "+name+" age = "+age; System.out.println(result); return result; }
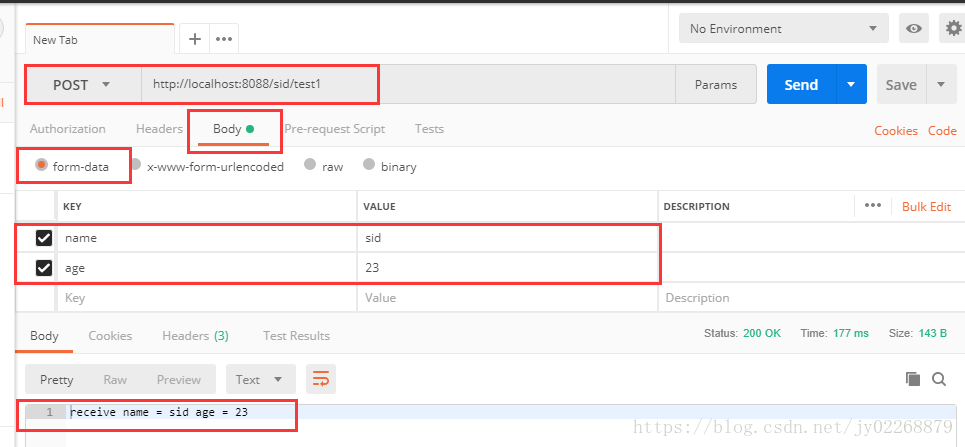
2.URL
代码跟1.form表单中的代码一样
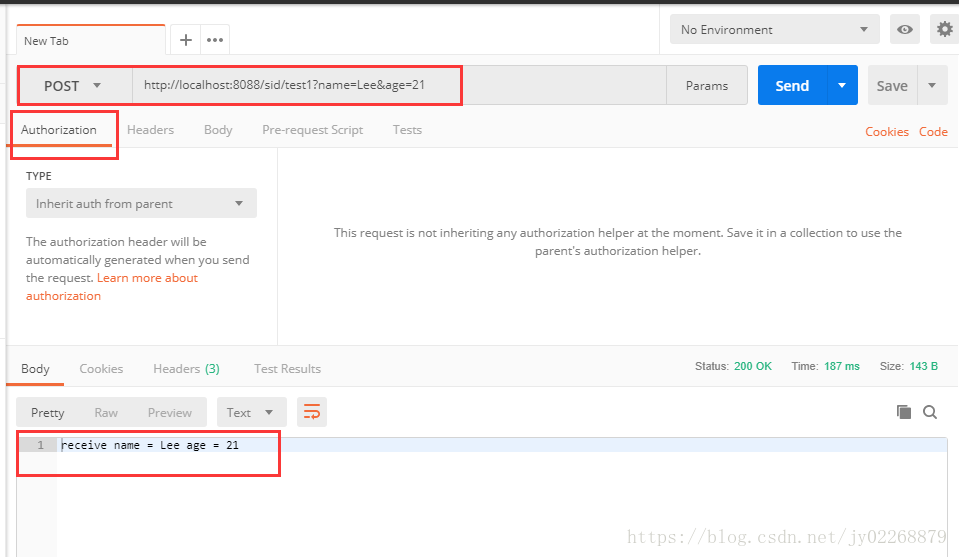
3.动态接收URL中的数据
@PathVariable将URL中的占位符参数绑定到控制器处理方法的入参
此种情况下,url求情中一定要带占位符pageNo,pageSize的值,不然访问失败
即访问时一定要用 http://localhost:8088/sid/test2/2/20
如果用 http://localhost:8088/sid/test2 则访问失败
/** * 测试动态接收URL中的数据 * */ @RequestMapping(value = "/test2/{pageNo}/{pageSize}", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String urlData(@PathVariable int pageNo , @PathVariable int pageSize){ String result = "receive pageNo = "+pageNo+" pageSize = "+pageSize; System.out.println(result); return result; }
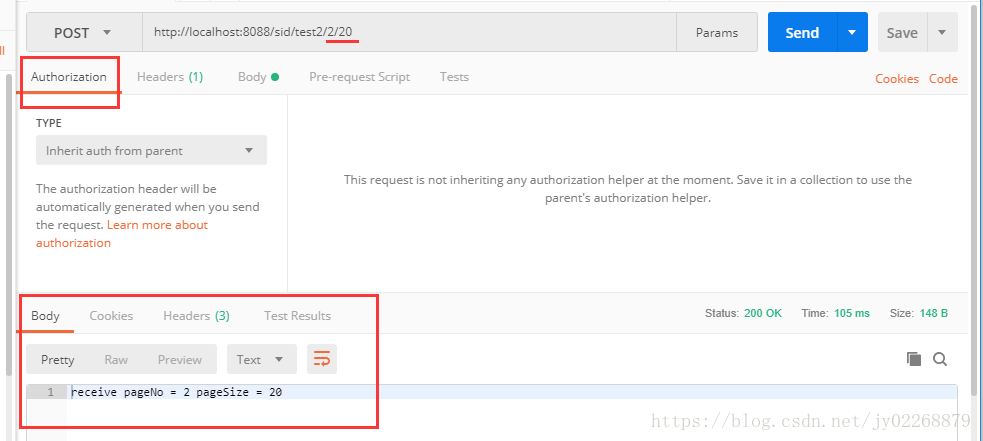
4.json
@RequestBody 接收Json格式的数据需要加这个注解。该注解不能接收URL、Form表单传参
/** * 测试接收json数据 * */ @RequestMapping(value = "/jsonData", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String jsonData(@RequestBody TestModel tm){ String result = "receive name = "+tm.getName()+" age = "+tm.getAge(); System.out.println(result); return result; }

5.@RequestMapping注解详细介绍
1.处理多个URL
@RestController @RequestMapping("/home") public class IndexController { @RequestMapping(value = { "", "/page", "page*", "view/*,**/msg" }) String indexMultipleMapping() { return "Hello from index multiple mapping."; } }
这些 URL 都会由 indexMultipleMapping() 来处理:
localhost:8080/home
localhost:8080/home/
localhost:8080/home/page
localhost:8080/home/pageabc
localhost:8080/home/view/
localhost:8080/home/view/view
2.HTTP的各种方法
如POST方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/test1", method = RequestMethod.POST)
3.produces、consumes
produces 指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头header中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回。结合@ResponseBody使用
---------------------
---------------------
@Controller @RequestMapping(value = "/t") public class TestController { //方法仅处理request请求中Accept头中包含了"text/html"的请求 @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/produces",produces = {"text/html"}) public String testProduces(String name) { return "test requestMapping produces attribute! "+name; } }
方法仅处理request请求中Accept头中包含了"text/html"的请求
比如用postman构建一个Accept=“application/json”的请求,请求会失败
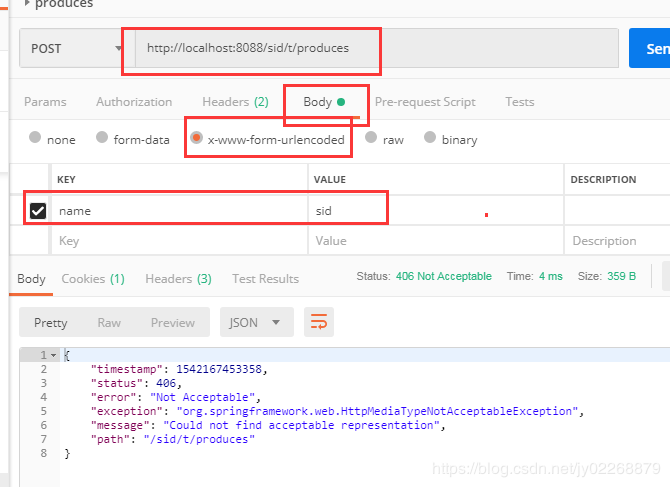

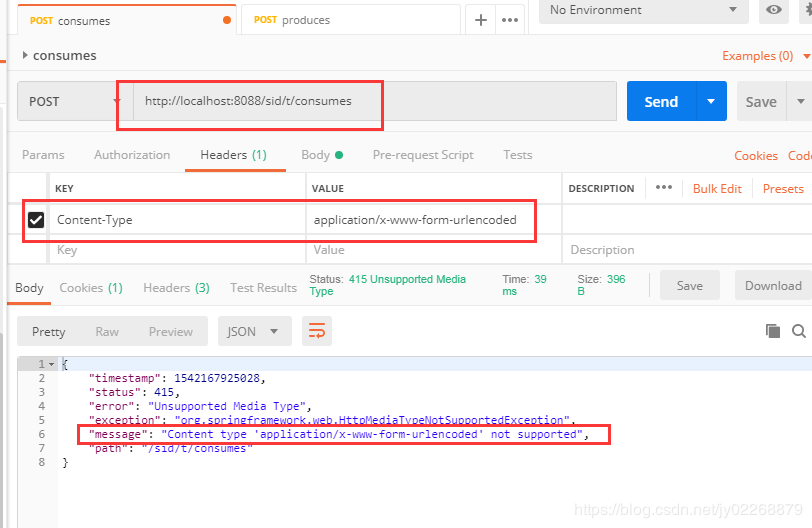
comsumes 指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如application/json, text/html。结合@RequestBody使用
@Controller @RequestMapping(value = "/t") public class TestController { //方法仅处理request Content-Type为"application/json"类型的请求 @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/consumes",consumes = {"application/json"}) public String testConsumes(@RequestBody String name) { return "test requestMapping consumes attribute! "+name; } }
方法仅处理request Content-Type为"application/json"类型的请求。
如果用postman构建一个Content-Type=“application/x-www-form-urlencoded”的请求,该方法不处理
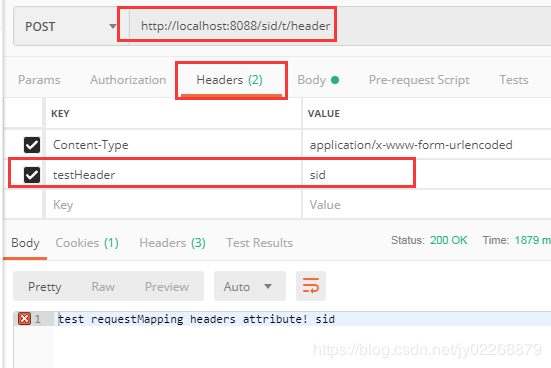
4.headers
根据请求中的消息头内容缩小请求映射的范围
例如:
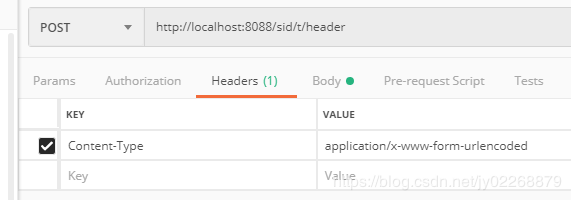
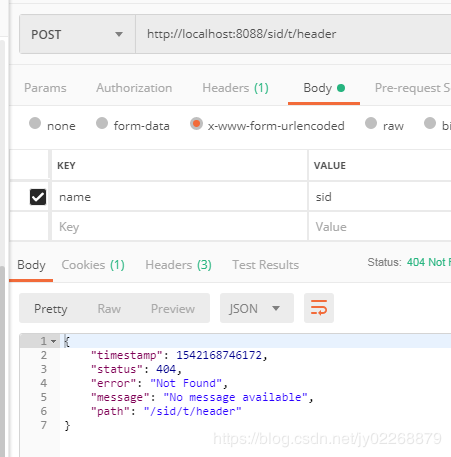
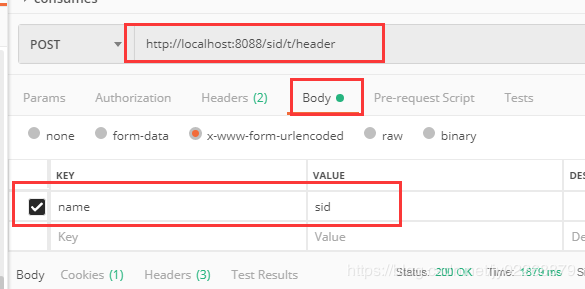
只处理header中testHeader = sid的请求
//方法仅处理header中testHeader = sid的请求 @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/header",headers = {"testHeader = sid"}) public String testHeader(String name) { return "test requestMapping headers attribute! "+name; }
构建一个header钟不带testHeader=sid的请求,会失败
必须要header中带testHeader=sid的请求的请求才处理
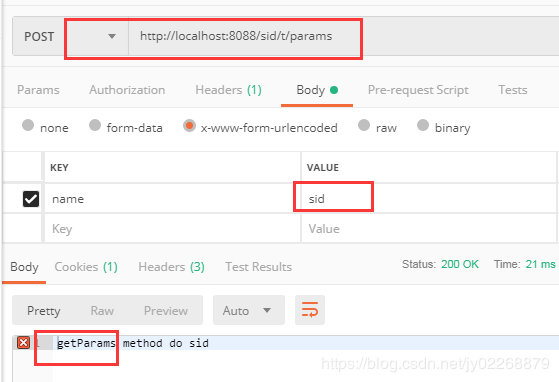
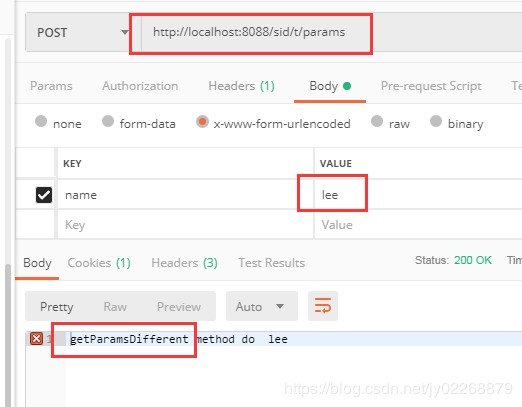
5.结合params属性处理请求参数
例如:
请求参数name=sid的时候由getParams方法处理
请求参数name=lee的时候由getParamsDifferent方法处理
@Controller @RequestMapping(value = "/t") public class TestController { @RequestMapping(value = "/params", params = { "name=sid" }) @ResponseBody public String getParams(@RequestParam("name") String name) { return "getParams method do " + name; } @RequestMapping(value = "/params", params = { "name=lee" }) @ResponseBody public String getParamsDifferent(@RequestParam("name") String name) { return "getParamsDifferent method do " + name; } }
二、返回值
@RestController注解,相当于@Controller+@ResponseBody两个注解的结合,返回json数据不需要在方法前面加@ResponseBody注解了,但使用@RestController这个注解,就不能返回jsp,html页面,视图解析器无法解析jsp,html页面
@RestController注解,相当于@Controller+@ResponseBody两个注解的结合,返回json数据不需要在方法前面加@ResponseBody注解了,但使用@RestController这个注解,就不能返回jsp,html页面,视图解析器无法解析jsp,html页面
1.返回静态html页面
application.yml
---------------------
application.yml
---------------------
server: port: 8088 servlet: context-path: /sid spring: mvc: view: prefix: / suffix: .html
/** * 返回界面 index.html * @Controller修饰的类 直接定义方法返回值为String * */ @RequestMapping(value = "/index") public String index(){ return "index"; } /**返回界面 index.html * @RestController修饰的类 * 需要配合视图解析器 * */ @RequestMapping("/indexmv") public ModelAndView indexmv() { ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView("index"); return mv; }
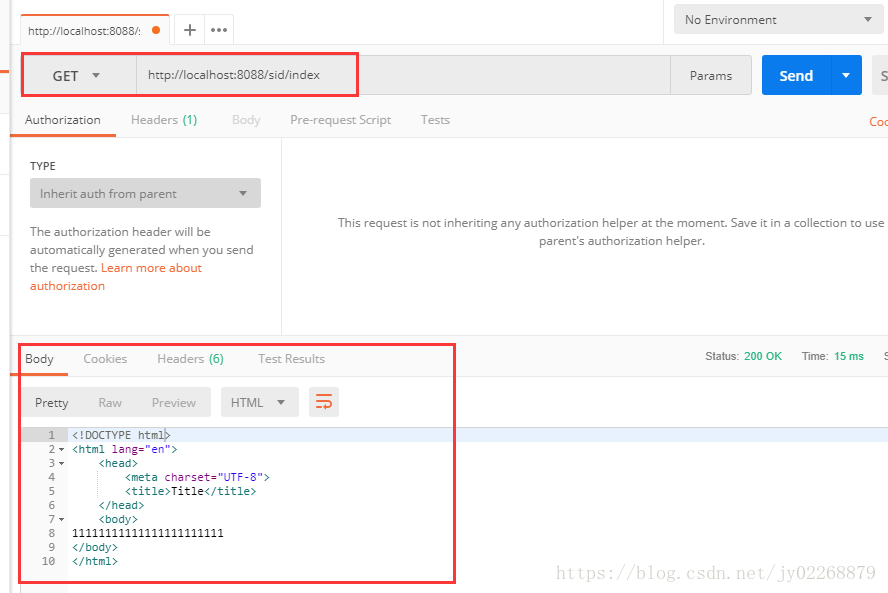
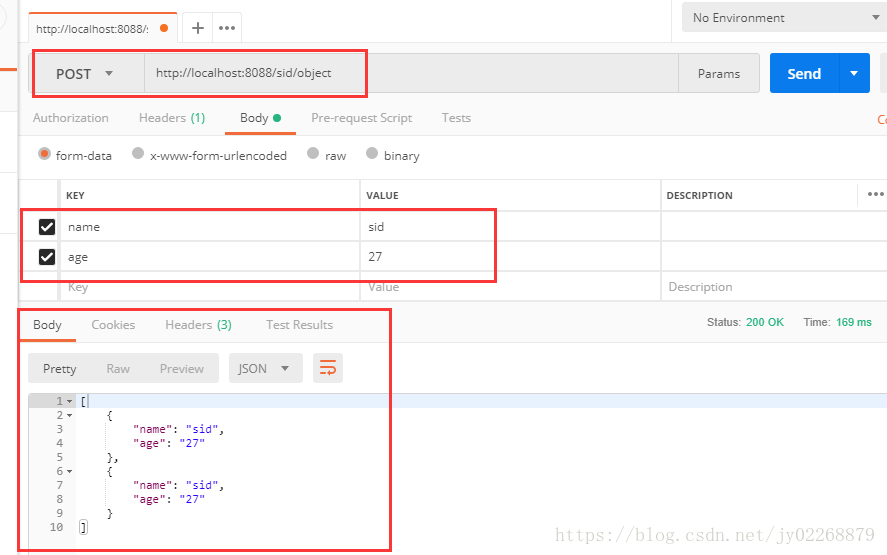
2.通过object返回查询结果
@ResponseBody会把返回值变成json
/** * 直接查询得到的model类,@ResponseBody会把返回值变成json * */ @RequestMapping(value = "/object", method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public Object object(@RequestParam("name") String name , @RequestParam("age") String age){ TestModel t =getModel( name , age); List<TestModel> list =new ArrayList(); list.add(t); return list; }
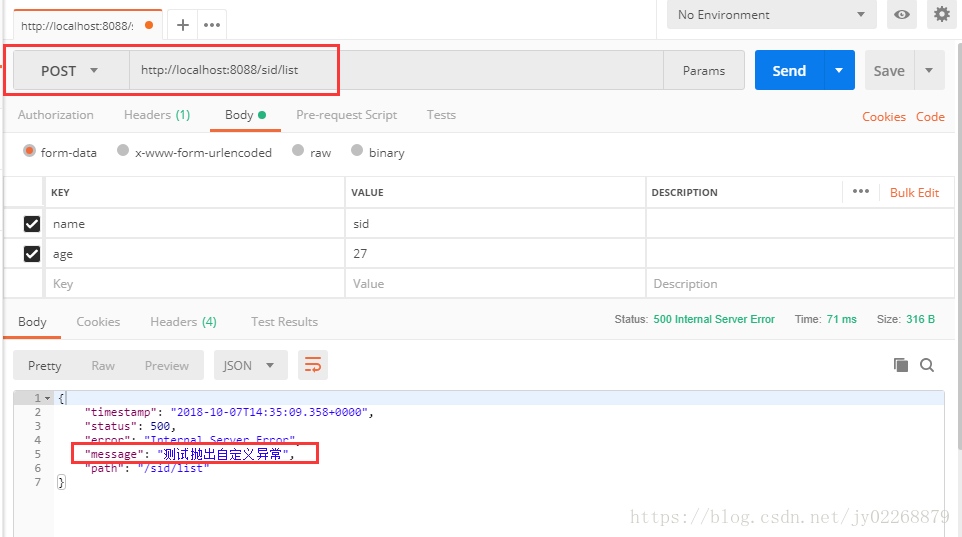
3.返回时直接抛出自定义异常
/** * 返回时直接抛出自定义异常 * */ @RequestMapping(value = "/list", method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public List<TestModel> list(@RequestParam("name") String name , @RequestParam("age") String age){ TestModel t =getModel( name , age); if(t != null){ throw new MyException("测试抛出自定义异常"); } List<TestModel> list =new ArrayList(); list.add(t); list.add(t); return list; }
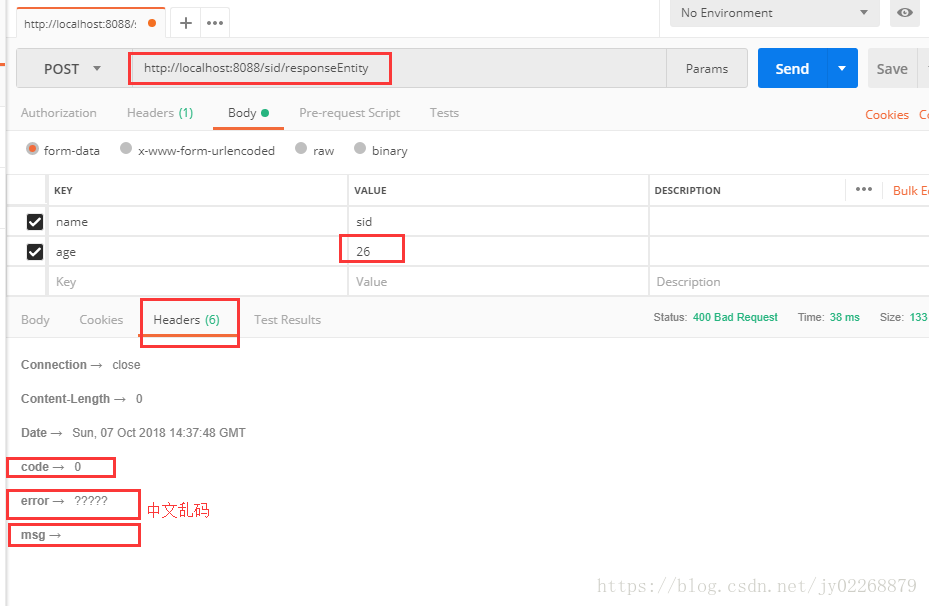
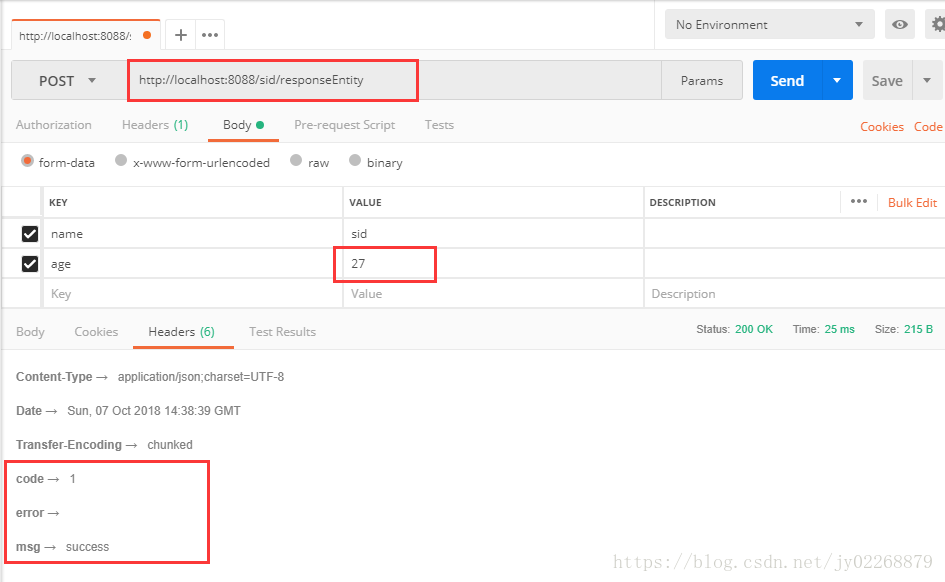
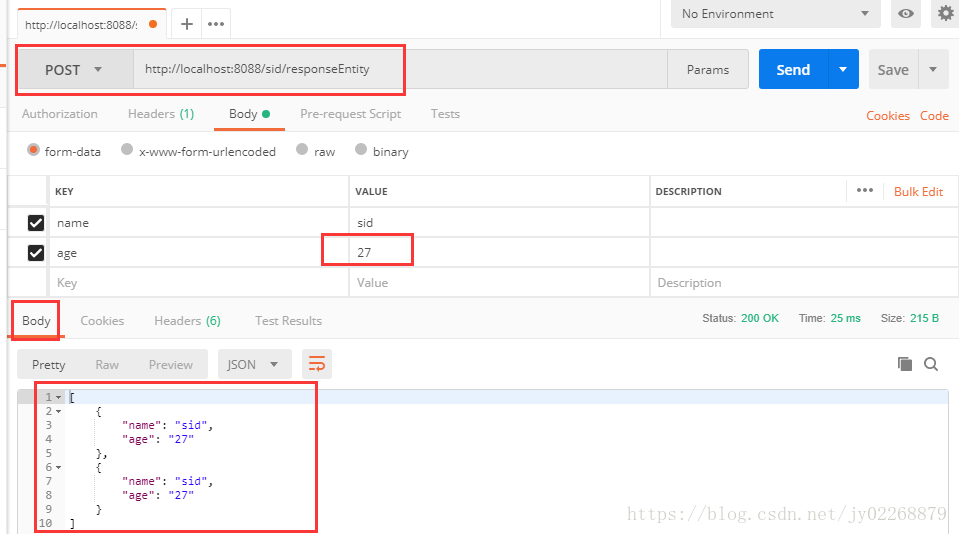
4.返回ResponseEntity
两种不同的创建ResponseEntity的方式
/** * 返回ResponseEntity * * ResponseEntity的优先级高于@ResponseBody。 * 在不是ResponseEntity的情况下才去检查有没有@ResponseBody注解。 * 如果响应类型是ResponseEntity可以不写@ResponseBody注解 * */ @RequestMapping(value = "/responseEntity", method = RequestMethod.POST) public ResponseEntity<?> responseEntity(@RequestParam("name") String name , @RequestParam("age") String age){ try{ TestModel t =getModel( name , age); if(!t.getAge().equals("27")){ throw new MyException("年龄错误!"); } List<TestModel> list =new ArrayList(); list.add(t); list.add(t); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); //headers.set("Content-type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8"); headers.add("code", "1"); headers.add("msg", "success"); headers.add("error", ""); return new ResponseEntity<List>(list,headers,HttpStatus.OK); }catch (MyException e){ return ResponseEntity.badRequest() //.header("Content-type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8") .header("code", "0") .header("msg", "") .header("error", e.getMessage())//中文乱码 .build();//build无返回值 body有返回值 } }
--------------------------------------
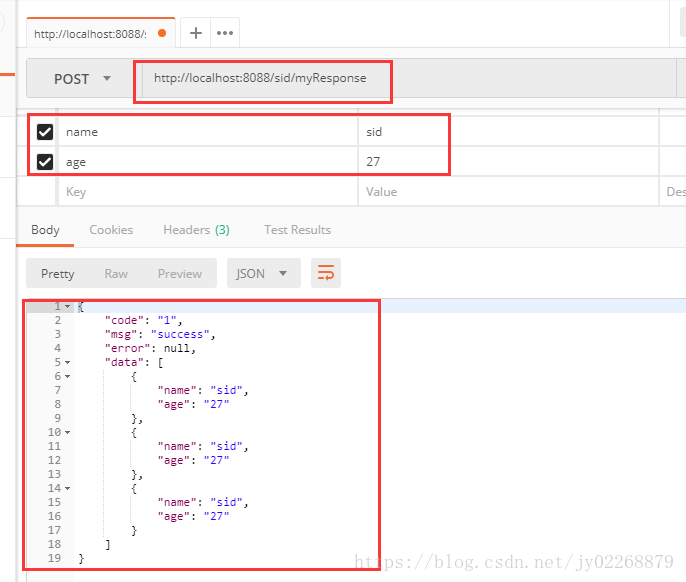
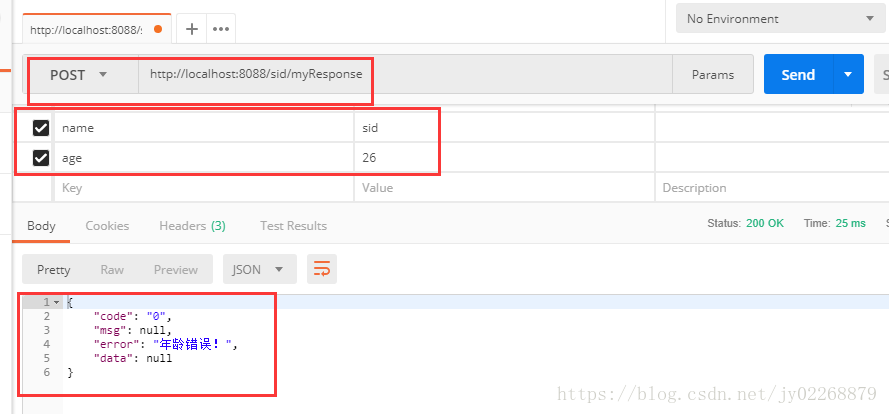
5.返回自定义类,其中有code msg error data 而查询结果在data中
MyResponse.java
package com.sid.springtboot.test.springboottest; public class MyResponse<T> { private String code; private String msg; private String error; private T data; public MyResponse(String code, String msg, String error, T data) { this.code = code; this.msg = msg; this.error = error; this.data = data; } public String getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(String code) { this.code = code; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } public String getError() { return error; } public void setError(String error) { this.error = error; } public T getData() { return data; } public void setData(T data) { this.data = data; } }
MyException.java
package com.sid.springtboot.test.springboottest; public class MyException extends RuntimeException{ private String errorCode; private String msg; public MyException(String message) { super(message); } public MyException(String errorCode, String msg) { this.errorCode = errorCode; this.msg = msg; } public String getErrorCode() { return errorCode; } public void setErrorCode(String errorCode) { this.errorCode = errorCode; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } }
controller
/** * 返回自定义类,其中有code msg error data 而查询结果在data中 * */ @RequestMapping(value = "/myResponse", method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public MyResponse<?> myResponse(@RequestParam("name") String name , @RequestParam("age") String age){ try{ TestModel t1 =getModel( name , age); if(!t1.getAge().equals("27")){ throw new MyException("年龄错误!"); } List<TestModel> list =new ArrayList(); list.add(t1); list.add(t1); list.add(t1); return new MyResponse<List>("1","success",null,list); }catch (MyException e){ return new MyResponse<>("0",null,e.getMessage(),null); } }
三、上传、下载文件
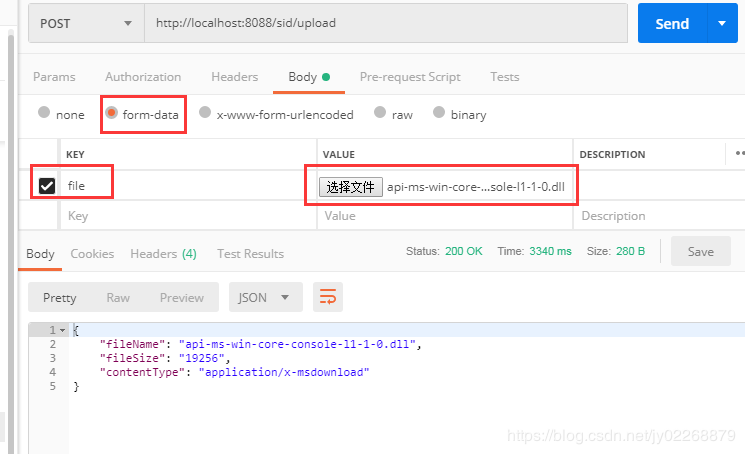
上传文件
@PostMapping("/upload")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, String> upload1(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
System.out.println("[文件类型] - [{}]"+ file.getContentType());
System.out.println("[文件名称] - [{}]"+ file.getOriginalFilename());
System.out.println("[文件大小] - [{}]"+ file.getSize());
//保存
file.transferTo(new File("D:\gitrep\springboot\testFile\" + file.getOriginalFilename()));
Map<String, String> result = new HashMap<>(16);
result.put("contentType", file.getContentType());
result.put("fileName", file.getOriginalFilename());
result.put("fileSize", file.getSize() + "");
return result;
}
下载文件
1.通过ResponseEntity<InputStreamResource>实现
封装ResponseEntity,将文件流写入body中。这里注意一点,就是文件的格式需要根据具体文件的类型来设置,一般默认为application/octet-stream。文件头中设置缓存,以及文件的名字。文件的名字写入了,都可以避免出现文件随机产生名字,而不能识别的问题。
---------------------
---------------------
@GetMapping("/download")
public ResponseEntity<InputStreamResource> downloadFile() throws IOException {
String filePath = "D:\gitrep\springboot\testFile\" + "api-ms-win-core-console-l1-1-0.dll";
FileSystemResource file = new FileSystemResource(filePath);
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Cache-Control", "no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate");
headers.add("Content-Disposition", String.format("attachment; filename="%s"", file.getFilename()));
headers.add("Pragma", "no-cache");
headers.add("Expires", "0");
return ResponseEntity.ok().headers(headers)
.contentLength(file.contentLength())
.contentType(MediaType.parseMediaType("application/octet-stream"))
.body(new InputStreamResource(file.getInputStream()));
}
2.用HttpServletResponse
@GetMapping("/download2")
public String downloadFile2( HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 获取指定目录下的文件
String fileName = "D:\gitrep\springboot\testFile\" + "api-ms-win-core-console-l1-1-0.dll";
File file = new File(fileName);
// 如果文件名存在,则进行下载
if (file.exists()) {
// 配置文件下载
response.setHeader("content-type", "application/octet-stream");
response.setContentType("application/octet-stream");
// 下载文件能正常显示中文
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
// 实现文件下载
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
FileInputStream fis = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
OutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
int i = bis.read(buffer);
while (i != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, i);
i = bis.read(buffer);
}
System.out.println("Download the song successfully!");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Download the song failed!");
} finally {
if (bis != null) {
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
return null;
}