前面介绍了批量处理的WorkCount是如何执行的
<从flink-example分析flink组件(1)WordCount batch实战及源码分析>
<从flink-example分析flink组件(2)WordCount batch实战及源码分析----flink如何在本地执行的?>
这篇从WordCount的流式处理开始
/** * Implements the "WordCount" program that computes a simple word occurrence * histogram over text files in a streaming fashion. * * <p>The input is a plain text file with lines separated by newline characters. * * <p>Usage: <code>WordCount --input <path> --output <path></code><br> * If no parameters are provided, the program is run with default data from * {@link WordCountData}. * * <p>This example shows how to: * <ul> * <li>write a simple Flink Streaming program, * <li>use tuple data types, * <li>write and use user-defined functions. * </ul> */ public class WordCount { // ************************************************************************* // PROGRAM // ************************************************************************* public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // Checking input parameters final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args); // set up the execution environment final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); // make parameters available in the web interface env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params); // get input data DataStream<String> text; if (params.has("input")) { // read the text file from given input path text = env.readTextFile(params.get("input")); } else { System.out.println("Executing WordCount example with default input data set."); System.out.println("Use --input to specify file input."); // get default test text data text = env.fromElements(WordCountData.WORDS); } DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> counts = // split up the lines in pairs (2-tuples) containing: (word,1) text.flatMap(new Tokenizer()) // group by the tuple field "0" and sum up tuple field "1" .keyBy(0).sum(1); //1 // emit result if (params.has("output")) { counts.writeAsText(params.get("output")); } else { System.out.println("Printing result to stdout. Use --output to specify output path."); counts.print(); } // execute program env.execute("Streaming WordCount");//2 } // ************************************************************************* // USER FUNCTIONS // ************************************************************************* /** * Implements the string tokenizer that splits sentences into words as a * user-defined FlatMapFunction. The function takes a line (String) and * splits it into multiple pairs in the form of "(word,1)" ({@code Tuple2<String, * Integer>}). */ public static final class Tokenizer implements FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>> { @Override public void flatMap(String value, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) { // normalize and split the line String[] tokens = value.toLowerCase().split("\W+"); // emit the pairs for (String token : tokens) { if (token.length() > 0) { out.collect(new Tuple2<>(token, 1)); } } } } }
整个执行流程如下图所示:
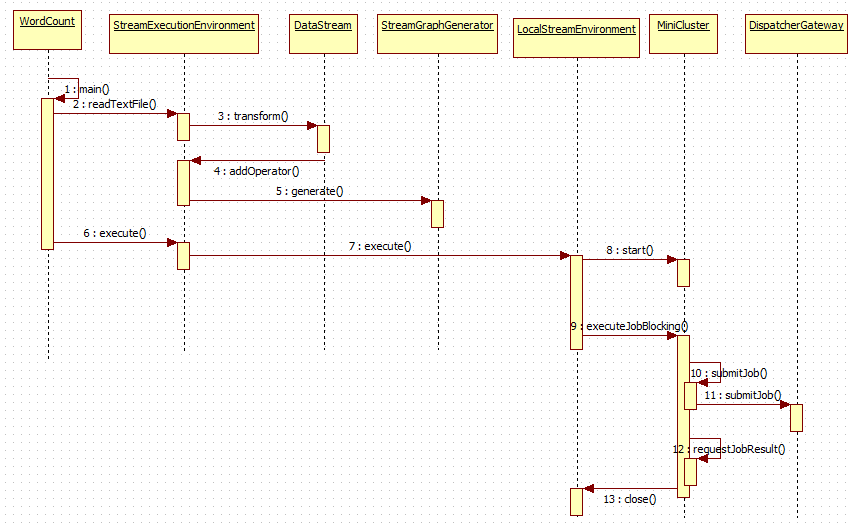
第1~4步:main方法读取文件,增加算子
private <OUT> DataStreamSource<OUT> createFileInput(FileInputFormat<OUT> inputFormat, TypeInformation<OUT> typeInfo, String sourceName, FileProcessingMode monitoringMode, long interval) { Preconditions.checkNotNull(inputFormat, "Unspecified file input format."); Preconditions.checkNotNull(typeInfo, "Unspecified output type information."); Preconditions.checkNotNull(sourceName, "Unspecified name for the source."); Preconditions.checkNotNull(monitoringMode, "Unspecified monitoring mode."); Preconditions.checkArgument(monitoringMode.equals(FileProcessingMode.PROCESS_ONCE) || interval >= ContinuousFileMonitoringFunction.MIN_MONITORING_INTERVAL, "The path monitoring interval cannot be less than " + ContinuousFileMonitoringFunction.MIN_MONITORING_INTERVAL + " ms."); ContinuousFileMonitoringFunction<OUT> monitoringFunction = new ContinuousFileMonitoringFunction<>(inputFormat, monitoringMode, getParallelism(), interval); ContinuousFileReaderOperator<OUT> reader = new ContinuousFileReaderOperator<>(inputFormat); SingleOutputStreamOperator<OUT> source = addSource(monitoringFunction, sourceName) .transform("Split Reader: " + sourceName, typeInfo, reader); //1 return new DataStreamSource<>(source); }
增加算子的方法,当调用execute方法时,此时增加的算子会被执行。
/** * Adds an operator to the list of operators that should be executed when calling * {@link #execute}. * * <p>When calling {@link #execute()} only the operators that where previously added to the list * are executed. * * <p>This is not meant to be used by users. The API methods that create operators must call * this method. */ @Internal public void addOperator(StreamTransformation<?> transformation) { Preconditions.checkNotNull(transformation, "transformation must not be null."); this.transformations.add(transformation); }
第5步:产生StreamGraph,从而可以得到JobGraph,即将Stream程序转换成JobGraph
// transform the streaming program into a JobGraph StreamGraph streamGraph = getStreamGraph(); streamGraph.setJobName(jobName); JobGraph jobGraph = streamGraph.getJobGraph(); jobGraph.setAllowQueuedScheduling(true);
第6~8步启动MiniCluster,为执行job做准备
/** * Starts the mini cluster, based on the configured properties. * * @throws Exception This method passes on any exception that occurs during the startup of * the mini cluster. */ public void start() throws Exception { synchronized (lock) { checkState(!running, "MiniCluster is already running"); LOG.info("Starting Flink Mini Cluster"); LOG.debug("Using configuration {}", miniClusterConfiguration); final Configuration configuration = miniClusterConfiguration.getConfiguration(); final boolean useSingleRpcService = miniClusterConfiguration.getRpcServiceSharing() == RpcServiceSharing.SHARED; try { initializeIOFormatClasses(configuration); LOG.info("Starting Metrics Registry"); metricRegistry = createMetricRegistry(configuration); // bring up all the RPC services LOG.info("Starting RPC Service(s)"); AkkaRpcServiceConfiguration akkaRpcServiceConfig = AkkaRpcServiceConfiguration.fromConfiguration(configuration); final RpcServiceFactory dispatcherResourceManagreComponentRpcServiceFactory; if (useSingleRpcService) { // we always need the 'commonRpcService' for auxiliary calls commonRpcService = createRpcService(akkaRpcServiceConfig, false, null); final CommonRpcServiceFactory commonRpcServiceFactory = new CommonRpcServiceFactory(commonRpcService); taskManagerRpcServiceFactory = commonRpcServiceFactory; dispatcherResourceManagreComponentRpcServiceFactory = commonRpcServiceFactory; } else { // we always need the 'commonRpcService' for auxiliary calls commonRpcService = createRpcService(akkaRpcServiceConfig, true, null); // start a new service per component, possibly with custom bind addresses final String jobManagerBindAddress = miniClusterConfiguration.getJobManagerBindAddress(); final String taskManagerBindAddress = miniClusterConfiguration.getTaskManagerBindAddress(); dispatcherResourceManagreComponentRpcServiceFactory = new DedicatedRpcServiceFactory(akkaRpcServiceConfig, jobManagerBindAddress); taskManagerRpcServiceFactory = new DedicatedRpcServiceFactory(akkaRpcServiceConfig, taskManagerBindAddress); } RpcService metricQueryServiceRpcService = MetricUtils.startMetricsRpcService( configuration, commonRpcService.getAddress()); metricRegistry.startQueryService(metricQueryServiceRpcService, null); ioExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool( Hardware.getNumberCPUCores(), new ExecutorThreadFactory("mini-cluster-io")); haServices = createHighAvailabilityServices(configuration, ioExecutor); blobServer = new BlobServer(configuration, haServices.createBlobStore()); blobServer.start(); heartbeatServices = HeartbeatServices.fromConfiguration(configuration); blobCacheService = new BlobCacheService( configuration, haServices.createBlobStore(), new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), blobServer.getPort()) ); startTaskManagers(); MetricQueryServiceRetriever metricQueryServiceRetriever = new RpcMetricQueryServiceRetriever(metricRegistry.getMetricQueryServiceRpcService()); dispatcherResourceManagerComponents.addAll(createDispatcherResourceManagerComponents( configuration, dispatcherResourceManagreComponentRpcServiceFactory, haServices, blobServer, heartbeatServices, metricRegistry, metricQueryServiceRetriever, new ShutDownFatalErrorHandler() )); resourceManagerLeaderRetriever = haServices.getResourceManagerLeaderRetriever(); dispatcherLeaderRetriever = haServices.getDispatcherLeaderRetriever(); webMonitorLeaderRetrievalService = haServices.getWebMonitorLeaderRetriever(); dispatcherGatewayRetriever = new RpcGatewayRetriever<>( commonRpcService, DispatcherGateway.class, DispatcherId::fromUuid, 20, Time.milliseconds(20L)); resourceManagerGatewayRetriever = new RpcGatewayRetriever<>( commonRpcService, ResourceManagerGateway.class, ResourceManagerId::fromUuid, 20, Time.milliseconds(20L)); webMonitorLeaderRetriever = new LeaderRetriever(); resourceManagerLeaderRetriever.start(resourceManagerGatewayRetriever); dispatcherLeaderRetriever.start(dispatcherGatewayRetriever); webMonitorLeaderRetrievalService.start(webMonitorLeaderRetriever); } catch (Exception e) { // cleanup everything try { close(); } catch (Exception ee) { e.addSuppressed(ee); } throw e; } // create a new termination future terminationFuture = new CompletableFuture<>(); // now officially mark this as running running = true; LOG.info("Flink Mini Cluster started successfully"); } }
第9~12步 执行job
/** * This method runs a job in blocking mode. The method returns only after the job * completed successfully, or after it failed terminally. * * @param job The Flink job to execute * @return The result of the job execution * * @throws JobExecutionException Thrown if anything went amiss during initial job launch, * or if the job terminally failed. */ @Override public JobExecutionResult executeJobBlocking(JobGraph job) throws JobExecutionException, InterruptedException { checkNotNull(job, "job is null"); final CompletableFuture<JobSubmissionResult> submissionFuture = submitJob(job); final CompletableFuture<JobResult> jobResultFuture = submissionFuture.thenCompose( (JobSubmissionResult ignored) -> requestJobResult(job.getJobID())); final JobResult jobResult; try { jobResult = jobResultFuture.get(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { throw new JobExecutionException(job.getJobID(), "Could not retrieve JobResult.", ExceptionUtils.stripExecutionException(e)); } try { return jobResult.toJobExecutionResult(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()); } catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new JobExecutionException(job.getJobID(), e); } }
先上传jar包文件,此时需要DispatcherGateway来执行上转任务,异步等待结果执行完毕
总结:
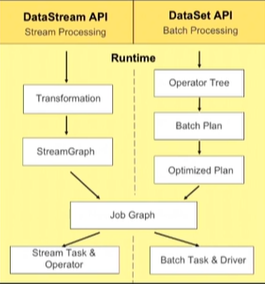
batch和stream的执行流程很相似,又有不同。
不同:Stream传递的是DataStream,Batch传递的是DataSet
相同:都转换成JobGraph执行