前端控制器是整个MVC框架中最为核心的一块,它主要用来拦截符合要求的外部请求,并把请求分发到不同的控制器去处理,根据控制器处理后的结果,生成相应的响应发送到客户端。前端控制器既可以使用Filter实现(Struts2采用这种方式),也可以使用Servlet来实现(spring MVC框架)。
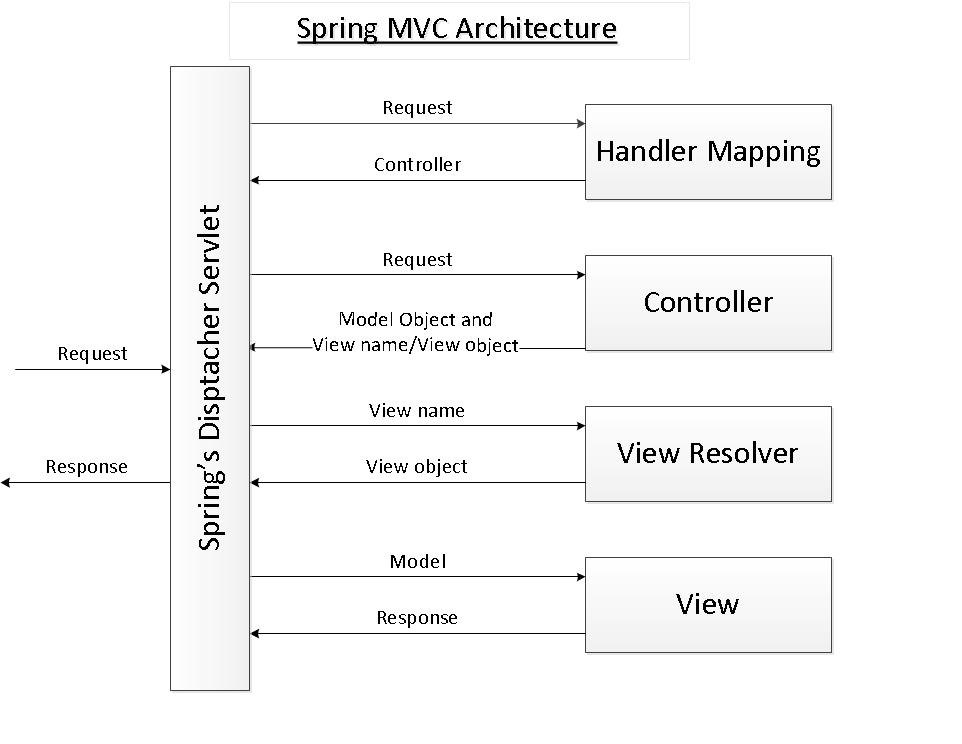
DispatcherServlet 作为前置控制器是web服务器的入口,是spring mvc最重要的一个类,通过它的生命周期可以加深对web服务器的理解。
servlet的生命周期
首先我们回忆一下servlet的生命周期:
Servlet生命周期分为三个阶段:【http://www.cnblogs.com/cuiliang/archive/2011/10/21/2220671.html】
1,初始化阶段 调用init()方法。Servlet被装载后,Servlet容器创建一个Servlet实例并且调用Servlet的init()方法进行初始化。在Servlet的整个生命周期内,init()方法只被调用一次。
2,响应客户请求阶段 调用service()方法
3,终止阶段 调用destroy()方法
Servlet初始化阶段:
在下列时刻Servlet容器装载Servlet:
1,Servlet容器启动时自动装载某些Servlet,实现它只需要在web.XML文件中的<Servlet></Servlet>之间添加如下代码:
<loadon-startup>1</loadon-startup>
2,在Servlet容器启动后,客户首次向Servlet发送请求
3,Servlet类文件被更新后,重新装载Servlet
DispatcherServlet的结构
复习了上述知识后我们来看看DispatcherServlet的结构:
DispatcherServlet继承自抽象类:FrameworkServlet,间接继承了HttpServlet (FrameworkServlet继承自HttpServletBean,而HttpServletBean继承自HttpServlet )
Servlet的初始化

protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); //文件上传解析,如果请求类型是multipart将通过MultipartResolver进行文件上传解析; initLocaleResolver(context); //本地化解析 initThemeResolver(context); //主题解析 initHandlerMappings(context); //通过HandlerMapping,将请求映射到处理器 initHandlerAdapters(context); //通过HandlerAdapter支持多种类型的处理器 initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); //如果执行过程中遇到异常将交给HandlerExceptionResolver来解析 initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); //直接解析请求到视图名 initViewResolvers(context); //通过ViewResolver解析逻辑视图名到具体视图实现 initFlashMapManager(context); //flash映射管理器 }
servlet如何处理请求:
servlet的service方法处理http请求。
FrameworkServlet.java 定义了servlet的service和destroy方法,如下所示:
/** * Override the parent class implementation in order to intercept PATCH * requests. */ @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String method = request.getMethod(); if (method.equalsIgnoreCase(RequestMethod.PATCH.name())) { processRequest(request, response); } else { super.service(request, response); } }
我们知道http请求类型有七种(外加一个option选项),定义如下:
public enum RequestMethod { GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, TRACE }
FrameworkServlet的service()处理不同的请求,我们以常见的post来说明:
/** * Process this request, publishing an event regardless of the outcome. * <p>The actual event handling is performed by the abstract * {@link #doService} template method. */ protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Throwable failureCause = null; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try { doService(request, response); } catch (ServletException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (IOException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { failureCause = ex; throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex); } finally { resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes); if (requestAttributes != null) { requestAttributes.requestCompleted(); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (failureCause != null) { this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause); } else { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing"); } else { this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request"); } } } publishRequestHandledEvent(request, startTime, failureCause); } }
FrameworkServlet 抽象定义了处理流程,留待子类来实现该方法,完成具体的请求处理。
/** * Subclasses must implement this method to do the work of request handling, * receiving a centralized callback for GET, POST, PUT and DELETE. * <p>The contract is essentially the same as that for the commonly overridden * {@code doGet} or {@code doPost} methods of HttpServlet. * <p>This class intercepts calls to ensure that exception handling and * event publication takes place. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure * @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#doGet * @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#doPost */ protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
具体实现如下:
/** * Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch} * for the actual dispatching. */ @Override protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : ""; logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]"); } // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } }
重头戏,作为请求分发器的实现:
功能:1. 把请求分发到handler(按照配置顺序获取servlet的映射关系获取handler);2. 根据servlet已安装的 HandlerAdapters 去查询第一个能处理的handler;3. handler激发处理请求
/** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } try { // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } } applyDefaultViewName(request, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Error err) { triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); return; } // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } }
servlet销毁
/** * Close the WebApplicationContext of this servlet. * @see org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#close() */ @Override public void destroy() { getServletContext().log("Destroying Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); // Only call close() on WebApplicationContext if locally managed... if (this.webApplicationContext instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext && !this.webApplicationContextInjected) { ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) this.webApplicationContext).close(); } }
小结:
本文因篇章限制,仅仅介绍了请求处理的流程,没有对代码进行深入的分析,接下来的文章将从细微处着手,分析spring的代码之美。