闲着没事,看看源码也是一种乐趣!
java操作数据库的基本步骤都是类似的:
1. 建立数据库连接
2. 创建Connection
3. 创建statement或者preparedStateement
4. 执行sql,返回ResultSet
5. 关闭resultSet
5.关闭statement
6.关闭Connection
Spring对数据库的操作在jdbc上面做了深层次的封装,使用spring的注入功能,可以把DataSource注册到JdbcTemplate之中。
1. 构造函数,三种形式
/** * Construct a new JdbcTemplate for bean usage. * <p>Note: The DataSource has to be set before using the instance. * @see #setDataSource */ public JdbcTemplate() { } /** * Construct a new JdbcTemplate, given a DataSource to obtain connections from. * <p>Note: This will not trigger initialization of the exception translator. * @param dataSource the JDBC DataSource to obtain connections from */ public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) { setDataSource(dataSource); afterPropertiesSet(); } /** * Construct a new JdbcTemplate, given a DataSource to obtain connections from. * <p>Note: Depending on the "lazyInit" flag, initialization of the exception translator * will be triggered. * @param dataSource the JDBC DataSource to obtain connections from * @param lazyInit whether to lazily initialize the SQLExceptionTranslator */ public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource, boolean lazyInit) { setDataSource(dataSource); setLazyInit(lazyInit); afterPropertiesSet(); }
一种思路:将datasource注入到JdbcTemplate。
2.获取Connection
//------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Methods dealing with static SQL (java.sql.Statement) //------------------------------------------------------------------------- @Override public <T> T execute(StatementCallback<T> action) throws DataAccessException { Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null"); Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(getDataSource()); Statement stmt = null; try { Connection conToUse = con; if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null && this.nativeJdbcExtractor.isNativeConnectionNecessaryForNativeStatements()) { conToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeConnection(con); } stmt = conToUse.createStatement(); applyStatementSettings(stmt); Statement stmtToUse = stmt; if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { stmtToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeStatement(stmt); } T result = action.doInStatement(stmtToUse); handleWarnings(stmt); return result; } catch (SQLException ex) { // Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock // in the case when the exception translator hasn't been initialized yet. JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt); stmt = null; DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); con = null; throw getExceptionTranslator().translate("StatementCallback", getSql(action), ex); } finally { JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt); DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); } }
Connection的获取方式:
2.1. 若是datasource直接使用jdbc而没有使用诸如c3p0,dbcp等第三方插件时则从下面的方法获取:
Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(getDataSource());
/** * Actually obtain a JDBC Connection from the given DataSource. * Same as {@link #getConnection}, but throwing the original SQLException. * <p>Is aware of a corresponding Connection bound to the current thread, for example * when using {@link DataSourceTransactionManager}. Will bind a Connection to the thread * if transaction synchronization is active (e.g. if in a JTA transaction). * <p>Directly accessed by {@link TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy}. * @param dataSource the DataSource to obtain Connections from * @return a JDBC Connection from the given DataSource * @throws SQLException if thrown by JDBC methods * @see #doReleaseConnection */ public static Connection doGetConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException { Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified"); ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource); if (conHolder != null && (conHolder.hasConnection() || conHolder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction())) { conHolder.requested(); if (!conHolder.hasConnection()) { logger.debug("Fetching resumed JDBC Connection from DataSource"); conHolder.setConnection(dataSource.getConnection()); } return conHolder.getConnection(); } // Else we either got no holder or an empty thread-bound holder here. logger.debug("Fetching JDBC Connection from DataSource"); Connection con = dataSource.getConnection(); if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) { logger.debug("Registering transaction synchronization for JDBC Connection"); // Use same Connection for further JDBC actions within the transaction. // Thread-bound object will get removed by synchronization at transaction completion. ConnectionHolder holderToUse = conHolder; if (holderToUse == null) { holderToUse = new ConnectionHolder(con); } else { holderToUse.setConnection(con); } holderToUse.requested(); TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization( new ConnectionSynchronization(holderToUse, dataSource)); holderToUse.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true); if (holderToUse != conHolder) { TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, holderToUse); } } return con; }
ConnectionHolder间接继承了ResourceHolder接口,ResourceHolder接口允许spring的事务基础可以在必要时检索和重置。通常我们只要继承ResourceHolderSupport即可。
2.2. 若使用了第三方插件时,则需要从插件中提取Connection。
conToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeConnection(con);
第三方插件的关系如下:
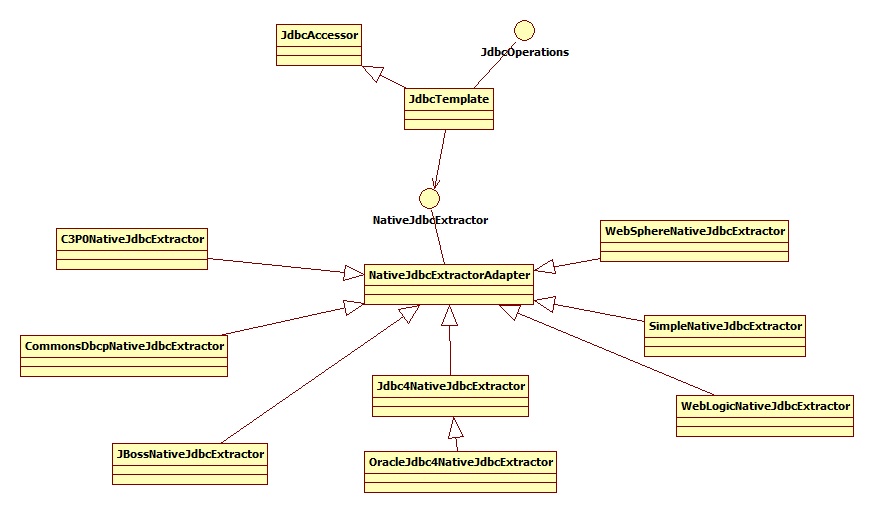
其具体方法如下:
/** * Check for a ConnectionProxy chain, then delegate to doGetNativeConnection. * <p>ConnectionProxy is used by Spring's TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy * and LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy. The target connection behind it is * typically one from a local connection pool, to be unwrapped by the * doGetNativeConnection implementation of a concrete subclass. * @see #doGetNativeConnection * @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.ConnectionProxy * @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils#getTargetConnection * @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy * @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy */ @Override public Connection getNativeConnection(Connection con) throws SQLException { if (con == null) { return null; } Connection targetCon = DataSourceUtils.getTargetConnection(con); Connection nativeCon = doGetNativeConnection(targetCon); if (nativeCon == targetCon) { // We haven't received a different Connection, so we'll assume that there's // some additional proxying going on. Let's check whether we get something // different back from the DatabaseMetaData.getConnection() call. DatabaseMetaData metaData = targetCon.getMetaData(); // The following check is only really there for mock Connections // which might not carry a DatabaseMetaData instance. if (metaData != null) { Connection metaCon = metaData.getConnection(); if (metaCon != null && metaCon != targetCon) { // We've received a different Connection there: // Let's retry the native extraction process with it. nativeCon = doGetNativeConnection(metaCon); } } } return nativeCon; }
具体的实现在其子类里面,以c3p0为例:
/** * Retrieve the Connection via C3P0's {@code rawConnectionOperation} API, * using the {@code getRawConnection} as callback to get access to the * raw Connection (which is otherwise not directly supported by C3P0). * @see #getRawConnection */ @Override protected Connection doGetNativeConnection(Connection con) throws SQLException { if (con instanceof C3P0ProxyConnection) { C3P0ProxyConnection cpCon = (C3P0ProxyConnection) con; try { return (Connection) cpCon.rawConnectionOperation( this.getRawConnectionMethod, null, new Object[] {C3P0ProxyConnection.RAW_CONNECTION}); } catch (SQLException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { ReflectionUtils.handleReflectionException(ex); } } return con; }
调用C3P0 API获取Connection。
3. 创建Statement
stmt = conToUse.createStatement(); applyStatementSettings(stmt); Statement stmtToUse = stmt; if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { stmtToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeStatement(stmt); }
3.1 不使用第三方插件
/** * Prepare the given JDBC Statement (or PreparedStatement or CallableStatement), * applying statement settings such as fetch size, max rows, and query timeout. * @param stmt the JDBC Statement to prepare * @throws SQLException if thrown by JDBC API * @see #setFetchSize * @see #setMaxRows * @see #setQueryTimeout * @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils#applyTransactionTimeout */ protected void applyStatementSettings(Statement stmt) throws SQLException { int fetchSize = getFetchSize(); if (fetchSize > 0) { stmt.setFetchSize(fetchSize); } int maxRows = getMaxRows(); if (maxRows > 0) { stmt.setMaxRows(maxRows); } DataSourceUtils.applyTimeout(stmt, getDataSource(), getQueryTimeout()); }
设置fetch size, max rows, and query timeout.其中过期时间在datasourceUtils中实现。
/** * Apply the specified timeout - overridden by the current transaction timeout, * if any - to the given JDBC Statement object. * @param stmt the JDBC Statement object * @param dataSource the DataSource that the Connection was obtained from * @param timeout the timeout to apply (or 0 for no timeout outside of a transaction) * @throws SQLException if thrown by JDBC methods * @see java.sql.Statement#setQueryTimeout */ public static void applyTimeout(Statement stmt, DataSource dataSource, int timeout) throws SQLException { Assert.notNull(stmt, "No Statement specified"); Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified"); ConnectionHolder holder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource); if (holder != null && holder.hasTimeout()) { // Remaining transaction timeout overrides specified value. stmt.setQueryTimeout(holder.getTimeToLiveInSeconds()); } else if (timeout > 0) { // No current transaction timeout -> apply specified value. stmt.setQueryTimeout(timeout); } }
3.2 第三方插件
以c3p0为例
/** * Extracts the innermost delegate from the given Commons DBCP object. * Falls back to the given object if no underlying object found. * @param obj the Commons DBCP Connection/Statement/ResultSet * @return the underlying native Connection/Statement/ResultSet */ private static Object getInnermostDelegate(Object obj) throws SQLException { if (obj == null) { return null; } try { Class<?> classToAnalyze = obj.getClass(); while (!Modifier.isPublic(classToAnalyze.getModifiers())) { classToAnalyze = classToAnalyze.getSuperclass(); if (classToAnalyze == null) { // No public provider class found -> fall back to given object. return obj; } } Method getInnermostDelegate = classToAnalyze.getMethod(GET_INNERMOST_DELEGATE_METHOD_NAME, (Class[]) null); Object delegate = ReflectionUtils.invokeJdbcMethod(getInnermostDelegate, obj); return (delegate != null ? delegate : obj); } catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) { return obj; } catch (SecurityException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Commons DBCP getInnermostDelegate method is not accessible: " + ex); } }
4. 执行statement并关闭之
T result = action.doInStatement(stmtToUse);
class QueryStatementCallback implements StatementCallback<T>, SqlProvider { @Override public T doInStatement(Statement stmt) throws SQLException { ResultSet rs = null; try { rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); ResultSet rsToUse = rs; if (nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { rsToUse = nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeResultSet(rs); } return rse.extractData(rsToUse); } finally { JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(rs); } } @Override public String getSql() { return sql; } }
4.1 不使用第三方插件
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
4.2 使用第三方插件
private static final String GET_INNERMOST_DELEGATE_METHOD_NAME = "getInnermostDelegate"; /** * Extracts the innermost delegate from the given Commons DBCP object. * Falls back to the given object if no underlying object found. * @param obj the Commons DBCP Connection/Statement/ResultSet * @return the underlying native Connection/Statement/ResultSet */ private static Object getInnermostDelegate(Object obj) throws SQLException { if (obj == null) { return null; } try { Class<?> classToAnalyze = obj.getClass(); while (!Modifier.isPublic(classToAnalyze.getModifiers())) { classToAnalyze = classToAnalyze.getSuperclass(); if (classToAnalyze == null) { // No public provider class found -> fall back to given object. return obj; } } Method getInnermostDelegate = classToAnalyze.getMethod(GET_INNERMOST_DELEGATE_METHOD_NAME, (Class[]) null); Object delegate = ReflectionUtils.invokeJdbcMethod(getInnermostDelegate, obj); return (delegate != null ? delegate : obj); } catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) { return obj; } catch (SecurityException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Commons DBCP getInnermostDelegate method is not accessible: " + ex); } }
4.3 提取数据
@Override public List<T> extractData(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { List<T> results = (this.rowsExpected > 0 ? new ArrayList<T>(this.rowsExpected) : new ArrayList<T>()); int rowNum = 0; while (rs.next()) { results.add(this.rowMapper.mapRow(rs, rowNum++)); } return results; }
或者
@Override public SqlRowSet extractData(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { return createSqlRowSet(rs); } /** * Create a SqlRowSet that wraps the given ResultSet, * representing its data in a disconnected fashion. * <p>This implementation creates a Spring ResultSetWrappingSqlRowSet * instance that wraps a standard JDBC CachedRowSet instance. * Can be overridden to use a different implementation. * @param rs the original ResultSet (connected) * @return the disconnected SqlRowSet * @throws SQLException if thrown by JDBC methods * @see #newCachedRowSet * @see org.springframework.jdbc.support.rowset.ResultSetWrappingSqlRowSet */ protected SqlRowSet createSqlRowSet(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { CachedRowSet rowSet = newCachedRowSet(); rowSet.populate(rs); return new ResultSetWrappingSqlRowSet(rowSet); }
4.4 关闭ResultSet
/** * Close the given JDBC ResultSet and ignore any thrown exception. * This is useful for typical finally blocks in manual JDBC code. * @param rs the JDBC ResultSet to close (may be {@code null}) */ public static void closeResultSet(ResultSet rs) { if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException ex) { logger.trace("Could not close JDBC ResultSet", ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { // We don't trust the JDBC driver: It might throw RuntimeException or Error. logger.trace("Unexpected exception on closing JDBC ResultSet", ex); } } }
5. 释放connection
/** * Close the given Connection, obtained from the given DataSource, * if it is not managed externally (that is, not bound to the thread). * @param con the Connection to close if necessary * (if this is {@code null}, the call will be ignored) * @param dataSource the DataSource that the Connection was obtained from * (may be {@code null}) * @see #getConnection */ public static void releaseConnection(Connection con, DataSource dataSource) { try { doReleaseConnection(con, dataSource); } catch (SQLException ex) { logger.debug("Could not close JDBC Connection", ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { logger.debug("Unexpected exception on closing JDBC Connection", ex); } } /** * Actually close the given Connection, obtained from the given DataSource. * Same as {@link #releaseConnection}, but throwing the original SQLException. * <p>Directly accessed by {@link TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy}. * @param con the Connection to close if necessary * (if this is {@code null}, the call will be ignored) * @param dataSource the DataSource that the Connection was obtained from * (may be {@code null}) * @throws SQLException if thrown by JDBC methods * @see #doGetConnection */ public static void doReleaseConnection(Connection con, DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException { if (con == null) { return; } if (dataSource != null) { ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource); if (conHolder != null && connectionEquals(conHolder, con)) { // It's the transactional Connection: Don't close it. conHolder.released(); return; } } logger.debug("Returning JDBC Connection to DataSource"); doCloseConnection(con, dataSource); }
6.事务处理
6.1 事务开始
DataSourceTransactionManager 的doBegin()方法
/** * This implementation sets the isolation level but ignores the timeout. */ @Override protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) { DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction; Connection con = null; try { if (txObject.getConnectionHolder() == null || txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) { Connection newCon = this.dataSource.getConnection(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction"); } txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true); } txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true); con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection(); Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition); txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel); // Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers, // so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly // configured the connection pool to set it already). if (con.getAutoCommit()) { txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit"); } con.setAutoCommit(false); } txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true); int timeout = determineTimeout(definition); if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) { txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout); } // Bind the session holder to the thread. if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) { TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(getDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder()); } } catch (Throwable ex) { if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) { DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.dataSource); txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false); } throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex); } }
6.2 事务提交
@Override protected void doCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) { DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction(); Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection(); if (status.isDebug()) { logger.debug("Committing JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]"); } try { con.commit(); } catch (SQLException ex) { throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not commit JDBC transaction", ex); } }
6.3 事务回滚
@Override protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) { DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction(); Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection(); if (status.isDebug()) { logger.debug("Rolling back JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]"); } try { con.rollback(); } catch (SQLException ex) { throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not roll back JDBC transaction", ex); } }
事务过程:
Spring 对DataSource进行事务管理的关键在于ConnectionHolder和TransactionSynchronizationManager。
0.先从TransactionSynchronizationManager中尝试获取连接
1.如果前一步失败则在每个线程上,对每个DataSouce只创建一个Connection
2.这个Connection用ConnectionHolder包装起来,由TransactionSynchronizationManager管理
3.再次请求同一个连接的时候,从TransactionSynchronizationManager返回已经创建的ConnectionHolder,然后调用ConnectionHolder的request将引用计数+1
4.释放连接时要调用ConnectionHolder的released,将引用计数-1
5.当事物完成后,将ConnectionHolder从TransactionSynchronizationManager中解除。当谁都不用,这个连接被close
以上所有都是可以调用DataSourceUtils化简代码,而JdbcTemplate又是调用DataSourceUtils的。所以在 Spring文档中要求尽量首先使用JdbcTemplate,其次是用DataSourceUtils来获取和释放连接。至于 TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy,那是下策的下策。不过可以将Spring事务管理和遗留代码无缝集成。
所以如某位朋友说要使用Spring的事务管理,但是又不想用JdbcTemplate,那么可以考虑TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy。这个类是原来DataSource的代理。
其次,想使用Spring事物,又不想对Spring进行依赖是不可能的。与其试图自己模拟DataSourceUtils,不如直接使用现成的。
小结:
JdbcTemplate将我们使用的JDBC的流程封装起来,包括了异常的捕捉、SQL的执行、查询结果的转换等等。
spring大量使用Template Method模式来封装固定流程的动作,XXXTemplate等类别都是基于这种方式的实现。
除了大量使用Template Method来封装一些底层的操作细节,spring也大量使用callback方式类回调相关类别的方法以提供JDBC相关类别的功能,使传统的JDBC的使用者也能清楚了解spring所提供的相关封装类别方法的使用。
参考文献:
【1】http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_53dd74430100haaj.html