1. hdfs定义
HDFS is the primary distributed storage used by Hadoop applications. A HDFS cluster primarily consists of a NameNode that manages the file system metadata and DataNodes that store the actual data.
2. hdfs架构
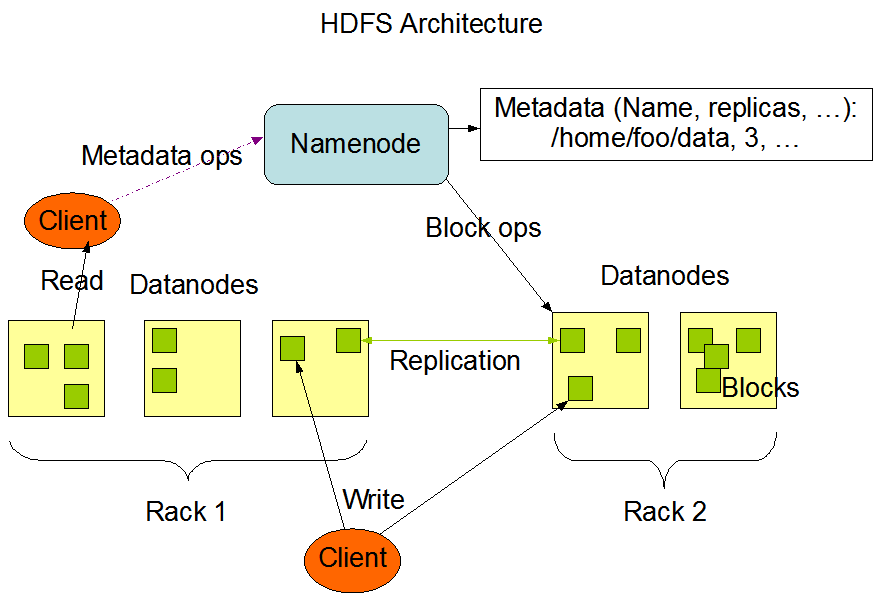
3. hdfs实例
作为文件系统,文件的读写才是核心:
/** * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one * or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file * distributed with this work for additional information * regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file * to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the * "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance * with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataOutputStream; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; public class HadoopDFSFileReadWrite { static void usage () { System.out.println("Usage : HadoopDFSFileReadWrite <inputfile> <output file>"); System.exit(1); } static void printAndExit(String str) { System.err.println(str); System.exit(1); } public static void main (String[] argv) throws IOException { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); if (argv.length != 2) usage(); // Hadoop DFS deals with Path Path inFile = new Path(argv[0]); Path outFile = new Path(argv[1]); // Check if input/output are valid if (!fs.exists(inFile)) printAndExit("Input file not found"); if (!fs.isFile(inFile)) printAndExit("Input should be a file"); if (fs.exists(outFile)) printAndExit("Output already exists"); // Read from and write to new file FSDataInputStream in = fs.open(inFile); FSDataOutputStream out = fs.create(outFile); byte buffer[] = new byte[256]; try { int bytesRead = 0; while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) > 0) { out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead); } } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("Error while copying file"); } finally { in.close(); out.close(); } } }
上述示例,将一个文件的内容复制到另一个文件中,具体步骤如下:
第一步:创建一个文件系统实例,给该实例传递新的配置。
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
第二步:获取文件路径
// Hadoop DFS deals with Path Path inFile = new Path(argv[0]); Path outFile = new Path(argv[1]); // Check if input/output are valid if (!fs.exists(inFile)) printAndExit("Input file not found"); if (!fs.isFile(inFile)) printAndExit("Input should be a file"); if (fs.exists(outFile)) printAndExit("Output already exists");
第三步:打开文件输入输出流,将输入流写到输出流中:
// Read from and write to new file FSDataInputStream in = fs.open(inFile); FSDataOutputStream out = fs.create(outFile); byte buffer[] = new byte[256]; try { int bytesRead = 0; while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) > 0) { out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead); } } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("Error while copying file"); } finally { in.close(); out.close(); }
上面文件读写功能涉及到了文件系统FileSystem、配置文件Configuration、输入流/输出流FSDataInputStream/FSDataOutputStream
4. 基本概念分析
4.1 文件系统
文件系统的层次结构如下所示:
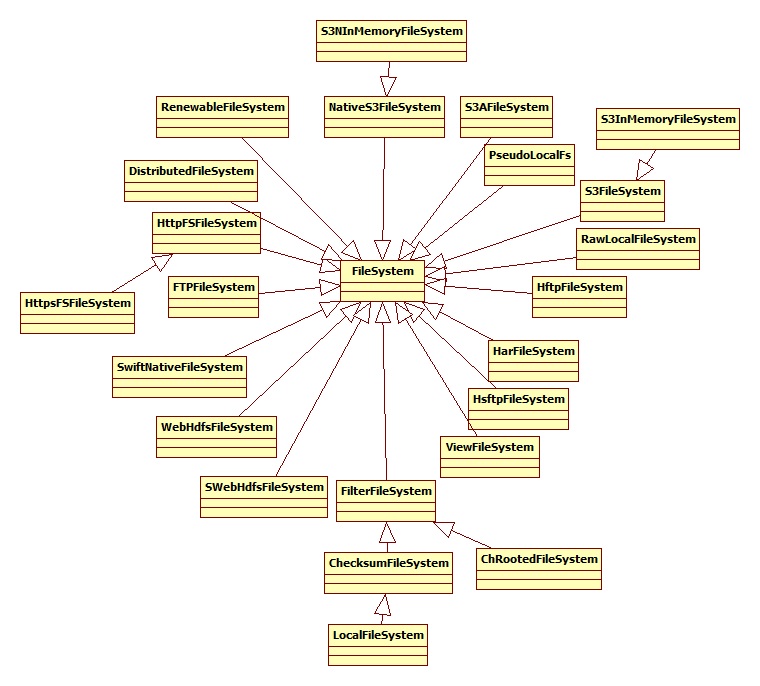
文件系统有两个重要的分支,一个是分布式文件系统,另一个是“本地”(映射到本地连接的磁盘)文件系统,本地磁盘适用于比较少的hadoop实例和测试。绝大部分情况下使用分布式文件系统,hadoop 分布式文件系统使用多个机器的系统,但对用户来说只有一个磁盘。它的容错性和大容量性使它非常有用。
4.2 配置文件
配置文件的层次结构如下:
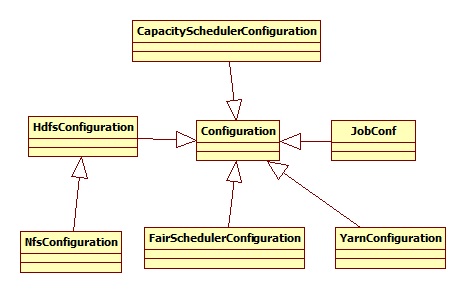
我们关注的是HdfsConfiguration,其涉及到的配置文件有hdfs-default.xml和hdfs-site.xml:
static { addDeprecatedKeys(); // adds the default resources Configuration.addDefaultResource("hdfs-default.xml"); Configuration.addDefaultResource("hdfs-site.xml"); }
4.3 输入/输出流
输入/输出流和文件系统相对应,先看一下输入流:
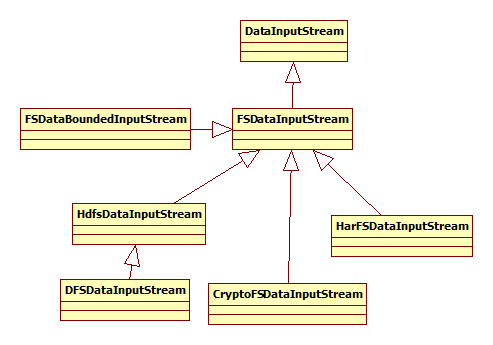
其中,HdfsDataInputStream是FSDataInputStream的实现,其构造函数为:
public HdfsDataInputStream(DFSInputStream in) throws IOException { super(in); }
DFSInputStream层次结构如下图所示:
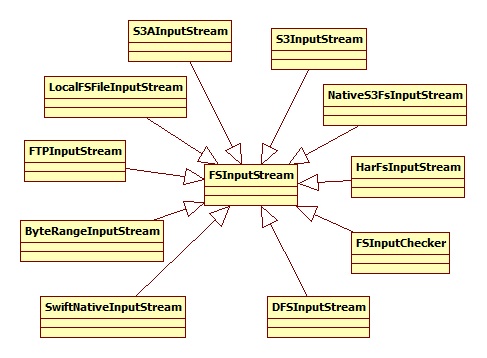
在了解一下输出流:
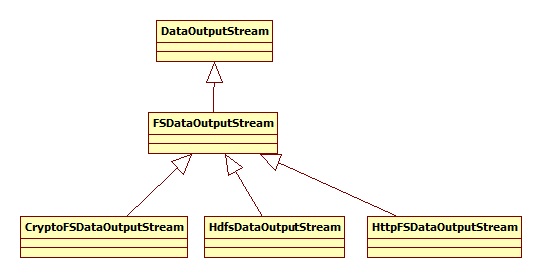
其中,重点是HdfsDataOutputStream,其构造函数为:
public HdfsDataOutputStream(DFSOutputStream out, FileSystem.Statistics stats, long startPosition) throws IOException { super(out, stats, startPosition); }
DFSOutputStream 的层次结构为:
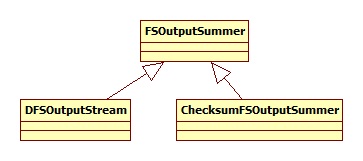
参考文献:
【1】http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r2.6.0/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-hdfs/HdfsUserGuide.html
【2】http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r2.6.0/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-hdfs/HdfsDesign.html
【3】http://wiki.apache.org/hadoop/HadoopDfsReadWriteExample
【4】http://blog.csdn.net/gaoxingnengjisuan/article/details/11177049