一、连接mysql
1.事前准备
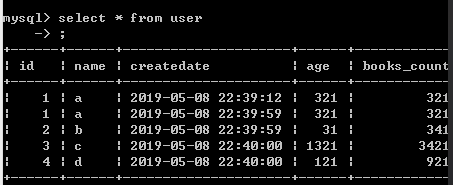
我们准备一个数据库,数据库一张表user,字段如下,乱起的名字不要在意哈
上代码,代码比较简单,不用注释也能看懂
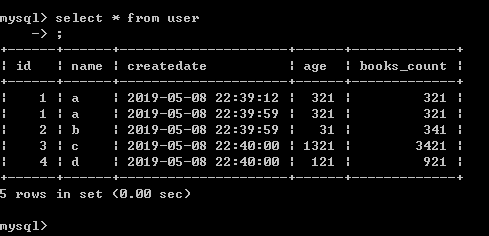
import pandas as pd from sqlalchemy import create_engine engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:root@localhost:3306/test') sql = "select * from user" df = pd.read_sql_query(sql, engine) print(df)
打印结果
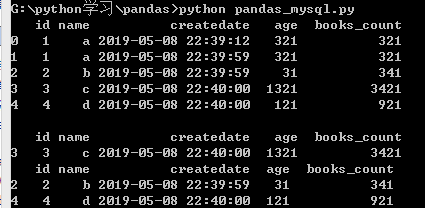
比较大小
import pandas as pd from sqlalchemy import create_engine engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:root@localhost:3306/test') sql = "select * from user" df = pd.read_sql_query(sql, engine) print(df) print("筛选") #print(df[df.id>2]) print(df[(df.id>2) & (df.age >1000)]) #and print(df[(df.id>3) | (df.age<50)]) #or
当你需要将一列作为变量的时候,就像下面这样就可以
import pandas as pd from sqlalchemy import create_engine engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:kWYM6%pnbVnvsR4K@localhost:3306/citystudy') sql = "select * from t_user" df = pd.read_sql_query(sql, engine) print(df) tmp = 'id' print(df[df[tmp]>2])
字符串也可以筛选
print(df[df[tmp].str.contains('ER')]) #包含ER的字符串
print(df[df[tmp].str.contains('ER')==False]) #不包含ER的字符串