发现自己有点懒了!也可能是越往后越难了,看书理解起来有点费劲,所以这两天就每天更新一点学习笔记吧。
4.5 将APM模式转化为任务
书上提供的三种方式
方式一:
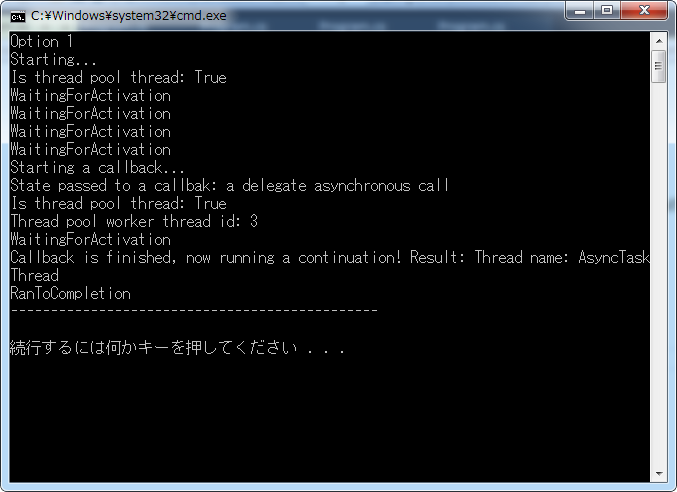
1 class Program 2 { 3 //定义一个委托 4 private delegate string AsynchronousTask(string threadName); 5 6 static void Main(string[] args) 7 { 8 //实例化一个委托对象,绑定Test函数 9 AsynchronousTask d = Test; 10 11 Console.WriteLine("Option 1"); 12 //调用TaskFactory<TResult> Factory.FromAsync()方法,这个方法有很多重载函数 13 //这个方法是 public Task<TResult> FromAsync(IAsyncResult asyncResult, Func<IAsyncResult, TResult> endMethod); 14 Task<string> task = Task<string>.Factory.FromAsync( 15 d.BeginInvoke("AsyncTaskThread", Callback, "a delegate asynchronous call"), d.EndInvoke); 16 //绑定任务执行完的后续操作 17 task.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("Callback is finished, now running a continuation! Result: {0}", 18 t.Result)); 19 20 //循环打印状态信息 21 while (!task.IsCompleted) 22 { 23 Console.WriteLine(task.Status); 24 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); 25 } 26 Console.WriteLine(task.Status); 27 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); 28 29 Console.WriteLine("----------------------------------------------"); 30 Console.WriteLine(); 31 } 32 33 //定义一个回调函数 34 private static void Callback(IAsyncResult ar) 35 { 36 Console.WriteLine("Starting a callback..."); 37 Console.WriteLine("State passed to a callbak: {0}", ar.AsyncState); 38 Console.WriteLine("Is thread pool thread: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 39 Console.WriteLine("Thread pool worker thread id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 40 } 41 42 //定义一个委托函数 43 private static string Test(string threadName) 44 { 45 Console.WriteLine("Starting..."); 46 Console.WriteLine("Is thread pool thread: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 47 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 48 Thread.CurrentThread.Name = threadName; 49 return string.Format("Thread name: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 50 }
方式二:
与方式一差不多,但是使用了TaskFactory<TResult> Factory.FromAsync()方法的另一种重载,该重载并不允许指定一个将会在异步委托调用后被调用的回调函数。但是可以使用后续操作替代它。如果回调函数非常重要,建议使用第一种。
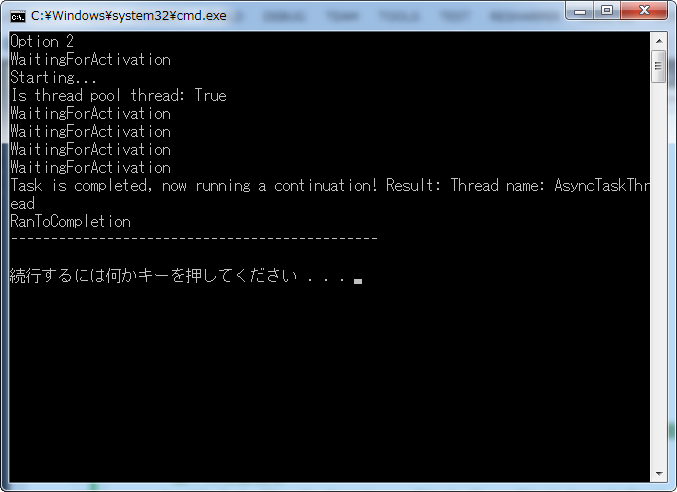
1 class Program 2 { 3 //定义一个委托 4 private delegate string AsynchronousTask(string threadName); 5 6 static void Main(string[] args) 7 { 8 //实例化一个委托对象,绑定Test函数 9 AsynchronousTask d = Test; 10 11 Console.WriteLine("Option 2"); 12 //调用TaskFactory<TResult> Factory.FromAsync()方法,这个方法有很多重载函数 13 /* 14 * 这个方法重载是 15 * public Task<TResult> FromAsync<TArg1>(Func<TArg1, AsyncCallback, object, IAsyncResult> beginMethod, 16 * Func<IAsyncResult, TResult> endMethod, 17 * TArg1 arg1, 18 * object state); 19 */ 20 Task<string> task= Task<string>.Factory.FromAsync(d.BeginInvoke,d.EndInvoke, 21 "AsyncTaskThread", 22 "a delegate asynchronous call"); 23 24 //绑定任务执行完的后续操作 25 task.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("Task is completed, now running a continuation! Result: {0}", 26 t.Result)); 27 28 //循环打印状态信息 29 while (!task.IsCompleted) 30 { 31 Console.WriteLine(task.Status); 32 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); 33 } 34 Console.WriteLine(task.Status); 35 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); 36 37 Console.WriteLine("----------------------------------------------"); 38 Console.WriteLine(); 39 } 40 41 //定义一个委托函数 42 private static string Test(string threadName) 43 { 44 Console.WriteLine("Starting..."); 45 Console.WriteLine("Is thread pool thread: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 46 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 47 Thread.CurrentThread.Name = threadName; 48 return string.Format("Thread name: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name); 49 }
方式三:
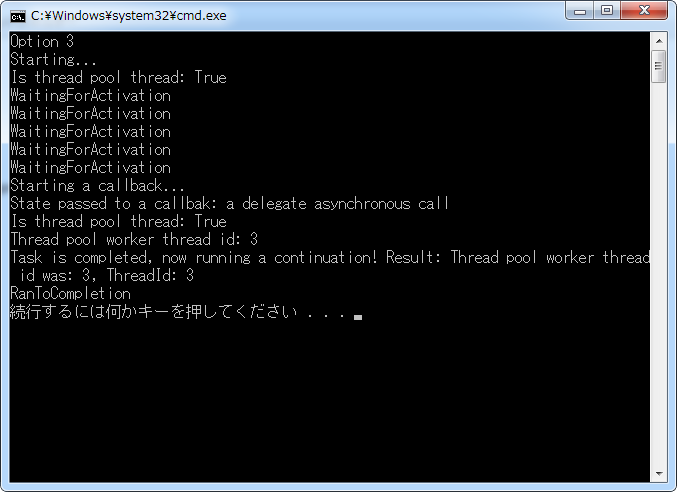
1 class Program 2 { 3 private delegate string IncompatibleAsynchronousTask(out int threadId); 4 5 static void Main(string[] args) 6 { 7 int threadId; 8 IncompatibleAsynchronousTask e = Test; 9 10 Console.WriteLine("Option 3"); 11 12 IAsyncResult ar = e.BeginInvoke(out threadId, Callback, "a delegate asynchronous call"); 13 14 /*这是一个小技巧,EndMethod使用了out参数,与FromAsync的方法重载并不兼容。 15 * 然而,可以很轻松地将EndMethod调用封装到一个lambda表达式当中,从而适合 16 * 工厂方法。 17 */ 18 Task<string> task = Task<string>.Factory.FromAsync(ar, _ => e.EndInvoke(out threadId, ar)); 19 task.ContinueWith(t => 20 Console.WriteLine("Task is completed, now running a continuation! Result: {0}, ThreadId: {1}", 21 t.Result, threadId)); 22 23 while (!task.IsCompleted) 24 { 25 Console.WriteLine(task.Status); 26 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); 27 } 28 Console.WriteLine(task.Status); 29 30 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); 31 } 32 33 private static void Callback(IAsyncResult ar) 34 { 35 Console.WriteLine("Starting a callback..."); 36 Console.WriteLine("State passed to a callbak: {0}", ar.AsyncState); 37 Console.WriteLine("Is thread pool thread: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 38 Console.WriteLine("Thread pool worker thread id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 39 } 40 41 private static string Test(out int threadId) 42 { 43 Console.WriteLine("Starting..."); 44 Console.WriteLine("Is thread pool thread: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 45 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 46 threadId = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId; 47 return string.Format("Thread pool worker thread id was: {0}", threadId); 48 } 49
总结:感觉这个在日常工作当中使用的真的不是很多,比较晦涩难懂,暂且记住有TaskFactory<TResult> Factory.FromAsync()这个方法,通过这个方法可以将APM转化成TPL
4.6 将EAP模式转换成任务
例子先上:
1 class Program 2 { 3 static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 //实例化一个TaskCompletionSource<TResult>,它是实现EAP转化成TPL的关键 6 var tcs = new TaskCompletionSource<int>(); 7 8 var worker = new BackgroundWorker(); 9 worker.DoWork += (sender, eventArgs) => 10 { 11 eventArgs.Result = TaskMethod("Background worker", 5); 12 }; 13 14 worker.RunWorkerCompleted += (sender, eventArgs) => 15 { 16 //如果有错就抛出异常 17 if (eventArgs.Error != null) 18 { 19 tcs.SetException(eventArgs.Error); 20 } 21 //如果是取消操作,就取消操作 22 else if (eventArgs.Cancelled) 23 { 24 tcs.SetCanceled(); 25 } 26 else 27 { 28 //正常情况返回结果 29 tcs.SetResult((int)eventArgs.Result); 30 } 31 }; 32 33 //运行任务 34 worker.RunWorkerAsync(); 35 36 //获取结果 37 int result = tcs.Task.Result; 38 39 Console.WriteLine("Result is: {0}", result); 40 } 41 42 static int TaskMethod(string name, int seconds) 43 { 44 Console.WriteLine("Task {0} is running on a thread id {1}. Is thread pool thread: {2}", 45 name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 46 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); 47 return 42 * seconds; 48 }

4.7 实现取消选项
我们在前面说过线程工作的取消需要依靠两个类来实现,分别是CancellationTokenSource和CancellationToken这两个类
1 class Program 2 { 3 private static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 //定义一个CancellationTokenSource类 6 var cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); 7 //创建第一个任务,这里有个很奇怪的第地方,cts.Token被传了两次 8 //分别传给了TaskMethod方法个Task的构造函数,为什么这么做呢? 9 var longTask = new Task<int>(() => TaskMethod("Task 1", 10, cts.Token), cts.Token); 10 //打印任务状态 11 Console.WriteLine(longTask.Status); 12 //取消任务 13 cts.Cancel(); 14 //再次打印任务状态 15 Console.WriteLine(longTask.Status); 16 Console.WriteLine("First task has been cancelled before execution"); 17 18 //创建第二个任务 19 cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); 20 longTask = new Task<int>(() => TaskMethod("Task 2", 10, cts.Token), cts.Token); 21 //启动任务 22 longTask.Start(); 23 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++ ) 24 { 25 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); 26 Console.WriteLine(longTask.Status); 27 } 28 //取消任务 29 cts.Cancel(); 30 //打印任务状态 31 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 32 { 33 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); 34 Console.WriteLine(longTask.Status); 35 } 36 37 Console.WriteLine("A task has been completed with result {0}.", longTask.Result); 38 } 39 40 private static int TaskMethod(string name, int seconds, CancellationToken token) 41 { 42 Console.WriteLine("Task {0} is running on a thread id {1}. Is thread pool thread: {2}", 43 name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 44 for (int i = 0; i < seconds; i ++) 45 { 46 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); 47 //如果任务被取消,就返回-1 48 if (token.IsCancellationRequested) return -1; 49 } 50 return 42*seconds; 51 } 52 }

cts.Token被传了两次为什么呢?如果在任务实际启动前取消它,该任务的TPL基础设施有责任处理该取消操作,因为这些代码根本不会被执行,通过得到第一个任务的状态可以知道它被取消了。如果尝试对该任务调用Start方法,将会得到InvalidOperationException异常。
解释:
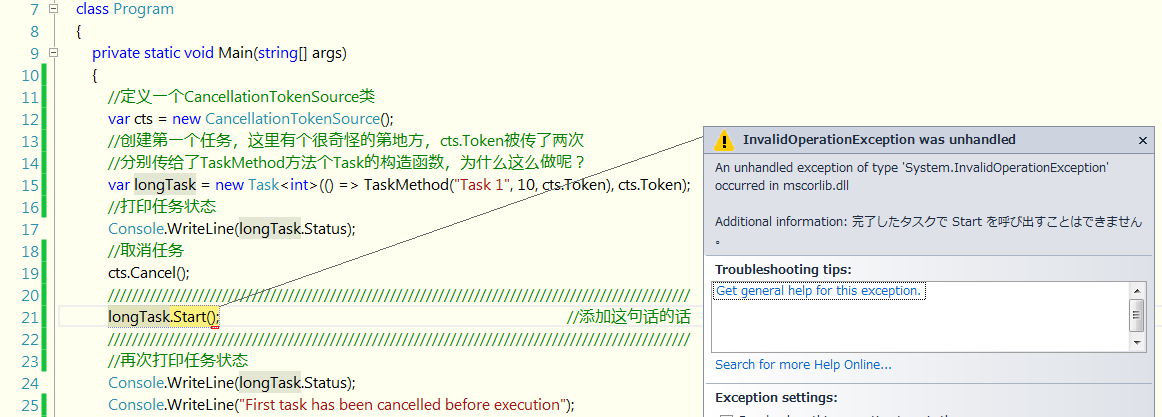
如果在Task构造函数当中取消了,cts.Token这个参数,那么在Cts.Cancel()后面执行longTask.Start(); 会出现什么情况呢?
如下图所示,任务只有在运行操作的时候才能检查到取消操作。所以才会有WaitingToRun这个状态出现。

如果添加了这个参数,结果如下:
这个时候,在取消操作执行完后,执行开始操作就会抛出异常。