官方文档:http://2.python-requests.org/zh_CN/latest/user/quickstart.html
安装
1. 首先有python环境
2. pip install requests / pip install requests == 2.18.4
pip uninstall requests 打y 卸载
pip list 查看目录 或 pip show requests
使用
重点:r.text 类型为str, r.json() 类型为dict
也有接口返回html,此时不能用json() 来打印
r.status_code # 状态码
r.cookies # 获取返回cookies 返回为jar类型
需要转换:dict(r.cookies)['xxx'] r.url # 获取url
r.encoding # 获取编码格式
r.text # 字符串方式的响应体,自动根据相应头部的字符编码进行解码
r.content # 字节方式的响应体
r.json() # requests中内置的json解码器,json转成python中的字典
r.headers # 头部 dict类型 取值为r.headers['xxx']
r.raise_for_status() # 失败请求 (非200相应) 抛出异常
1. 要通过GET访问一个页面,只需要几行代码:

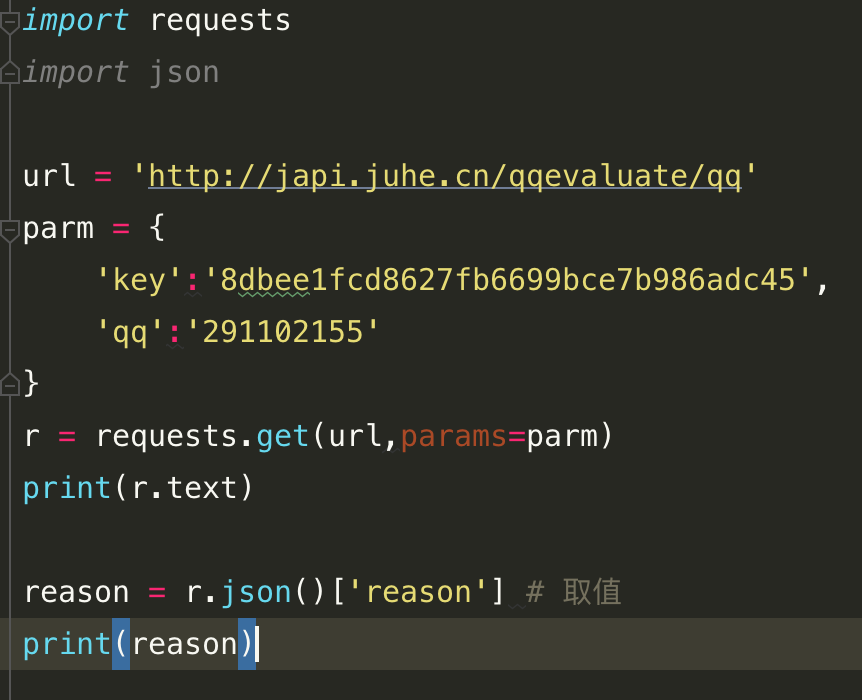
对于带参数的URL,传入一个dict作为params参数:
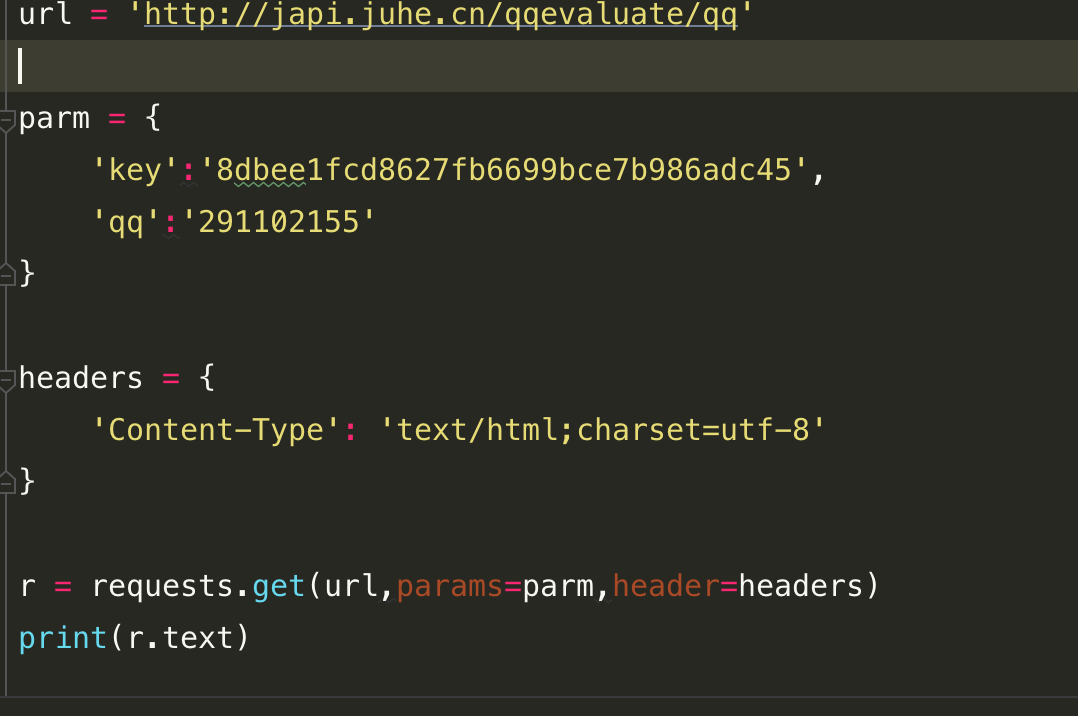
需要传入HTTP Header时,我们传入一个dict作为headers参数:
>
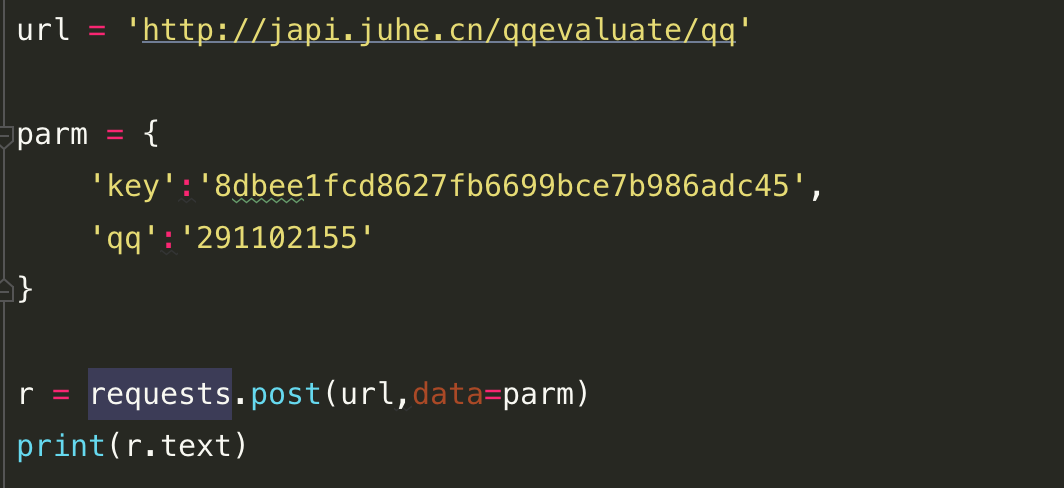
2.发送POST请求,只需要把get()方法变成post(),然后传入data参数作为POST请求的数据:
requests默认使用application/x-www-form-urlencoded对POST数据编码。如果要传递JSON数据,可以直接传入json参数:

类似的,上传文件需要更复杂的编码格式,但是requests把它简化成files参数:
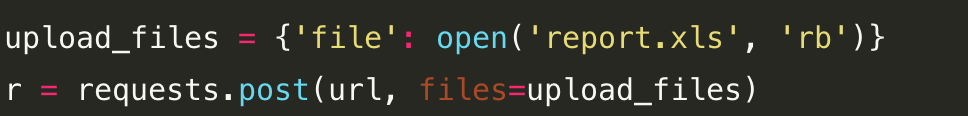
在读取文件时,注意务必使用'rb'即二进制模式读取,这样获取的bytes长度才是文件的长度。
把post()方法替换为put(),delete()等,就可以以PUT或DELETE方式请求资源。
3.requests对Cookie做了特殊处理,使得我们不必解析Cookie就可以轻松获取指定的Cookie:
r.cookies['ts']要在请求中传入Cookie,只需准备一个dict传入cookies参数:
cs = {'token': '12345', 'status': 'working'}
r = requests.get(url, cookies=cs)
最后,要指定超时,传入以秒为单位的timeout参数:
r = requests.get(url, timeout=2.5) # 2.5秒后超时