.Net core 的Pipeline 是由各种各样的中间件组成的(个人理解),通过一张图我们大体认识一样中间件的请求流程。

从图中我们可以看出 请求 middleware1->middleware2->middleware,响应:middleware3->middleware2->middleware1,他的请求流程很像 俄罗斯套娃模型
中间件基本使用:
我们在 使用 ApplicationBuilder Use 就可以轻松的注册中间件。
app.Use(next =>
{
Console.WriteLine("this is middleware 1");
return new RequestDelegate(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is hello world1 start");
await next.Invoke(context);
await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is hello world1 end");
});
});
app.Use(next =>
{
Console.WriteLine("this is middleware 2");
return new RequestDelegate(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is hello world2 start");
await next.Invoke(context);
await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is hello world2 end");
});
});
app.Use(next =>
{
Console.WriteLine("this is middleware 3");
return new RequestDelegate(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is hello world3 start");
await context.Response.WriteAsync("this is hello world3 end");
});
});
上段代码相应结果:
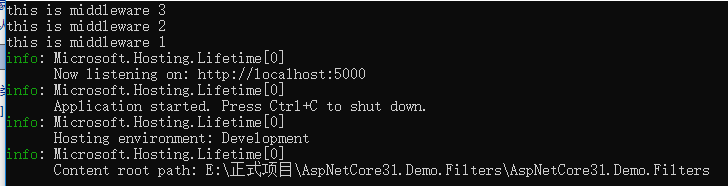
cmd 下:
浏览器下:

我们发现在 控制台显示的是 Middleware3->middleware2->middleware1
但是在浏览器中显示的是 middleware1->middleware2->middleware3 middleware3->middleware2->middleware1
这时候我们求助源码:
// Copyright (c) .NET Foundation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See License.txt in the project root for license information.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Features;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Internal;
namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder
{
public class ApplicationBuilder : IApplicationBuilder
{
private const string ServerFeaturesKey = "server.Features";
private const string ApplicationServicesKey = "application.Services";
private readonly IList<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>> _components = new List<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>();
public ApplicationBuilder(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
Properties = new Dictionary<string, object>(StringComparer.Ordinal);
ApplicationServices = serviceProvider;
}
public ApplicationBuilder(IServiceProvider serviceProvider, object server)
: this(serviceProvider)
{
SetProperty(ServerFeaturesKey, server);
}
private ApplicationBuilder(ApplicationBuilder builder)
{
Properties = new CopyOnWriteDictionary<string, object>(builder.Properties, StringComparer.Ordinal);
}
public IServiceProvider ApplicationServices
{
get
{
return GetProperty<IServiceProvider>(ApplicationServicesKey);
}
set
{
SetProperty<IServiceProvider>(ApplicationServicesKey, value);
}
}
public IFeatureCollection ServerFeatures
{
get
{
return GetProperty<IFeatureCollection>(ServerFeaturesKey);
}
}
public IDictionary<string, object> Properties { get; }
private T GetProperty<T>(string key)
{
object value;
return Properties.TryGetValue(key, out value) ? (T)value : default(T);
}
private void SetProperty<T>(string key, T value)
{
Properties[key] = value;
}
public IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware)
{
_components.Add(middleware);
return this;
}
public IApplicationBuilder New()
{
return new ApplicationBuilder(this);
}
public RequestDelegate Build()
{
RequestDelegate app = context =>
{
// If we reach the end of the pipeline, but we have an endpoint, then something unexpected has happened.
// This could happen if user code sets an endpoint, but they forgot to add the UseEndpoint middleware.
var endpoint = context.GetEndpoint();
var endpointRequestDelegate = endpoint?.RequestDelegate;
if (endpointRequestDelegate != null)
{
var message =
$"The request reached the end of the pipeline without executing the endpoint: '{endpoint.DisplayName}'. " +
$"Please register the EndpointMiddleware using '{nameof(IApplicationBuilder)}.UseEndpoints(...)' if using " +
$"routing.";
throw new InvalidOperationException(message);
}
context.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status404NotFound;
return Task.CompletedTask;
};
foreach (var component in _components.Reverse())
{
app = component(app);
}
return app;
}
}
}
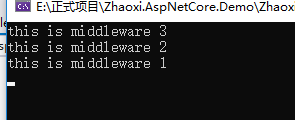
app.Use 主要把 中间件记录下来,系统会自动掉调用 Build 方法执行,调用Build 之后。按照上面的代码 在控制台会显示 Middleware3->middleware2->middleware1,其次最终返回的中间件是middleware1 ,这时候 系统会 Kestrel 服务器会从上到下执行中间件。
方便理解原来,模仿了 ApplicationBuilder 注册流程。
public class ApplicationBuilder
{
private readonly Stack<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>> _components = new Stack<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>();
public ApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware)
{
_components.Push(middleware);
return this;
}
public RequestDelegate Build()
{
RequestDelegate app = async s =>
{
Console.WriteLine("http 404");
await Task.CompletedTask;
};
while (this._components.Any())
{
app = this._components.Pop()(app);
}
return app;
}
}
public delegate Task RequestDelegate(string context);
调用:
ApplicationBuilder app = new ApplicationBuilder();
app.Use(next => {
Console.WriteLine("this is middleware 1");
return new RequestDelegate(async context => {
Console.WriteLine("this is hello world 1 start");
await next.Invoke(context);
Console.WriteLine("this is hello world 1 end");
});
});
app.Use(next => {
Console.WriteLine("this is middleware 2");
return new RequestDelegate(async context => {
Console.WriteLine("this is hello world 2 start");
await next.Invoke(context);
Console.WriteLine("this is hello world 2 end");
});
});
app.Use(next => {
Console.WriteLine("this is middleware 3");
return new RequestDelegate(async context => {
Console.WriteLine("this is hello world 3 start");
Console.WriteLine("this is hello world 3 end");
await Task.CompletedTask;
});
});
app.Build();
至于后面的操作是 Kestrel 服务器干的事情了。