1、什么是JSP
JSP,全称JavaServer Pages,是由Sun Microsystems公司倡导和许多公司参与共同建立的一种使软件开发者可以响应客户端请求,而动态生成HTML、XML或其他格式文档的Web网页的技术标准。
什么意思?
在 [01] Servlet是什么 的文尾我曾经提到过,早期的网页都是静态的,也就是最普通的html形式,网页内容写了啥,就只能显示啥,为了能根据不同的情况生成不同内容的动态网页(比如不同用户的账户管理页面总不能都一样吧),由Servlet接下了重任,通过数不清的out.println()来输出html标签和内容,就像下面这样写代码:
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">");
out.println("<HTML>");
out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>This is my Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
out.println(" <BODY>");
out.print(" This is ");
out.print(this.getClass());
out.println(", using the GET method");
out.println(" </BODY>");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
out.println("<font color='red'>i=" + i + "</font><br>");
}
out.println("</HTML>");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}25
1
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { 2
3
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {4
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");5
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();6
out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">");7
out.println("<HTML>");8
out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>This is my Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");9
out.println(" <BODY>");10
out.print(" This is ");11
out.print(this.getClass());12
out.println(", using the GET method");13
out.println(" </BODY>");14
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {15
out.println("<font color='red'>i=" + i + "</font><br>");16
}17
out.println("</HTML>");18
out.flush();19
out.close();20
}21
22
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {23
doGet(request, response);24
}25
}显然太冗杂了,后来JSP出现,Servlet就卸任专心去做控制器了。那么JSP是什么呢?JSP在表面上看来就是 "HTML+Java代码" 的组合,其中HTML实现静态部分,Java代码实现动态部分。主要表现在于普通的html代码中,以<% %>形式来标记Java代码。
比如我想要生成一个1-3的多选框,我可以这些写我的JSP页面:
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>
<body>
<%
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
%>
<input type="checkbox"> <%=i%> <br>
<%
}
%>
</body>
</html>13
1
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>2
<html>3
<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>4
<body>5
<%6
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {7
%>8
<input type="checkbox"> <%=i%> <br>9
<%10
}11
%>12
</body>13
</html>而得到的效果如下图,这显然比你傻乎乎地写静态html好多了,因为这里的i是可变的,你也可以通过Java代码获取其他的数据进行展示。
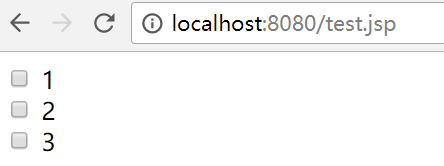
在上述的代码中,我们可以看到,JSP中Java代码最基本的表达有两种方式:
| <% Java代码 %> | 脚本元素 |
| <%= 输出表达式 %> | 输出表达式 |
2、JSP基本运行过程
为什么JSP可以做到执行Java代码呢?原因很简单,JSP在技术上来说,最终它的本质就是一个Servlet,你说它能不能执行Java代码?
那么它实际是由容器执行的(比如Tomcat),大致流程是这样:
- 翻译:将JSP文件翻译成Java文件(存放在tomcat目录下的 /work/Catalina/localhost/)
- 编译:将Java文件便宜成class文件
- 实例化:由Tomcat创建JSP类的对象
- 提供服务:由Tomcat调用JSP对象的_jspService方法,生成响应,返回给浏览器进行显示
我们试着写了两个JSP页面,一个是上述例中生成1-3多选框的代码,一个是空的JSP,并启动了tomcat,然后可以看到tomcat生成了如下文件:
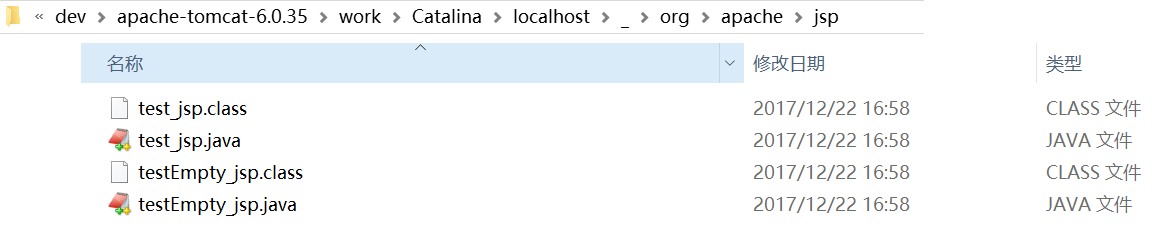
我们先看空的JSP生成的java类中,即上图中testEmpty_jsp.java的_jspService()方法:
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {
PageContext pageContext = null;
HttpSession session = null;
ServletContext application = null;
ServletConfig config = null;
JspWriter out = null;
Object page = this;
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try {
response.setContentType("text/html");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)) {
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try {
out.clearBuffer();
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
}
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}37
1
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)2
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {3
4
PageContext pageContext = null;5
HttpSession session = null;6
ServletContext application = null;7
ServletConfig config = null;8
JspWriter out = null;9
Object page = this;10
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;11
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;12
13
try {14
response.setContentType("text/html");15
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,16
null, true, 8192, true);17
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;18
application = pageContext.getServletContext();19
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();20
session = pageContext.getSession();21
out = pageContext.getOut();22
_jspx_out = out;23
24
} catch (Throwable t) {25
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)) {26
out = _jspx_out;27
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)28
try {29
out.clearBuffer();30
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {31
}32
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);33
}34
} finally {35
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);36
}37
}可见,即便是空的JSP文件,也会翻译出java类,而且该类中已经有一些代码,且是“固定”的,也就是说,任何的JSP文件,最终翻译生成的类中,都有这些代码。
那么我们再看另一个写了内容的JSP文件,也就是我们举例用过的JSP,如下:
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>
<body>
<%
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
%>
<input type="checkbox"> <%=i%> <br>
<%
}
%>
</body>
</html>13
1
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>2
<html>3
<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>4
<body>5
<%6
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {7
%>8
<input type="checkbox"> <%=i%> <br>9
<%10
}11
%>12
</body>13
</html>它的java类中的_jspService()是这样的:
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {
PageContext pageContext = null;
HttpSession session = null;
ServletContext application = null;
ServletConfig config = null;
JspWriter out = null;
Object page = this;
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write("
");
out.write("<html>
");
out.write("<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>
");
out.write("<body>
");
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
out.write("
");
out.write(" <input type="checkbox"> ");
out.print(i);
out.write(" <br>
");
}
out.write("
");
out.write("</body>
");
out.write("</html>");
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)) {
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try {
out.clearBuffer();
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
}
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}52
1
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)2
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {3
4
PageContext pageContext = null;5
HttpSession session = null;6
ServletContext application = null;7
ServletConfig config = null;8
JspWriter out = null;9
Object page = this;10
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;11
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;12
13
try {14
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");15
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,16
null, true, 8192, true);17
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;18
application = pageContext.getServletContext();19
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();20
session = pageContext.getSession();21
out = pageContext.getOut();22
_jspx_out = out;23
24
out.write("
");25
out.write("<html>
");26
out.write("<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>
");27
out.write("<body>
");28
29
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {30
out.write("
");31
out.write(" <input type="checkbox"> ");32
out.print(i);33
out.write(" <br>
");34
}35
36
out.write("
");37
out.write("</body>
");38
out.write("</html>");39
} catch (Throwable t) {40
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)) {41
out = _jspx_out;42
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)43
try {44
out.clearBuffer();45
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {46
}47
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);48
}49
} finally {50
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);51
}52
}可以看到,JSP中的内容怎么来的?就是这里来的,这些代码插入到那些“固定代码”之后进行输出,包括了HTML和Java代码的执行。
这些,都是 <% Java代码 %> 和 <%= 输出表达式 %> 两种表达式的变化,实际上,在JSP中,还可以通过 <%! Java代码 %> 定义Java变量和方法,不过翻译后其位置不再是在 _jspService() 中了,而是在类中,是全局的变量或方法。
如我们把之前的页面稍微修改一下:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>
<body>
<%
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
%>
<input type="checkbox"> <%=i%> <br>
<%
}
%>
<%!
double giveMeNumber() {
return Math.random();
}
%>
This is a random number between 0.0 and 1.0 : <%=giveMeNumber()%>
</body>
</html>21
1
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>2
<html>3
<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>4
<body>5
<%6
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {7
%>8
<input type="checkbox"> <%=i%> <br>9
<%10
}11
%>12
13
<%!14
double giveMeNumber() {15
return Math.random();16
}17
%>18
19
This is a random number between 0.0 and 1.0 : <%=giveMeNumber()%>20
</body>21
</html>翻译出来的Java类如下,可以看到,giveMeNumber()这个我们在JSP页面定义的方法,在Java类中是一个独立的方法,而不是将代码嵌入到 _jspService()中。因为现在Java Web大都采用MVC模式,所以很少会在JSP页面申明变量和方法。
public final class test_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent {
double giveMeNumber() {
return Math.random();
}
private static final JspFactory _jspxFactory = JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();
private static java.util.List _jspx_dependants;
private javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory;
private org.apache.AnnotationProcessor _jsp_annotationprocessor;
public Object getDependants() {
return _jspx_dependants;
}
public void _jspInit() {
_el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory();
_jsp_annotationprocessor = (org.apache.AnnotationProcessor) getServletConfig().getServletContext().getAttribute(org.apache.AnnotationProcessor.class.getName());
}
public void _jspDestroy() {
}
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {
PageContext pageContext = null;
HttpSession session = null;
ServletContext application = null;
ServletConfig config = null;
JspWriter out = null;
Object page = this;
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write("
");
out.write("<html>
");
out.write("<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>
");
out.write("<body>
");
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
out.write("
");
out.write(" <input type="checkbox"> ");
out.print(i);
out.write(" <br>
");
}
out.write("
");
out.write("
");
out.write("
");
out.write("
");
out.write("This is a random number between 0.0 and 1.0 : ");
out.print(giveMeNumber());
out.write("
");
out.write("</body>
");
out.write("</html>");
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)){
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try { out.clearBuffer(); } catch (java.io.IOException e) {}
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}
}x
1
public final class test_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase2
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent {3
4
double giveMeNumber() {5
return Math.random();6
}7
8
private static final JspFactory _jspxFactory = JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();9
10
private static java.util.List _jspx_dependants;11
12
private javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory;13
private org.apache.AnnotationProcessor _jsp_annotationprocessor;14
15
public Object getDependants() {16
return _jspx_dependants;17
}18
19
public void _jspInit() {20
_el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory();21
_jsp_annotationprocessor = (org.apache.AnnotationProcessor) getServletConfig().getServletContext().getAttribute(org.apache.AnnotationProcessor.class.getName());22
}23
24
public void _jspDestroy() {25
}26
27
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)28
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {29
30
PageContext pageContext = null;31
HttpSession session = null;32
ServletContext application = null;33
ServletConfig config = null;34
JspWriter out = null;35
Object page = this;36
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;37
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;38
39
try {40
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");41
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,42
null, true, 8192, true);43
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;44
application = pageContext.getServletContext();45
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();46
session = pageContext.getSession();47
out = pageContext.getOut();48
_jspx_out = out;49
50
out.write("
");51
out.write("<html>
");52
out.write("<head><title>Simple jsp page</title></head>
");53
out.write("<body>
");54
55
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {56
out.write("
");57
out.write(" <input type="checkbox"> ");58
out.print(i);59
out.write(" <br>
");60
}61
62
out.write("
");63
out.write("
");64
out.write("
");65
out.write("
");66
out.write("This is a random number between 0.0 and 1.0 : ");67
out.print(giveMeNumber());68
out.write("
");69
out.write("</body>
");70
out.write("</html>");71
} catch (Throwable t) {72
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)){73
out = _jspx_out;74
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)75
try { out.clearBuffer(); } catch (java.io.IOException e) {}76
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);77
}78
} finally {79
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);80
}81
}82
}3、JSP基本认知的总结
最后,由此可以看出,JSP文件的究竟是怎么回事:
- JSP文件本质是一个Java类,这个类遵守Servlet的规范,所以也可以说JSP就是一个Servlet
- JSP文件对应的Java类由容器翻译生成
- JSP文件中的所有内容,会翻译到Java类中,其中不同的JSP表达式翻译到类中的位置不同
- 我们写的大部分JSP代码,无非就是Java类_jspService方法中方法体的一部分(<%! Java代码 %>形式实际上用得很少)
总结下基本的表达式:
| 语法 | 说明 | 备注 |
| <% Java代码 %> | 脚本元素 | 翻译在 _jspService() 中 |
| <%= 输出表达式 %> | 输出表达式 | 翻译在 _jspService() 中 |
| <%! Java代码 %> | 定义表达式 | 翻译在类中,定义类中的全局变量和方法 |
另附上JSP页面中可能用到的三种注释:
| 语法 | 说明 | 备注 |
| <!-- ... --> | HTML注释 | 客户端可以查看网页源码看到 |
| <% //... %> <% /* ... */ %> | Java注释 | 网页上无法查看,会出现在翻译后的Java类中 |
| <%-- ... --%> | JSP注释 | 不翻译到Java类中,仅在JSP源文件中可见 |