前言
在 Spring mvc 中,DispatcherServlet主要起着控制客户端请求分发到具体处理程序的作用,并支持对请求进行拦截、参数处理、本地化、文件上传等功能。现查看它的分发的具体流程。
1. DispatcherServlet 映射配置
在spring 启动时,如果有 mvc 模块,会将 DispatcherServlet 加载到 web 容器中,进行映射用于处理客户端请求。
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet,
WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties,
ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfig)
{
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration =
new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,
// 项目请求路径,也就是 dispatcherServlet 映射在web服务器中的路径
webMvcProperties.getServlet().getPath());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
multipartConfig.ifAvailable(registration::setMultipartConfig);
return registration;
}
2. DispatcherServlet 结构
通过下图,可以看到 DispatcherServlet 继承自 FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet 实现了 HttpServletBean,而 HttpServletBean 实现了 Servlet 接口,这使 DispatcherServlet 能够在注册进容器实例化后就进行初始化,或者在第一次请求调用时进行初始化。
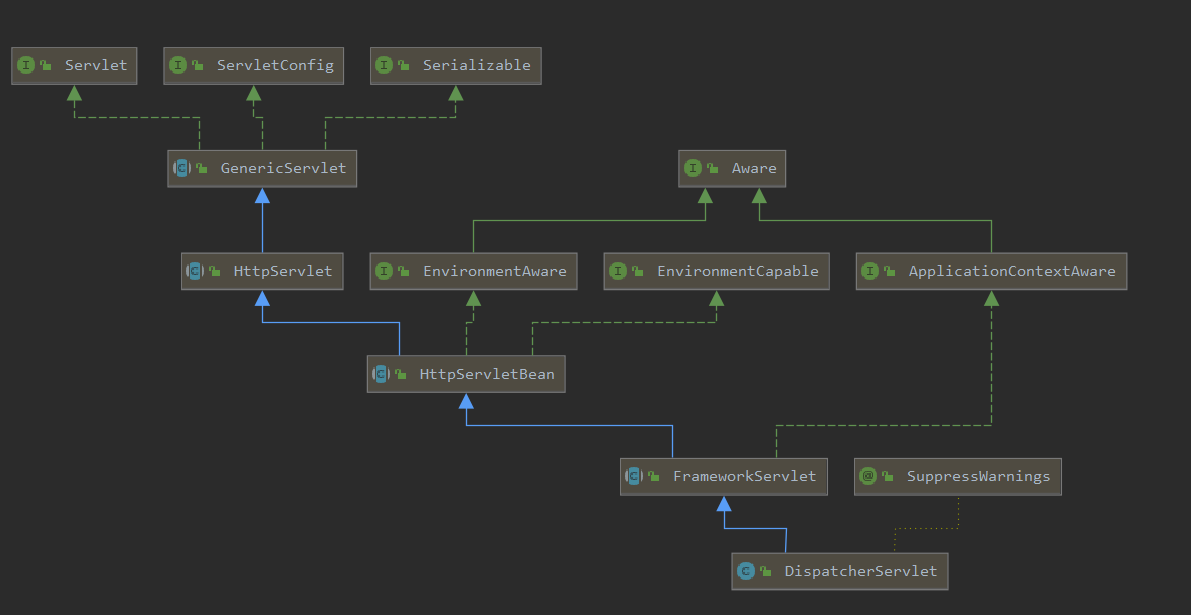
HttpServletBean 实现了 Servlet#init() 方法,对servlet必要的参数进行配置,然后提供了一个供子类扩展的方法 HttpServletBean#initServletBean()。
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// 为子类提供的初始化接口
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
FrameworkServlet 实现了 HttpServletBean#initServletBean() 方法,提供了 WebApplicationContext 属性和initFrameworkServlet 方法,支持子类的自定义初始化操作, FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext() 中调用了 FrameworkServlet#onRefresh() 方法,DispatcherServlet 通过实现 FrameworkServlet#onRefresh() 方法来进行初始化。
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
// .... 略
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
// .... 略
}
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 获取 spring ioc 容器
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// webApplicationContext 将在servlet创建时就传递进来
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
// 检查类型
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
// 上下文未处于活动状态时进入
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// 设置上级
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 配置并添加监听器,并重新刷新 ApplicationContext
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// 查找 WebApplicationContext,肯定存在,不存在会抛出异常,一般也不会进入该方法
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// 创建 WebApplicationContext
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
// 未触发刷新事件时,触发 onRefresh 事件
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// 调用 onRefresh
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
// 将上下文与servlet对应
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
// ... 略
// 设置监听器 ContextRefreshListener,监听ContextRefreshedEvent事件
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// ... 略
// 刷新
wac.refresh();
}
// 刷新操作
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
// 响应 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}
}
// ContextRefresh监听器
private class ContextRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
3. DispatcherServlet 初始化
在加载 DispatcherServlet 类时会进入静态块加载 DispatcherServlet.properties 配置文件,这个配置文件中配置了 DispatcherServlet 默认加载的属性类,如下
static {
// 从配置文件中加载默认实现,spring内部实现,不打算让开发程序人员自定义实现
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load '" + DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
由于 FrameworkServlet 的 initServletBean() 方法提供了 FrameworkServlet#onRefresh() 方法来触发刷新, DispatcherServlet 实现 FrameworkServlet#onRefresh() 方法来在刷新时完成初始化操作。
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
// 下面初始化的bean都有默认的类,如果没有自定义,则使用默认的,在 DispatcherServlet.properties 中定义
// 初始化上传文件处理器
initMultipartResolver(context);
// 初始化i18n国际化资源处理器
initLocaleResolver(context);
// 初始化themeResolver
initThemeResolver(context);
// 初始化请求映射器
initHandlerMappings(context);
// 初始化请求处理适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
// 初始化异常处理器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
// 初始化请求视图转换器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
// 初始化视图解析器
initViewResolvers(context);
// 初始化请求参数在请求之间传递
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
4. DispatcherServlet 处理请求流程
FrameworkServlet 重写了 HttpServlet#service(),在实现中添加了 Http Patch 类型请求的支持,将处理委托给 FrameworkServlet#processRequest(), FrameworkServlet#processRequest()控制了请求的处理流程,提供了FrameworkServlet#doService(),让子类实现来自定义处理请求。
在将 DispatcherServlet 注册进 WebServer 中时,将会映射项目的访问路径,当有请求与该路径匹配,并且实现了 FrameworkServlet,进入 DispatcherServlet#doService() 中响应请求。
FrameworkServlet#service() 方法代码
/**
* FrameworkServlet 实现了支持 PATCH 请求,Servlet 是不支持 PATCH 请求的
* doGetdoPostdoDeletedoPut 方法的实现都是直接调用 processRequest(),
* 而 doOptionsdoTrace 需要进行专门的处理后在调用processRequest()
*/
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
FrameworkServlet#processRequest() 中,在请求上绑定 Attributes 和LocaleContext 、添加并发处理控制器。
FrameworkServlet#processRequest() 方法代码
/**
* spring mvc 处理请求的入口
*/
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 异常
Throwable failureCause = null;
// 获取之前的语言环境,可能在RequestContextFilter 中已经设置
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
// 本次请求的语言环境
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
// 获取之前的attribute,可能在RequestContextFilter 中已经设置
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
// 构建请求的attribute
// 如果 previousAttributes 不为空或 previousAttributes 是 ServletRequestAttributes 的实例,则创建一个新的,否则返回null
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
// 获取 WebAsyncManager,用于管理异步请求的处理
// 他是绑定在这个请求的 RequestAttributes 中的,如果没有对应的将会绑定一个新的 WebAsyncManager
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
// 注册回调Interceptor
// 固定增加了 RequestBindingInterceptor 拦截器,用于绑定 LocaleContext 和 RequestAttributes,他的绑定逻辑与下面的
// initContextHolders 逻辑一样,在RequestBindingInterceptor#preProcess 中调用,
// 并且在 RequestBindingInterceptor#postProcess 中将LocaleContext 和 RequestAttributes清空
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
// 将 localeContext 和 requestAttributes 绑定在当前线程上
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
// 处理请求
try {
// 这个方法中将会处理所有的spring请求逻辑,有子类实现
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
// 记录异常信息
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 记录异常信息
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
// 清空当前线程绑定的 localContext 和 Attribute,与 RequestBindingInterceptor#postProcess 中的逻辑一样
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
// 请求执行结束,注销回调
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
//debug: 打印日志,如果有异常信息打印异常
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
// 向spring Context 发布请求处理完成事件 ServletRequestHandledEvent
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
FrameworkServlet 重写了 HttpServlet#service(),并将处理请求交给子类实现,提供了doService方法。
doService 方法中,对请求做准备、清理工作,将请求的处理工作交给了 doDispatcher() 。
在 doDispatcher 方法里面,主要逻辑有:
-
根据请求路径匹配业务执行器
MapperHandler,并与HandlerInterceptor组成执行器链后交给处理适配器HandlerAdapter, -
调用过虑器链
mapperHandler#getInterceptors() -
执行
HandlerAdapter#handler()执行具体业务逻辑,返回结果 -
根据返回结果进行视图解析或直接返回数据结果。
-
执行完具体业务逻辑后,执行
HandlerInterceptor#afterCompletion(),最后执行清理工作HandlerInterceptor#afterCompletion() -
响应数据,请求完成。
查看 DispatcherServlet 实现 FrameworkServlet#doService() 的代码。
/**
* 在该方法中,会将实际的请求处理委托给 doDispatch 方法,这个方法会绑定属性以供处理请求时使用。
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 打印请求内容, debug 下才会打印
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
// 临时存储该请求的 attribute 的快照,供处理完请求后将 attribute 还原。
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
// 绑定属性到 attribute
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
// 缓存 attribute
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
// 删除过期缓存
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try {
// 将请求映射委托给 doDispatch
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
// 异步处理未完成时
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
// 还原快照
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 执行doDispatcher,该方法执行了所有请求的基本逻辑
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 当前处理的请求
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 检查是否上传文件,如果是将转换为 MultipartHttpServletRequest 请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
// 是上传文件操作?
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//1. 获取 handler
// 获取当前的请求对应的处理器,使用 @Conatroller 或 @RequestMapper 注解的处理程序。
// 返回的是一个 HandlerExecutionChain 拦截器链,由处理程序对象(方法)和 拦截器组成
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//2. 获取handlerAdapter
// 获取handlerAdapter 对应的处理器适配器,通过 HandlerAdapter#supports 来进行判断应该使用哪个 HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
// 如果是get或head方法,判断他是否改变过。
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
// 使用对应的 handler 来判断资源是否修改过
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 执行 interceptor#preHandle 方法
// 如果 interceptor#preHandle 返回false,将会调用匹配拦截器的 interceptor#afterCompletion 方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
//3. 执行业务逻辑
//4. 内部已经处理了部分 响应逻辑
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 是否是并发处理,如果是并发处理直接返回
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 对视图名称进行处理
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 执行匹配拦截器 interceptor.postHandle 方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 解析视图,如果发生了异常,则会解析异常视图,
// 解析视图完成后,是在并发处理请求中,则直接返回,
// 不在并发执行流程中,将会并执行匹配所有拦截器的 interceptor#afterCompletion 方法
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// 执行匹配所有拦截器的 interceptor#afterCompletion 方法
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// 执行匹配拦截器的 interceptor#afterCompletion 方法
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
// 如果是在并发执行,则在这里调用 interceptor#afterCompletion 方法
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// 是上传请求,则将清除 Multipart
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
1. 获取handler
在spring mvc项目启动时,会将 HandlerMapping注册进 spring 容器中,HandlerMapping 接口提供了获取执行业务方法的能力。
public interface HandlerMapping {
@Nullable
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}
使用 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 进行举例,他是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的实现类,AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 实现了 InitializingBean ,可以在项目启动后进行初始化,对 controller 与 RequestMapping 进行解析,结果保存进AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#mappingRegistry 中。
在请求到达时,则是通过请求的路径来获取 HandlerMethod ,与拦截器组成拦截器链对象 HandlerExecutionChain。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 根据请求获取 handler 对象
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
// 不存在返回空
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 获取执行器链对象,并将拦截器装入其中
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
// 跨域处理
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
/**
* 获取 HandlerExecutionChain
*/
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, LOOKUP_PATH);
// 将拦截器加入到执行器链
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
}
2. 获取HandlerAdapter
使用 HandlerAdapter#supports() 判断是否匹配,如果匹配,返回对应的 HandlerAdapter。
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
3. 执行业务逻辑
执行具体业务逻辑主要是通过 HandlerAdapter 来执行, AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter 抽象类实现了HandlerAdapter , 并提供了一个供子类实现的抽象方法 AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter#handleInternal() 。
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 通过实现了 AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter#handleInternal() 来执行具体的业务逻辑。
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
// 检查是否支持该请求,比如是否支持该请求的类型
checkRequest(request);
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
// 是否同步响应同一客户端的请求,以session为单位
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
// 获取session
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
// 根据session获取同步互斥变量,通过在 request#attribute 中保存 session 对象来实现
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
// 同步执行业务逻辑
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// 没有session不同步执行业务逻辑
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// 不进行同步执行业务逻辑
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
// 对响应进行缓存
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
/**
* 执行业务逻辑
*/
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
//1. 对本次请求和响应进行封装,他是一个适配器,管理了request、response、request attribute。
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
//2.专门处理使用 @InitBinder 注解的方法的工厂,binderFactory 中包含了 Validator、FormattingConversionService
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
//3. 处理使用 @ModelAttribute 注解的方法
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
//4. 创建业务方法调用器,由他来通过反射调用业务方法
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
// 设置参数解析器
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
// 设置返回值处理器
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
// 设置 @InitBinder 处理工厂
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
// 设置参数名称解析器
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
// 创建modelAndView容器
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
// 设置其他请求转发到该请求的 Attributes 属性值
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
// 初始化model:执行使用了 @InitBinder 注解的方法,并将绑定结果与 @ModelAttribute 注解标记的属性进行匹配
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
// 创建异步请求
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
// 设置超时时间
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
// 获取异步请求管理器
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
// 设置
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
// 并发相关处理?
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
//5. 调用请求对应的方法
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
// 处理视图,这里是对返回的视图名称或 ModelAndView 进行组装
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
/**
* 2. 生成处理 使用 @InitBinder 注解的方法的工厂
* @InitBinder 是标记在请求到达方法前对参数进行额外处理,比如修改参数、忽略参数等操作 (WebDataBinder)
*/
private WebDataBinderFactory getDataBinderFactory(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
// 2.1 查找使用了@RequestMapper 的类和使用了 @InitBinder 注解的方法,并缓存进对象中
// 作用域只针对该handlerType
Class<?> handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
Set<Method> methods = this.initBinderCache.get(handlerType);
if (methods == null) {
methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, INIT_BINDER_METHODS);
this.initBinderCache.put(handlerType, methods);
}
// 保存使用了 @InitBinder 注解的方法
List<InvocableHandlerMethod> initBinderMethods = new ArrayList<>();
//2.2 项目中使用 @ControllerAdvice 注解标记类,并且这个类中有使用 @InitBinder 注解的方法
// 作用域针对全局
this.initBinderAdviceCache.forEach((controllerAdviceBean, methodSet) -> {
// 检查请求处理类 controller 是否满足 @ControllerAdvice 注解的要求
if (controllerAdviceBean.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
// 找到 @ControllerAdvice 注解使用类的实例
Object bean = controllerAdviceBean.resolveBean();
// 保存使用了 @InitBinder 注解的方法
for (Method method : methodSet) {
initBinderMethods.add(createInitBinderMethod(bean, method));
}
}
});
//2.3 保存使用了 @InitBinder 注解的方法
for (Method method : methods) {
Object bean = handlerMethod.getBean();
initBinderMethods.add(createInitBinderMethod(bean, method));
}
//2.4 创建数据绑定工程:用于生成 解析用了 @InitBinder 注解的方法的工厂类。
return createDataBinderFactory(initBinderMethods);
}
/**
* 3. 生成处理使用 @ModelAttribute 注解的 ModelFactory
*/
private ModelFactory getModelFactory(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) {
// 3.1 查找在该类中未使用 @RequestMapper 注解但是使用了 @ModelAttribute 注解的方法
SessionAttributesHandler sessionAttrHandler = getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod);
Class<?> handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
Set<Method> methods = this.modelAttributeCache.get(handlerType);
if (methods == null) {
methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS);
this.modelAttributeCache.put(handlerType, methods);
}
List<InvocableHandlerMethod> attrMethods = new ArrayList<>();
// Global methods first
//3.2 项目中使用 @ControllerAdvice 注解类中的所有方法
// 作用域针对全局
this.modelAttributeAdviceCache.forEach((controllerAdviceBean, methodSet) -> {
// 查找使用了 @ControllerAdvice 注解的类中的方法,并为每个方法创建 InvocableHandlerMethod 对象
if (controllerAdviceBean.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
Object bean = controllerAdviceBean.resolveBean();
for (Method method : methodSet) {
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
}
});
//3.3 创建 InvocableHandlerMethod 对象
for (Method method : methods) {
Object bean = handlerMethod.getBean();
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
//3.4 创建 ModelFactory,其中保存了每个方法和这个方法使用了 @ModelAttribute 注解的属性。
return new ModelFactory(attrMethods, binderFactory, sessionAttrHandler);
}
invokeHandlerMethod 通过执行 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod#invokeAndHandle() 来调用业务方法。
/**
* 使用反射调用业务方法
*/
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 1. 调用业务方法
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
// 设置响应状态
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
// 返回值为空,检查资源是否改变过、响应状态不为空、请求已经处理完成
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
// 请求内容为改变
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
// 请求已在业务处理程序中完成
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
// 请求已在业务处理程序中完成
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
// 请求未完成
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
// 在 invokeHandlerMethod 方法中将默认的返回值处理器设置进 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 中了
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
// 根据返回值或使用的注解,找到对应的返回值处理器,然后将请求结果刷新到响应中,
// 或者将返回值设置进 mavContainer 中,方便后面解析
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
/**
* 1 调用业务方法
*/
@Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
//1.1 解析方法的入参,使用对应的参数解析器对请求进行解析,得到参数 : HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
//1.2 调用方法
return doInvoke(args);
}
/**
* 1.2 调用业务方法
*/
@Nullable
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(getBridgedMethod());
// 使用反射调用业务方法
return getBridgedMethod().invoke(getBean(), args);
}
4. 返回请求结果
业务执行后,返回结果会根据返回值类型和使用的注解等信息来匹配对应的 `HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler` ,取到对应的返回值处理器后,就会调用 `HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler#handleReturnValue()`对进行处理。
如 HttpEntityMethodProcessor 处理使用 HttpEntity 做为返回值的方法,也可以解析请求方法入参类型使用 RequestEntity 或 HttpEntity 的方法参数进行解析 。
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 则对使用 @RequestBody 注解的方法进行参数解析,和使用@ResponseBody注解的方法进行返回值处理,而 @RestController 注解定义时使用了 @ResponseBody 注解,所以 @RestController 和 @ResponseBody 的功能一样。
ModelAndViewMethodReturnValueHandler 则解析返回值类型为 ModelAndView 的结果,与其他类型的返回值处理程序不同的是,该类不会直接返回结果,而是根据结果解析出对应的视图对象 ModelAndView,交给 DispatcherServlet中的 ViewResolver 来渲染视图,响应给客户端。