SIGCHLD信号
只要子进程发生变化就会产生SIGCHLD信号通知父进程:
1.子进程终止时;
2.子进程接收到SIGSTOP信号停止时;
3.子进程处在停止态,接收到了SIGCONT唤醒时。
利用信号捕捉函数回收子进程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
void func(int arg)
{
pid_t wpid;
int status;
while((wpid = waitpid(-1, &status, 0)) != -1) //一次响应回收多次
{
printf("waitpid:%d
", wpid);
if (WIFEXITED(status))
{
printf("catch child id = %d ret_val:%d
", wpid, WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pid_t pid;
sigset_t set;
int ret;
//设置SIGCHLD信号阻塞
ret = sigemptyset(&set);
if (-1 == ret)
{
perror("sigemptyset error");
return -2;
}
ret = sigaddset(&set, SIGCHLD);
if (-1 == ret)
{
perror("sigaddset error");
return -1;
}
ret = sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, &set, NULL);
if (-1 == ret)
{
perror("sigprocmask error");
return -1;
}
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
if ((pid = fork()) == 0)
break;
if (5 == i)
{
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = func;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGCHLD, &act, NULL);
// 解除阻塞
ret = sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, &set, NULL);
if (-1 == ret)
{
perror("sigprocmask error");
return -1;
}
printf("I am parent, pid = %d
", getpid());
while(1);
}
else
{
printf("I am child , pid = %d
", getpid());
return i;
}
return 0;
}
输出结果:
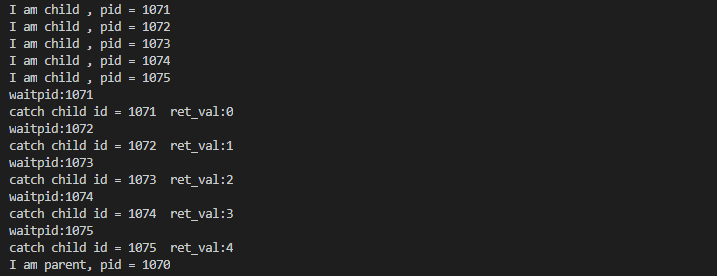
注意:
1.SIGCHLD信号默认是忽略的;
2.当多个子进程同时死亡时产生多个SIGCHLD信号,但是只会处理一个,因为常规信号不排队,所以在信号响应函数中应该循环判断是否有子进程死亡;
3.需要注意程序一开始应该阻塞SIGCHLD信号,防止子进程运行过快,还没有设置信号响应函数就已进运行完了。
4.父进程不应先与子进程死亡。