经过前面几篇文章的铺垫,我们正式来探讨 Sentinel 的 entry 方法的实现流程。即探究进入 Alibaba Sentinel 核心的一把钥匙。
@
无论是从 Sentinel 适配 Dubbo 也好,还是 SphU 源码中的注释中能看出,对一个资源进行限流或熔断,通常需要调用 SphU 的 entry 方法,例如如下示例代码。
public void foo() {
Entry entry = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry("abc");
} catch (BlockException blockException) {
// when goes there, it is blocked
// add blocked handle logic here
} catch (Throwable bizException) {
// business exception
Tracer.trace(bizException);
} finally {
// ensure finally be executed
if (entry != null){
entry.exit();
}
}
}
那本文将来探讨 SphU.entry 的实现原理。SphU 类定义了很多 entry 重载方法,我们就以下面这个方法为例来探究其实现原理。
1、SphU.entry 流程分析
public static Entry entry(String name, EntryType type, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException { // @1
return Env.sph.entry(name, type, count, args); // @2
}
代码@1:我们先来简单介绍其核心参数的含义:
- String name
资源的名称。 - EntryType type
进入资源的方式,主要包含 EntryType.IN、EntryType.OUT。 - int count
可以理解为本次进入需要消耗的“令牌数”。 - Object... args
其他参数。
代码@2:调用 Env.sph.entry 的方法,其最终会调用 CtSph 的 entry 方法。
接下来我们将重点查看 CtSph 的 entry 方法。
public Entry entry(String name, EntryType type, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException {
StringResourceWrapper resource = new StringResourceWrapper(name, type); // @1
return entry(resource, count, args); // @2
}
代码@1:由于该方法用来表示资源的方式为一个字符串,故创建一个 StringResourceWrapper 对象来表示一个 Sentinel 中的资源,另外一个实现为 MethodResourceWrapper,用来表示方法类的资源。
代码@2:继续调用 CtSph 的另外一个 entry 重载方法,最终会调用 entryWithPriority 方法。
CtSph#entryWithPriority
private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) // @1
throws BlockException {
Context context = ContextUtil.getContext(); // @2
if (context instanceof NullContext) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
if (context == null) {
// Using default context.
context = InternalContextUtil.internalEnter(Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME);
}
if (!Constants.ON) { // @3
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
ProcessorSlot<Object> chain = lookProcessChain(resourceWrapper); // @4
if (chain == null) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
Entry e = new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, chain, context); // @5
try {
chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args); // @6
} catch (BlockException e1) { // @7
e.exit(count, args);
throw e1;
} catch (Throwable e1) {
RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", e1);
}
return e;
}
代码@1:我们先来介绍一下该方法的参数:
- ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper
资源的包装类型,可以是字符串类型的资源描述,也可以是方法类的。 - int count
此次需要消耗的令牌。 - boolean prioritized
是否注重优先级。 - Object... args
额外参数。
代码@2:获取方法调用的上下文环境,上下环境对象存储在线程本地变量:ThreadLocal 中,这里先“剧透”一下,上下文环境中存储的是整个调用链,后续文章会重点介绍。
代码@3:Sentinel 提供一个全局关闭的开关,如果关闭,返回的 CtEntry 中的 chain 为空,从这里可以看出,如果 chain 为空,则不会触发 Sentinel 流控相关的逻辑,从侧面也反应了该属性的重要性。
代码@4:为该资源加载处理链链,这里是最最重要的方法,将在下文详细介绍。
代码@5:根据资源ID、处理器链、上下文环境构建 CtEntry 对象。
代码@6:调用 chain 的 entry 方法。
代码@7:如果出现 BlockException ,调用 CtEntry 的 exit 方法。
2、Sentienl ProcessorSlot 处理链
我们接下来重点看一下 lookProcessChain 方法的实现细节。
CtSph#lookProcessChain
ProcessorSlot<Object> lookProcessChain(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) {
ProcessorSlotChain chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper); // @1
if (chain == null) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
if (chain == null) {
// Entry size limit.
if (chainMap.size() >= Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE) { // @2
return null;
}
chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain(); // @3
Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> newMap = new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>(
chainMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(chainMap);
newMap.put(resourceWrapper, chain);
chainMap = newMap;
}
}
}
return chain;
}
代码@1:chainMap 一个全局的缓存表,即同一个资源 ResourceWrapper (同一个资源名称) 会共同使用同一个 ProcessorSlotChain ,即不同的线程在访问同一个资源保护的代码时,这些线程将共同使用 ProcessorSlotChain 中的各个 ProcessorSlot 。注意留意 ResourceWrapper 的 equals 方法与 hashCode 方法。
代码@2:这里重点想突出,如果同时在进入的资源个数超过 MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE,默认为 6000,会返回 null,则不对本次请求执行限流,熔断计算,而是直接跳过,这个点还是值得我们注意的。
代码@3:通过 SlotChainProvider 创建对应的处理链。
SlotChainProvider#newSlotChain
public static ProcessorSlotChain newSlotChain() {
if (slotChainBuilder != null) { // @1
return slotChainBuilder.build();
}
slotChainBuilder = SpiLoader.loadFirstInstanceOrDefault(SlotChainBuilder.class, DefaultSlotChainBuilder.class); // @2
if (slotChainBuilder == null) { // @3
RecordLog.warn("[SlotChainProvider] Wrong state when resolving slot chain builder, using default");
slotChainBuilder = new DefaultSlotChainBuilder();
} else {
RecordLog.info("[SlotChainProvider] Global slot chain builder resolved: "
+ slotChainBuilder.getClass().getCanonicalName());
}
return slotChainBuilder.build(); // @4
}
代码@1:如果 slotChainBuilder 不为空,则直接调用其 build 方法构建处理器链。
代码@2:如果为空,首先通过 JAVA 的 SPI 机制,尝试加载自定义的 Slot Chain 构建器实现类。如果需要实现自定义的 Chain 构建器,只需实现 SlotChainBuilder 接口,然后将其放在 classpath 下即可,如果存在多个,以找到的第一个为准。
代码@3:如果从 SPI 机制中加载失败,则使用默认的构建器:DefaultSlotChainBuilder。
代码@4:调用其 build 方法构造 Slot Chain。
那接下来我们先来看看 Sentinel 的 SlotChainBuilder 类体系,然后看看 DefaultSlotChainBuilder 的 build 方法。
2.1 SlotChainBuilder 类体系
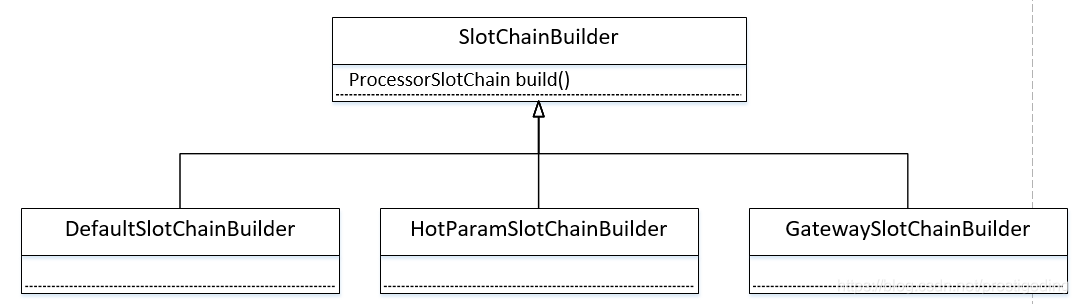
主要有三个实现类,对应热点、接口网关以及普通场景。我们接下来将重点介绍 DefaultSlotChainBuilder ,关于热点限流与网关限流将在后面的文章中详细探讨。
2.2 DefaultSlotChainBuilder build 方法
DefaultSlotChainBuilder#build
public class DefaultSlotChainBuilder implements SlotChainBuilder {
public ProcessorSlotChain build() {
ProcessorSlotChain chain = new DefaultProcessorSlotChain();
chain.addLast(new NodeSelectorSlot());
chain.addLast(new ClusterBuilderSlot());
chain.addLast(new LogSlot());
chain.addLast(new StatisticSlot());
chain.addLast(new AuthoritySlot());
chain.addLast(new SystemSlot());
chain.addLast(new FlowSlot());
chain.addLast(new DegradeSlot());
return chain;
}
}
就问大家激不激动,开不开心,从这些 Slot 的名字基本就能得出其含义。
- NodeSelectorSlot
主要用于构建调用链。 - ClusterBuilderSlot
用于集群限流、熔断。 - LogSlot
用于记录日志。 - StatisticSlot
用于实时收集实时消息。 - AuthoritySlot
用于权限校验的。 - SystemSlot
用于验证系统级别的规则。 - FlowSlot
实现限流机制。 - DegradeSlot
实现熔断机制。
经过上面的方法,就构建一条 Slot 处理链。其实到这里我们就不难发现,调用 ProcessorSlotChain 的 entry 方法,就是依次调用这些 slot 的方法。关于 ProcessorSlotChain 的类层次结构就不再多说明了,其实现比较简单,大家如果有兴趣的话,可以关注这部分的实现,这里代表一类场景:一对多、责任链的设计模式。
3、Sentinel SphU.entry 处理流程图
经过上面的探索,我们其实已经找到了 Sentinel 的关于限流、熔断核心处理逻辑的入口,就是 FlowSlot、DegradeSlot。接下来我们以一张流程图来结束本文的讲解。
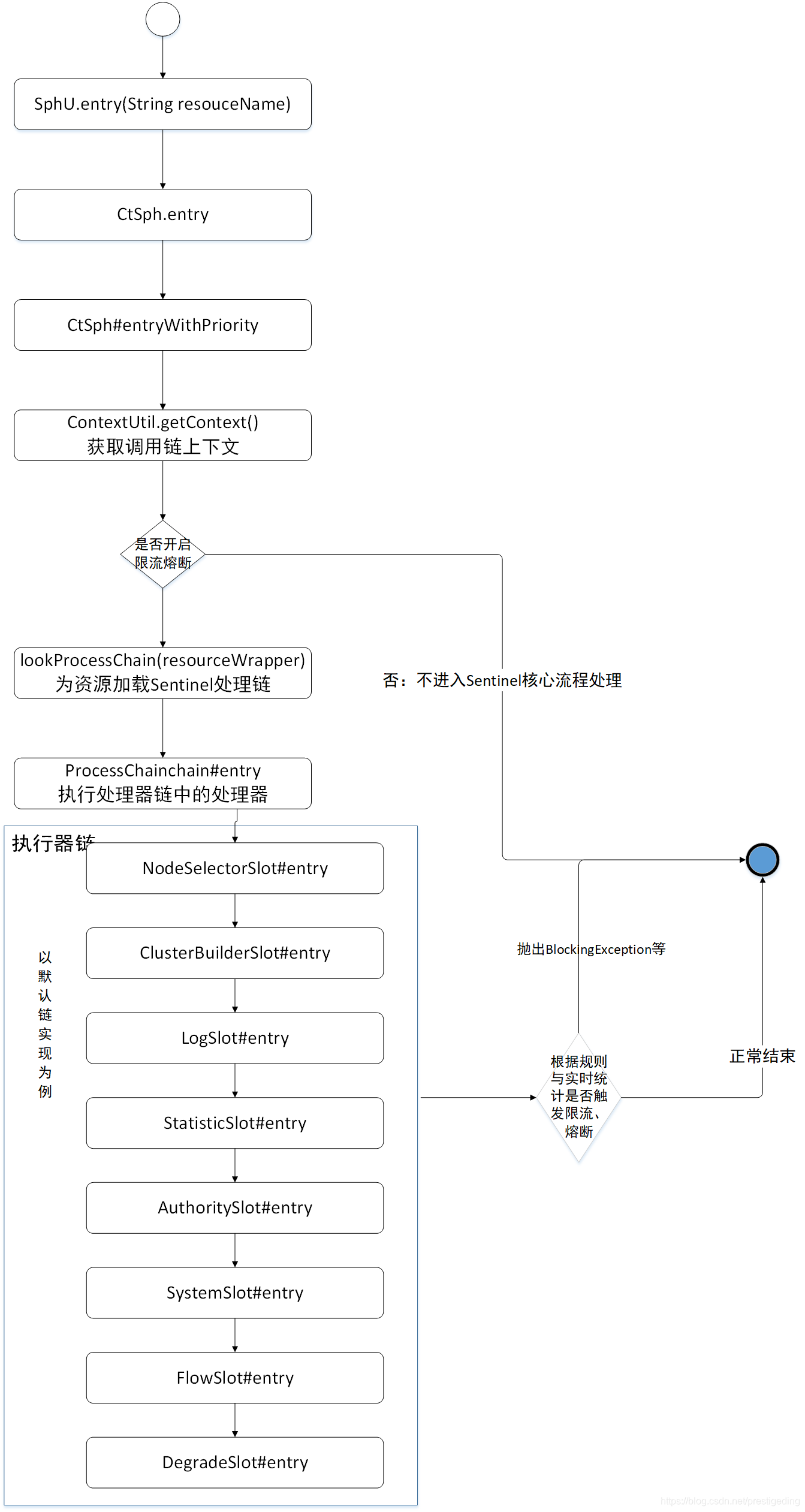
本文的目的就是打开 Sentinel 的大门,即寻找实时数据收集、限流、熔断实现机制的入口,从而正式探寻 Sentienl 的核心实现原理,更多精彩请继续期待该专栏的后续内容。
点赞是一种美德,如果觉得本文写的不错的话,还请帮忙点个赞,您的认可是我持续创造的最大动力,谢谢。
推荐阅读:源码分析 Alibaba Sentinel 专栏。
1、Alibaba Sentinel 限流与熔断初探(技巧篇)
2、源码分析 Sentinel 之 Dubbo 适配原理
3、源码分析 Alibaba sentinel 滑动窗口实现原理(文末附原理图)
作者信息:丁威,《RocketMQ技术内幕》作者,目前担任中通科技技术平台部资深架构师,维护 中间件兴趣圈公众号,目前主要发表了源码阅读java集合、JUC(java并发包)、Netty、ElasticJob、Mycat、Dubbo、RocketMQ、mybaits等系列源码。点击链接:加入笔者的知识星球,一起探讨高并发、分布式服务架构,分享阅读源码心得。