1. 前言
这篇文章介绍了继承并自定义Shape的方法,不过,恐怕,事实上,100个xaml的程序员99个都不会用到。写出来是因为反正都学了,当作写个笔记。
通过这篇文章,你可以学到如下知识点:
- 自定义Shape。
- DeferRefresh模式。
- InvalidateArrange的应用。
2. 从Path派生
UWP中的Shape大部分都是密封类--除了Path。所以要自定义Shape只能从Path派生。Template10给出了这个例子:RingSegment 。
从这个类中可以看到,自定义Shape只需要简单地在每个自定义属性的属性值改变时或SizeChanged时调用private void UpdatePath()为Path.Data赋值就完成了,很简单吧。
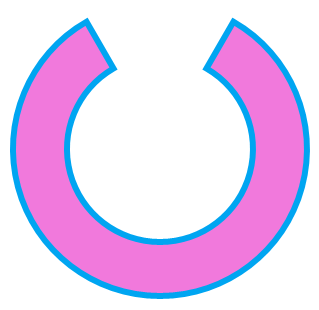
RingSegment.StartAngle = 30;
RingSegment.EndAngle = 330;
RingSegment.Radius = 50;
RingSegment.InnerRadius = 30;
3. BeginUpdate、EndUpdate与DeferRefresh
这段代码会产生一个问题:每更改一个属性的值后都会调用UpdatePath(),那不就会重复调用四次?
事实上真的会,显然这个类的作者也考虑过这个问题,所以提供了public void BeginUpdate()和public void EndUpdate()函数。
/// <summary>
/// Suspends path updates until EndUpdate is called;
/// </summary>
public void BeginUpdate()
{
_isUpdating = true;
}
/// <summary>
/// Resumes immediate path updates every time a component property value changes. Updates the path.
/// </summary>
public void EndUpdate()
{
_isUpdating = false;
UpdatePath();
}
使用这两个方法重新写上面那段代码,就是这样:
try
{
RingSegment.BeginUpdate();
RingSegment.StartAngle = 30;
RingSegment.EndAngle = 330;
RingSegment.Radius = 100;
RingSegment.InnerRadius = 80;
}
finally
{
RingSegment.EndUpdate();
}
这样就保证了只有在调用EndUpdate()时才执行UpdatePath(),而且只执行一次。
在WPF中,DeferRefresh是一种更成熟的方案。相信很多开发者在用DataGrid时多多少少有用过(主要是通过CollectionView或CollectionViewSource)。典型的实现方式可以参考DataSourceProvider。在UWPCommunityToolkit中也通过AdvancedCollectionView实现了这种方式。
在RingSegment中添加实现如下:
private int _deferLevel;
public virtual IDisposable DeferRefresh()
{
++_deferLevel;
return new DeferHelper(this);
}
private void EndDefer()
{
Debug.Assert(_deferLevel > 0);
--_deferLevel;
if (_deferLevel == 0)
{
UpdatePath();
}
}
private class DeferHelper : IDisposable
{
public DeferHelper(RingSegment source)
{
_source = source;
}
private RingSegment _source;
public void Dispose()
{
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
if (_source != null)
{
_source.EndDefer();
_source = null;
}
}
}
使用如下:
using (RingSegment.DeferRefresh())
{
RingSegment.StartAngle = 30;
RingSegment.EndAngle = 330;
RingSegment.Radius = 100;
RingSegment.InnerRadius = 80;
}
使用DeferRefresh模式有两个好处:
- 调用代码比较简单
- 通过
_deferLevel判断是否需要UpdatePath(),这样即使多次调用DeferRefresh()也只会执行一次UpdatePath()。譬如以下的调用方式:
using (RingSegment.DeferRefresh())
{
RingSegment.StartAngle = 30;
RingSegment.EndAngle = 330;
RingSegment.Radius = 50;
RingSegment.InnerRadius = 30;
using (RingSegment.DeferRefresh())
{
RingSegment.Radius = 51;
RingSegment.InnerRadius = 31;
}
}
也许你会觉得一般人不会写得这么复杂,但在复杂的场景DeferRefresh模式是有存在意义的。假设现在要更新一个复杂的UI,这个UI由很多个代码模块驱动,但不清楚其它地方有没有对需要更新的UI调用过DeferRefresh(),而创建一个DeferHelper 的消耗比起更新一次复杂UI的消耗低太多,所以执行一次DeferRefresh()是个很合理的选择。
看到
++_deferLevel这句代码条件反射就会考虑到线程安全问题,但其实是过虑了。UWP要求操作UI的代码都只能在UI线程中执行,所以理论上来说所有UIElement及它的所有操作都是线程安全的。
4. InvalidateArrange
每次更改属性都要调用DeferRefresh显然不是一个聪明的做法,而且在XAML中也不可能做到。另一种延迟执行的机制是利用CoreDispatcher的public IAsyncAction RunAsync(CoreDispatcherPriority priority, DispatchedHandler agileCallback)函数异步地执行工作项。要详细解释RunAsync可能需要一整篇文章的篇幅,简单来说RunAsync的作用就是将工作项发送到一个队列,UI线程有空的时候会从这个队列获取工作项并执行。InvalidateArrange就是利用这种机制的典型例子。MSDN上对InvalidateArrange的解释是:
使 UIElement 的排列状态(布局)无效。失效后,UIElement 将以异步方式更新其布局。
将InvalidateArrange的逻辑简化后大概如下:
protected bool ArrangeDirty { get; set; }
public void InvalidateArrange()
{
if (ArrangeDirty == true)
return;
ArrangeDirty = true;
Dispatcher.RunAsync(Windows.UI.Core.CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, () =>
{
ArrangeDirty = false;
lock (this)
{
//Measure
//Arrange
}
});
}
调用InvalidateArrange后将ArrangeDirty标记为True,然后异步执行Measure及Arrange代码进行布局。多次调用InvalidateArrange会检查ArrangeDirty的状态以免重复执行。利用InvalidateArrange,我们可以在RingSegment的自定义属性值改变事件中调用InvalidateArrange,异步地触发LayoutUpdated并在其中改变Path.Data。
修改后的代码如下:
private bool _realizeGeometryScheduled;
private Size _orginalSize;
private Direction _orginalDirection;
private void OnStartAngleChanged(double oldStartAngle, double newStartAngle)
{
InvalidateGeometry();
}
private void OnEndAngleChanged(double oldEndAngle, double newEndAngle)
{
InvalidateGeometry();
}
private void OnRadiusChanged(double oldRadius, double newRadius)
{
this.Width = this.Height = 2 * Radius;
InvalidateGeometry();
}
private void OnInnerRadiusChanged(double oldInnerRadius, double newInnerRadius)
{
if (newInnerRadius < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentException("InnerRadius can't be a negative value.", "InnerRadius");
}
InvalidateGeometry();
}
private void OnCenterChanged(Point? oldCenter, Point? newCenter)
{
InvalidateGeometry();
}
protected override Size ArrangeOverride(Size finalSize)
{
if (_realizeGeometryScheduled == false && _orginalSize != finalSize)
{
_realizeGeometryScheduled = true;
LayoutUpdated += OnTriangleLayoutUpdated;
_orginalSize = finalSize;
}
base.ArrangeOverride(finalSize);
return finalSize;
}
protected override Size MeasureOverride(Size availableSize)
{
return new Size(base.StrokeThickness, base.StrokeThickness);
}
public void InvalidateGeometry()
{
InvalidateArrange();
if (_realizeGeometryScheduled == false )
{
_realizeGeometryScheduled = true;
LayoutUpdated += OnTriangleLayoutUpdated;
}
}
private void OnTriangleLayoutUpdated(object sender, object e)
{
_realizeGeometryScheduled = false;
LayoutUpdated -= OnTriangleLayoutUpdated;
RealizeGeometry();
}
private void RealizeGeometry()
{
//other code here
Data = pathGeometry;
}
这些代码参考了ExpressionSDK的Silverlight版本。ExpressionSDK提供了一些Shape可以用作参考。(安装Blend后通常可以在这个位置找到它:C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft SDKsExpressionBlendSilverlightv5.0LibrariesMicrosoft.Expression.Drawing.dll)由于比起WPF,Silverlight更接近UWP,所以Silverlight的很多代码及经验更有参考价值,遇到难题不妨找些Silverlight代码来作参考。

InvalidateArrange属于比较核心的API,文档中也充斥着“通常不建议“、”通常是不必要的”、“慎重地使用它”等字句,所以平时使用最好要谨慎。如果不是性能十分敏感的场合还是建议使用Template10的方式实现。
5. 使用TemplatedControl实现
除了从Path派生,自定义Shape的功能也可以用TemplatedControl实现,一般来说这种方式应该是最简单最通用的方式。下面的代码使用TemplatedControl实现了一个三角形:
[TemplatePart(Name = PathElementName,Type =typeof(Path))]
[StyleTypedProperty(Property = nameof(PathElementStyle), StyleTargetType =typeof(Path))]
public class TriangleControl : Control
{
private const string PathElementName = "PathElement";
public TriangleControl()
{
this.DefaultStyleKey = typeof(TriangleControl);
this.SizeChanged += OnTriangleControlSizeChanged;
}
/// <summary>
/// 标识 Direction 依赖属性。
/// </summary>
public static readonly DependencyProperty DirectionProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Direction", typeof(Direction), typeof(TriangleControl), new PropertyMetadata(Direction.Up, OnDirectionChanged));
/// <summary>
/// 获取或设置Direction的值
/// </summary>
public Direction Direction
{
get { return (Direction)GetValue(DirectionProperty); }
set { SetValue(DirectionProperty, value); }
}
private static void OnDirectionChanged(DependencyObject obj, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs args)
{
var target = obj as TriangleControl;
var oldValue = (Direction)args.OldValue;
var newValue = (Direction)args.NewValue;
if (oldValue != newValue)
target.OnDirectionChanged(oldValue, newValue);
}
protected virtual void OnDirectionChanged(Direction oldValue, Direction newValue)
{
UpdateShape();
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取或设置PathElementStyle的值
/// </summary>
public Style PathElementStyle
{
get { return (Style)GetValue(PathElementStyleProperty); }
set { SetValue(PathElementStyleProperty, value); }
}
/// <summary>
/// 标识 PathElementStyle 依赖属性。
/// </summary>
public static readonly DependencyProperty PathElementStyleProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("PathElementStyle", typeof(Style), typeof(TriangleControl), new PropertyMetadata(null));
private Path _pathElement;
public override void OnApplyTemplate()
{
base.OnApplyTemplate();
_pathElement = GetTemplateChild("PathElement") as Path;
}
private void OnTriangleControlSizeChanged(object sender, SizeChangedEventArgs e)
{
UpdateShape();
}
private void UpdateShape()
{
var geometry = new PathGeometry();
var figure = new PathFigure { IsClosed = true };
geometry.Figures.Add(figure);
switch (Direction)
{
case Direction.Left:
figure.StartPoint = new Point(ActualWidth, 0);
var segment = new LineSegment { Point = new Point(ActualWidth, ActualHeight) };
figure.Segments.Add(segment);
segment = new LineSegment { Point = new Point(0, ActualHeight / 2) };
figure.Segments.Add(segment);
break;
case Direction.Up:
figure.StartPoint = new Point(0, ActualHeight);
segment = new LineSegment { Point = new Point(ActualWidth / 2, 0) };
figure.Segments.Add(segment);
segment = new LineSegment { Point = new Point(ActualWidth, ActualHeight) };
figure.Segments.Add(segment);
break;
case Direction.Right:
figure.StartPoint = new Point(0, 0);
segment = new LineSegment { Point = new Point(ActualWidth, ActualHeight / 2) };
figure.Segments.Add(segment);
segment = new LineSegment { Point = new Point(0, ActualHeight) };
figure.Segments.Add(segment);
break;
case Direction.Down:
figure.StartPoint = new Point(0, 0);
segment = new LineSegment { Point = new Point(ActualWidth, 0) };
figure.Segments.Add(segment);
segment = new LineSegment { Point = new Point(ActualWidth / 2, ActualHeight) };
figure.Segments.Add(segment);
break;
}
_pathElement.Data = geometry;
}
}
<Style TargetType="Path"
x:Key="PathElementStyle">
<Setter Property="Stroke"
Value="RoyalBlue" />
<Setter Property="StrokeThickness"
Value="10" />
<Setter Property="Stretch"
Value="Fill" />
</Style>
<Style TargetType="local:TriangleControl">
<Setter Property="PathElementStyle"
Value="{StaticResource PathElementStyle}" />
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="local:TriangleControl">
<Border Background="{TemplateBinding Background}"
BorderBrush="{TemplateBinding BorderBrush}"
BorderThickness="{TemplateBinding BorderThickness}">
<Path x:Name="PathElement"
Style="{TemplateBinding PathElementStyle}" />
</Border>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
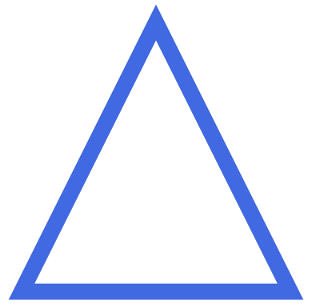
这种方式的好处是容易实现,而且兼容WPF和UWP。缺点是只能通过PathElementStyle修改Path的外观,毕竟它不是Shape,而且增加了VisualTree的层次,不适合于性能敏感的场合。
6. 结语
自定义Shape真的很少用到,网上也没有多少这方面的资料,如果你真的用到的话希望这篇文章对你有帮助。
其次,希望其它的知识点,例如DeferRefresh模式、InvalidateArrange的应用等也对你有帮助。
7. 参考
UIElement.InvalidateArrange Method
Template10.Controls.RingSegment