With dsu on tree we can answer queries of this type:
How many vertices in subtree of vertex v has some property in O(n lg n) time (for all of the queries).
For example:
Given a tree, every vertex has color. Query is how many vertices in subtree of vertex v are colored with color c?
要点:记录每棵子树的大小,启发式合并。
模板整理如下:
1. easy to code but 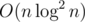

1 //O(nlognlogn) 2 map<int, int> *cnt[maxn]; 3 void dfs(int v, int p){ 4 int mx = -1, bigChild = -1; 5 for(auto u : g[v]) 6 if(u != p){ 7 dfs(u, v); 8 if(sz[u] > mx) 9 mx = sz[u], bigChild = u; 10 } 11 if(bigChild != -1) 12 cnt[v] = cnt[bigChild]; 13 else 14 cnt[v] = new map<int, int> (); 15 (*cnt[v])[ col[v] ] ++; 16 for(auto u : g[v]) 17 if(u != p && u != bigChild){ 18 for(auto x : *cnt[u]) 19 (*cnt[v])[x.first] += x.second; 20 } 21 //now (*cnt)[c] is the number of vertices in subtree of vertex v that has color c. You can answer the queries easily. 22 23 }
2. easy to code and 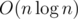

1 vector<int> *vec[maxn]; 2 int cnt[maxn]; 3 void dfs(int v, int p, bool keep){ 4 int mx = -1, bigChild = -1; 5 for(auto u : g[v]) 6 if(u != p && sz[u] > mx) 7 mx = sz[u], bigChild = u; 8 for(auto u : g[v]) 9 if(u != p && u != bigChild) 10 dfs(u, v, 0); 11 if(bigChild != -1) 12 dfs(bigChild, v, 1), vec[v] = vec[bigChild]; 13 else 14 vec[v] = new vector<int> (); 15 vec[v]->push_back(v); 16 cnt[ col[v] ]++; 17 for(auto u : g[v]) 18 if(u != p && u != bigChild) 19 for(auto x : *vec[u]){ 20 cnt[ col[x] ]++; 21 vec[v] -> push_back(x); 22 } 23 //now (*cnt)[c] is the number of vertices in subtree of vertex v that has color c. You can answer the queries easily. 24 // note that in this step *vec[v] contains all of the subtree of vertex v. 25 if(keep == 0) 26 for(auto u : *vec[v]) 27 cnt[ col[u] ]--; 28 }
3. heavy-light decomposition style 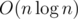

1 int cnt[maxn]; 2 bool big[maxn]; 3 void add(int v, int p, int x){ 4 cnt[ col[v] ] += x; 5 for(auto u: g[v]) 6 if(u != p && !big[u]) 7 add(u, v, x) 8 } 9 void dfs(int v, int p, bool keep){ 10 int mx = -1, bigChild = -1; 11 for(auto u : g[v]) 12 if(u != p && sz[u] > mx) 13 mx = sz[u], bigChild = u; 14 for(auto u : g[v]) 15 if(u != p && u != bigChild) 16 dfs(u, v, 0); // run a dfs on small childs and clear them from cnt 17 if(bigChild != -1) 18 dfs(bigChild, v, 1), big[bigChild] = 1; // bigChild marked as big and not cleared from cnt 19 add(v, p, 1); 20 //now cnt[c] is the number of vertices in subtree of vertex v that has color c. You can answer the queries easily. 21 if(bigChild != -1) 22 big[bigChild] = 0; 23 if(keep == 0) 24 add(v, p, -1); 25 }
4. My invented style 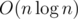

1 This implementation for "Dsu on tree" technique is new and invented by me. This implementation is easier to code than others. Let st[v] dfs starting time of vertex v, ft[v] be it's finishing time and ver[time] is the vertex which it's starting time is equal to time. 2 3 int cnt[maxn]; 4 void dfs(int v, int p, bool keep){ 5 int mx = -1, bigChild = -1; 6 for(auto u : g[v]) 7 if(u != p && sz[u] > mx) 8 mx = sz[u], bigChild = u; 9 for(auto u : g[v]) 10 if(u != p && u != bigChild) 11 dfs(u, v, 0); // run a dfs on small childs and clear them from cnt 12 if(bigChild != -1) 13 dfs(bigChild, v, 1); // bigChild marked as big and not cleared from cnt 14 for(auto u : g[v]) 15 if(u != p && u != bigChild) 16 for(int p = st[u]; p < ft[u]; p++) 17 cnt[ col[ ver[p] ] ]++; 18 cnt[ col[v] ]++; 19 //now cnt[c] is the number of vertices in subtree of vertex v that has color c. You can answer the queries easily. 20 if(keep == 0) 21 for(int p = st[v]; p < ft[v]; p++) 22 cnt[ col[ ver[p] ] ]--; 23 }
时间复杂度分析
4. My invented style
考虑每个节点最多会被清零几次?
显然被清零的次数即为该节点到根节点的链上轻儿子的个数
联系树链剖分,任意一个节点到根节点的链最多被划分为O(logn)段重链,最多被清零O(logn)次.
故时间复杂度为O(nlogn).
2, 3, 4时间复杂度分析类似.
启发式合并算法复杂度总结
线段树合并 => O(nlogU), U为线段树权值域,从势能分析,合并的复杂度为O(总节点数减小的个数)
平衡树合并+树链剖分+单次插入删除O(logn) => O(nlognlogn)
平衡树合并+树链剖分+单次插入删除O(1) => O(nlogn)
set合并 => O(nlognlogn), 显然set合并复杂度不会高于multiset(平衡树)合并复杂度
