1,catch 语句块中可以抛出异常:
1,示意图:
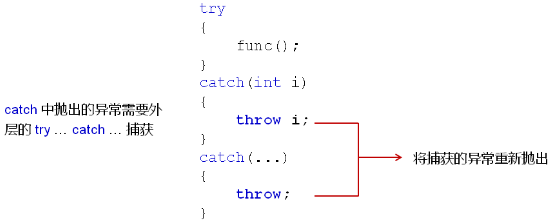
2,func() 在 try 语句块中,说明它有可能抛出异常,抛出的异常有可能是整型或其它类型;
3,catch 语句块处理方式是将异常重新抛出去,其它什么也不干;
4,此时需要外层的其它 try ... catch 语句块处理;
5,catch() 中的参数类似于函数里面的参数,当 try() 里面抛出的异常在逐个匹配时,匹配上了以后异常元素就用来初始化 catch() 中的形参变量,因此 catch() 中的参数才会代表扔出来的异常,其实类似于函数调用过程有一个初始化的工作;
6,函数调用里面实参和形参有可能进行类型转换,但是在 try ... catch 异常语句中绝对不会有任何的类型转换,严格匹配, 然后初始化;
7,接受异常是任意类型时,只能通过 throw 扔出异常;
2,为什么要在 catch 中重新抛出异常?
3,catch 中捕获的异常可以被重新解释后抛出,工程中使用这样的统一异常类型:
1,示意图:
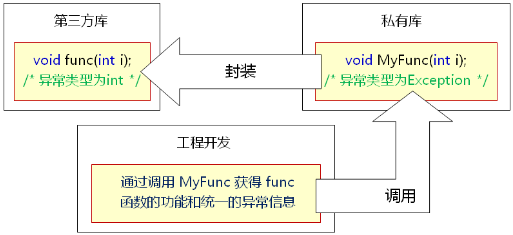
2,工程开发中使用 catch 中可以再次扔出异常的特性来重新解释一个异常;
3,工程开发中一般会基于已有的库来进行,比如 STL 标准库,也有可能是我们自己的私有库;
4,当我们发现私有库中有一些功能没有,但需要的功能在第三方库中是有的,所以我们要进行一层封装;
5,在私有库中定义一个 MyFunc(int i) 函数,这个函数用来直接调用第三方库中的 func() 函数;
6,进行封装的原因是 func() 函数的异常类型为 int 类型,比较简单,然而在私有库中我们定义了自己的异常类型为 Exception, 我们不想使用 int 类型,我们想要统一异常的类型,于是我们就在私有库中的 MyFunc() 函数中去捕获第三方库中 func() 函数抛出的异常,然后根据捕获的异常重新解释为我们想要的异常,这样我们工程开发中所面对的异常类型就是一致的;
7,这就是工程中利用 catch 中可以重新抛出异常的特性来统一异常的类型;
4,异常的重新解释编程实验:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 void Demo() 7 { 8 try 9 { 10 try 11 { 12 throw 'c'; 13 } 14 catch(int i) 15 { 16 cout << "Inner: catch(int i)" << endl; 17 throw i; 18 } 19 catch(...) 20 { 21 cout << "Inner: catch(...)" << endl; 22 throw; 23 } 24 } 25 catch(...) 26 { 27 cout << "Outer: catch(...)" << endl; 28 } 29 } 30 31 /* 32 假设: 当前的函数是第三方库中的函数,因此,我们无法修改源代码 33 34 函数名: void func(int i) 35 抛出异常的类型: int 36 -1 ==》 参数异常 37 -2 ==》 运行异常 38 -3 ==》 超时异常 39 */ 40 41 /* 第三方库函数,编写好后不能修改,因为我们一般没有源代码,这里仅是用于模拟 */ 42 void func(int i) 43 { 44 if( i < 0 ) 45 { 46 throw -1; 47 } 48 49 if( i > 100 ) 50 { 51 throw -2; 52 } 53 54 if( i == 11 ) 55 { 56 throw -3; 57 } 58 59 cout << "Run func..." << endl; // 没有异常,则执行 func() 函数功能; 60 } 61 62 /* 不能修改 func() 函数,则我们定义 MyFunc() 函数重解释 func() 的异常 */ 63 void MyFunc(int i) 64 { 65 try 66 { 67 func(i); // 直接通过第三方库中的 func() 来实现我们需要的功能; 68 } 69 catch(int i) 70 { 71 switch(i) 72 { 73 case -1: 74 throw "Invalid Parameter"; 75 break; 76 case -2: 77 throw "Runtime Exception"; 78 break; 79 case -3: 80 throw "Timeout Exception"; 81 break; 82 } 83 } 84 } 85 86 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 87 { 88 // Demo(); 89 90 try 91 { 92 MyFunc(11); // 如果在这里调用 func(11),则下面 catch 语句块中会打印:Exception Info: -3; 这样就不能立刻反应出来出了什么事儿,此时要去找 func() 中的文档说明,这样的开发是非常痛苦的; 93 } 94 catch(const char* cs) 95 { 96 cout << "Exception Info: " << cs << endl; // 打印:Exception Info: Timeout Exception 97 } 98 99 return 0; 100 }
1,本例展示了工程中利用 catch 中可以重新抛出异常的特性来统一异常的类型;
2,解释异常,重新抛出新的意义更加丰富的异常,字符串是不够的,可以定义自己的异常类类型,
5,异常的操作特性:
1,异常的类型可以是自定义类类型;
2,对于类类型异常的匹配依旧是自上而下严格匹配;
1,只有赋值兼容性是意外;
3,赋值兼容性原则在异常匹配中依然适用;
1,子类的异常对象可以被父类的 catch 语句块抓住;
4,一般而言(这里是将异常类型编程自定义的类类型应该遵守的原则):
1,匹配子类异常的 catch 放在下部;
2,匹配父类异常的 catch 放在上部;
6,工程中异常类的特性:
1,在工程中会定义一系列的异常类;
1,这些类是一个类族,有很严格的继承层次结构;
2,每个类代表工程中可能出现的一种异常类型;
3,代码复用时可能需要重解释不同的异常类;
1,刚才展示的 catch 的特性;
4,在定义 catch 语句块时推荐使用引用作为参数;
1,catch 语句块要捕获的异常是类对象异常的时候,推荐使用引用作为参数,避免拷贝构造,提高程序效率;
7,类型的异常编程实验:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Base 7 { 8 }; 9 10 /* 定义异常类 */ 11 class Exception : public Base 12 { 13 int m_id; 14 string m_desc; 15 public: 16 Exception(int id, string desc) 17 { 18 m_id = id; 19 m_desc = desc; 20 } 21 22 int id() const 23 { 24 return m_id; 25 } 26 27 string description() const 28 { 29 return m_desc; 30 } 31 }; 32 33 /* 34 假设: 当前的函数式第三方库中的函数,因此,我们无法修改源代码 35 函数名: void func(int i) 36 抛出异常的类型: int 37 -1 ==》 参数异常 38 -2 ==》 运行异常 39 -3 ==》 超时异常 40 */ 41 42 /* 第三方库函数,编写好后不能修改,因为我们一般没有源代码,这里仅是用于模拟 */ 43 void func(int i) 44 { 45 if( i < 0 ) 46 { 47 throw -1; 48 } 49 50 if( i > 100 ) 51 { 52 throw -2; 53 } 54 55 if( i == 11 ) 56 { 57 throw -3; 58 } 59 60 cout << "Run func..." << endl; 61 } 62 63 /* 使用自定义的类类型来优化 */ 64 void MyFunc(int i) 65 { 66 try 67 { 68 func(i); 69 } 70 catch(int i) 71 { 72 switch(i) 73 { 74 case -1: 75 throw Exception(-1, "Invalid Parameter"); // 直接调用构造函数生成异常对象; 76 break; 77 case -2: 78 throw Exception(-2, "Runtime Exception"); // 直接调用构造函数生成异常对象; 79 break; 80 case -3: 81 throw Exception(-3, "Timeout Exception"); // 直接调用构造函数生成异常对象; 82 break; 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 87 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 88 { 89 try 90 { 91 MyFunc(11); 92 } 93 catch(const Exception& e) // 这里使用异常类,为了防止拷贝构造、提高程序效率,用引用,同时也为了防止无休止递归调用导致栈溢出; 94 { 95 cout << "Exception Info: " << endl; // Exception Info: 96 cout << " ID: " << e.id() << endl; // ID: -3; 97 cout << " Description: " << e.description() << endl; // Description: Timeout Exception; 98 } 99 catch(const Base& e) // 如果把父类放到子类上面,则编译器显示: 100 // warning: exception of type 'Exception' will be caught(子类这一行) 101 // warning: by earlier handler for 'Base' (父类这一行); 102 { 103 cout << "catch(const Base& e)" << endl; 104 } 105 106 return 0; 107 }
1,异常信息更加丰富,更加方便的定位问题所在;
2,工程开发中,一般以自定义类类型来描述可能出现的异常;
3,工程开发中,子类上,父类下;
4,本例告诉大家实际工程开发中定义完异常类的层次结构之后,如何来进行使用;
8,C++ 标准库中的异常类:
1,C++ 标准库中提供了实用异常类族;
2,标准库中的异常都是从 exception 类派生的;
3,exception 类有两个主要的分支:
1,logic_error:
1,常用于程序中的可避免逻辑错误;
1,空指针,函数参数错误,下标越界等;
2,runtime_error:
1,常用于程序中无法避免的恶心错误;
1,运算产生越界、溢出等;
4,标准库中的异常类继承图:
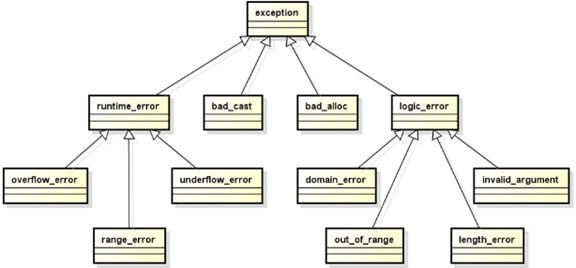
1,可以查看 C++ 标准库文档,看异常怎么使用;
9,标准库中的异常使用编程实验(用异常类优化数组类):
1,Array.h 的优化:
1 #ifndef _ARRAY_H_ 2 #define _ARRAY_H_ 3 4 #include <stdexcept> // 标准库中的异常类头文件; 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 template 9 < typename T, int N > 10 class Array 11 { 12 T m_array[N]; 13 public: 14 int length() const; 15 bool set(int index, T value); 16 bool get(int index, T& value); 17 T& operator[] (int index); 18 T operator[] (int index) const; 19 virtual ~Array(); 20 }; 21 22 template 23 < typename T, int N > 24 int Array<T, N>::length() const 25 { 26 return N; 27 } 28 29 template 30 < typename T, int N > 31 bool Array<T, N>::set(int index, T value) 32 { 33 bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < N); 34 35 if( ret ) 36 { 37 m_array[index] = value; 38 } 39 40 return ret; 41 } 42 43 template 44 < typename T, int N > 45 bool Array<T, N>::get(int index, T& value) 46 { 47 bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < N); 48 49 if( ret ) 50 { 51 value = m_array[index]; 52 } 53 54 return ret; 55 } 56 57 template 58 < typename T, int N > 59 T& Array<T, N>::operator[] (int index) 60 { 61 if( (0 <= index) && (index < N) ) 62 { 63 return m_array[index]; // 这里之前没有验证 index 是否合法,因为验证了也没办法处理; 64 } 65 else 66 { 67 throw out_of_range("T& Array<T, N>::operator[] (int index)"); 68 } 69 } 70 71 template 72 < typename T, int N > 73 T Array<T, N>::operator[] (int index) const 74 { 75 if( (0 <= index) && (index < N) ) 76 { 77 return m_array[index]; // 这里之前没有验证 index 是否合法,因为验证了也没办法处理; 78 } 79 else 80 { 81 throw out_of_range("T Array<T, N>::operator[] (int index) const"); 82 } 83 } 84 85 template 86 < typename T, int N > 87 Array<T, N>::~Array() 88 { 89 90 } 91 92 #endif
2,HeapArray.h 的优化:
1 #ifndef _HEAPARRAY_H_ 2 #define _HEAPARRAY_H_ 3 4 #include <stdexcept> // 添加标准头文件; 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 template 9 < typename T > 10 class HeapArray 11 { 12 private: 13 int m_length; 14 T* m_pointer; 15 16 HeapArray(int len); 17 HeapArray(const HeapArray<T>& obj); 18 bool construct(); 19 public: 20 static HeapArray<T>* NewInstance(int length); 21 int length() const; 22 bool get(int index, T& value); 23 bool set(int index ,T value); 24 T& operator [] (int index); 25 T operator [] (int index) const; 26 HeapArray<T>& self(); 27 const HeapArray<T>& self() const; // 要考虑成员函数有没有必要成为 const 函数,const 函数主要是给 cosnt 函数调用; 28 ~HeapArray(); 29 }; 30 31 template 32 < typename T > 33 HeapArray<T>::HeapArray(int len) 34 { 35 m_length = len; 36 } 37 38 template 39 < typename T > 40 bool HeapArray<T>::construct() 41 { 42 m_pointer = new T[m_length]; 43 44 return m_pointer != NULL; 45 } 46 47 template 48 < typename T > 49 HeapArray<T>* HeapArray<T>::NewInstance(int length) 50 { 51 HeapArray<T>* ret = new HeapArray<T>(length); 52 53 if( !(ret && ret->construct()) ) 54 { 55 delete ret; 56 ret = 0; 57 } 58 59 return ret; 60 } 61 62 template 63 < typename T > 64 int HeapArray<T>::length() const 65 { 66 return m_length; 67 } 68 69 template 70 < typename T > 71 bool HeapArray<T>::get(int index, T& value) 72 { 73 bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < length()); 74 75 if( ret ) 76 { 77 value = m_pointer[index]; 78 } 79 80 return ret; 81 } 82 83 template 84 < typename T > 85 bool HeapArray<T>::set(int index, T value) 86 { 87 bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < length()); 88 89 if( ret ) 90 { 91 m_pointer[index] = value; 92 } 93 94 return ret; 95 } 96 97 template 98 < typename T > 99 T& HeapArray<T>::operator [] (int index) 100 { 101 if( (0 <= index) && (index < length()) ) 102 { 103 return m_pointer[index]; // 优化这里,越界抛异常; 104 } 105 else 106 { 107 throw out_of_range("T& HeapArray<T>::operator [] (int index)"); 108 } 109 } 110 111 template 112 < typename T > 113 T HeapArray<T>::operator [] (int index) const 114 { 115 if( (0 <= index) && (index < length()) ) 116 { 117 return m_pointer[index]; // 优化这里,越界抛异常; 118 } 119 else 120 { 121 throw out_of_range("T HeapArray<T>::operator [] (int index) const"); 122 } 123 } 124 125 template 126 < typename T > 127 HeapArray<T>& HeapArray<T>::self() 128 { 129 return *this; 130 } 131 132 template 133 < typename T > 134 const HeapArray<T>& HeapArray<T>::self() const 135 { 136 return *this; 137 } 138 139 template 140 < typename T > 141 HeapArray<T>::~HeapArray() 142 { 143 delete[]m_pointer; 144 } 145 146 #endif
3,使用:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include "Array.h" 4 #include "HeapArray.h" 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void TestArray() 9 { 10 Array<int, 5> a; 11 12 for(int i=0; i<a.length(); i++) 13 { 14 a[i] = i; // 如果访问越界,则编译器显示: terminate called after throwing an instance of 'std::out_of_range' what(): T& Array<T, N>::operator[] (int index);已放弃 15 } 16 17 for(int i=0; i<a.length(); i++) 18 { 19 cout << a[i] << endl; 20 } 21 } 22 23 void TestHeapArray() 24 { 25 HeapArray<double>* pa = HeapArray<double>::NewInstance(5); 26 27 if( pa != NULL ) 28 { 29 HeapArray<double>& array = pa->self(); 30 31 for(int i=0; i<array.length(); i++) 32 { 33 array[i] = i; 34 } 35 36 for(int i=0; i<array.length(); i++) 37 { 38 cout << array[i] << endl; 39 } 40 } 41 42 delete pa; 43 } 44 45 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 46 { 47 48 try 49 { 50 TestArray(); 51 52 cout << endl; 53 54 TestHeapArray(); 55 } 56 catch(...) 57 { 58 cout << "Exception" << endl; 59 } 60 61 return 0; 62 }
1,在以后开发需要使用标准库的时候,要有当前开发所使用的函数或类会不会出现异常这个意识,这个时候需要查标准库的文档,看看每个函数的说明,每个类的说明;
10,小结:
1,catch 语句块中可以抛出异常;
2,异常的类型可以是自定义类类型;
3,赋值兼容性原则在异常匹配中依然适用;
4,标准库中的异常都是从 exception 类派生的;