1,什么是循环链表:
1,概念上:
1,任意数据元素都有一个前驱和一个后继;
2,所有的数据元素的关系构成一个逻辑上的环;
2,实际上:
1,循环链表是一种特殊的单链表;
2,尾结点的指针域保存了首结点(不是头结点)的地址;
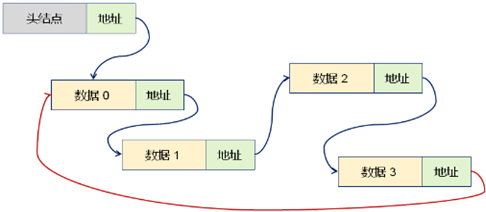
2,循环链表逻辑构成:
3,循环链表继承层次结构:
4,循环链表实现思路:
1,通过模板定义 CircleList 类,继承自 LinkList 类;
2,定义内部函数 last_to_first(),用于将单链表首尾相连;
3,特殊处理:首元素的插入操作和删除操作;
4,重新实现:清空操作和遍历操作;
5,循环链表实现要点:
1,插入位置为 0 时:
1,头结点和尾结点均指向新结点;
2,新结点成为首结点插入链表;
2,删除位置为 0 时:
1,头结点和尾结点指向位置为 1 的结点;
2,安全销毁首结点;
3,删除首结点;
6,CircleList 循环链表的实现:
1 #ifndef CIRCLELIST_H 2 #define CIRCLELIST_H 3 4 #include "LinkList.h" 5 6 namespace DTLib 7 { 8 9 template <typename T> 10 class CircleList : public LinkList<T> 11 { 12 protected: 13 typedef typename LinkList<T>::Node Node; 14 15 Node* last() const // O(n),获得自信最后结点的指针; 16 { 17 return this->position(this->m_length - 1)->next; 18 } 19 20 void last_to_first() const // O(n),将链表首尾相连; 21 { 22 last()->next = this->m_header.next; 23 } 24 25 int mod(int i) const // O(1),归一化 i; 26 { 27 return (this->m_length == 0)? 0 : (i % this->m_length); 28 } 29 30 public: // 这里都是父类的属性,所以不用构造; 31 bool insert(const T& e) // O(n) 32 { 33 return insert(this->m_length, e); // 这里是可以插入到原来最后一个节点后面的,所以是为 this->m_length; 34 } 35 36 bool insert(int i, const T& e) // O(n),注意删除位置为 0 的操作; 37 { 38 bool ret = true; 39 i = i % (this->m_length + 1); // 这里是插入共 m_length + 1 个数字,归一化 i 的值,特意加 1,为了让最后的 m_length 位置不是在 0 位置处,这样才可以利用单链表; 40 ret = LinkList<T>::insert(i, e); // 取余是为了用父类实现子类;O(n) 41 42 if(ret && (i == 0)) // 首尾相连; 43 { 44 last_to_first(); // O(n) 45 } 46 47 return ret; 48 } 49 50 bool remove(int i) // 删除第 i 个节点 O(n),要注意删除位置为 0 的操作 51 { 52 bool ret = true; 53 i = mod(i); 54 55 if( i == 0 ) // 为了应对首尾相连的情况 56 { 57 Node* toDel = this->m_header.next; 58 59 if( toDel != NULL ) // 为了应对原生链表节点数为 0 的情况 60 { 61 this->m_header.next = toDel->next; // 要连接到第二个节点上 62 this->m_length--; 63 64 if( this->m_length > 0 ) // 为了应对原生链表节点数大于 1 的情况 65 { 66 last_to_first(); // O(n) 67 68 if (this->m_current == toDel ) // 使得当前节点不再指向被删除的节点 69 { 70 this->m_current = this->m_current->next; 71 } 72 } 73 else 74 { 75 this->m_header.next = NULL; 76 this->m_current = NULL; 77 } 78 } 79 else 80 { 81 ret = false; // 删除节点为零的链表将产生错误 82 } 83 84 this->destroy(toDel); // 异常安全 85 } 86 else 87 { 88 LinkList<T>::remove(i); // 删除非 0 节点按照顺序表删除 o(n) 89 } 90 91 return ret; 92 } 93 94 bool set(int i, const T& e) // O(n) 95 { 96 return LinkList<T>::set(mod(i), e); 97 } 98 99 T get(int i) const // O(n) 100 { 101 return LinkList<T>::get(mod(i)); 102 } 103 104 T get(int i, const T& e) const // O(n) 105 { 106 return LinkList<T>::get(mod(i), e); 107 } 108 109 int find(const T& e) const // O(n) 110 { 111 int ret = -1; 112 /* 113 last()->next = NULL; 114 ret = LinkList<T>::find(e); // 如果 find() 中比较操作符在类中抛出异常,这里又没有 try() catch(),则会造成链表属性改变; 115 last_to_first(); 116 */ 117 Node* slider = this->m_header.next; 118 119 for(int i=0; i<this->m_length; i++) // O(n),遍历所有的结点; 120 { 121 if( slider->value == e ) // 相等操作抛出异常时,链表状态不会改变; 122 { 123 ret = i; 124 break; 125 } 126 127 slider = slider->next; 128 } 129 130 return ret; 131 } 132 133 void clear() // O(n) 134 { 135 while( this->m_length > 1 ) // O(n) 136 { 137 remove(1); // O(1),这里没有调用 remove(0) 是因为避免大量移动指针,提高效率; 138 } 139 140 if( this->m_length == 1 ) // O(1) 141 { 142 Node* toDel = this->m_header.next; 143 this->m_header.next = NULL; 144 this->m_current = NULL; 145 this->m_length = 0; 146 147 this->destroy( toDel ); 148 } 149 } 150 151 bool move(int i, int step) // O(n) 152 { 153 return LinkList<T>::move(i, step); // O(n) 154 } 155 156 bool end() // O(1) 157 { 158 return ((this->m_length == 0) || (this->m_current == NULL)); 159 } 160 161 ~CircleList() // O(n) 162 { 163 clear(); 164 } 165 }; 166 167 } 168 169 #endif // CIRCLELIST_H
7,约瑟夫环测试 CircleLisnt:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "CircleList.h" 3 4 using namespace std; 5 using namespace DTLib; 6 7 void josephus(int n, int s, int m) 8 { 9 CircleList<int> c1; 10 11 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) 12 { 13 c1.insert(i); // 这里插入的位置是 i - 1,值是 i; 14 } 15 16 c1.move(s-1, m-1);// 链表是从 0 开始的,所以为 s - 1; 移动 m - 1步,就到 m 了; 17 18 while(c1.length() > 0) 19 { 20 c1.next(); // 每次移动 m - 1 步; 21 cout << c1.current() << endl; // 显示的最后两个人则可以活 22 23 c1.remove(c1.find(c1.current())); // 自杀了后从环中移除; 24 } 25 } 26 27 int main() 28 { 29 josephus(41, 1, 3); 30 31 return 0; 32 }
8,有可能用 CircleList 代替 LinkList 工作,所以 LinkList 中的成员函数都要变成虚函数才可以,已经在“线性表的链式存储结构——单链表的实现”中的4 中实现;
9,循环链表的应用:
1,约瑟夫环问题:
10,小结:
1,循环链表是一种特殊的单链表;
2,尾结点的指针域保存了首结点的地址;
3,特殊处理首元素的插入操作和删除操作;
4,重新实现清空操作和遍历操作;