| 项目 |
内容 |
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 |
课程链接 |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 |
作业要求链接 |
| 学号-姓名 |
17041512-戴利斌 |
| 作业学习目标 |
1.掌握Linux系统环境C语言编程概念。2.学习Linux系统进程概念。 |
实验内容
1.请举例说明静态链接库的创建与使用。
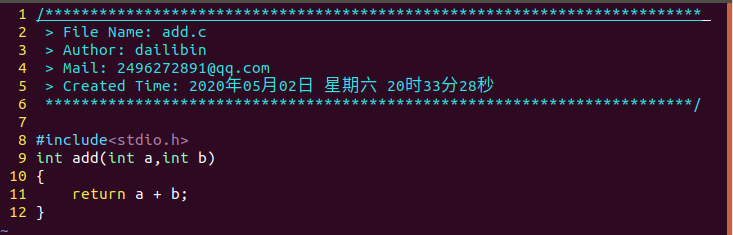
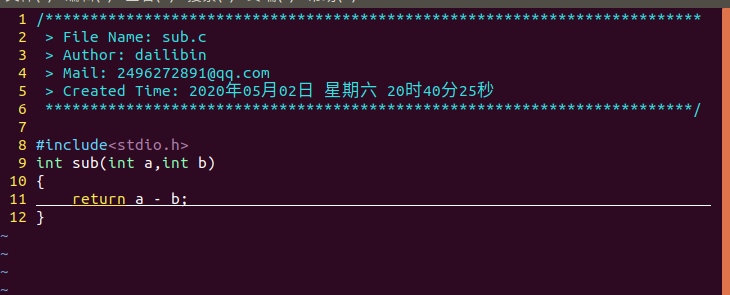

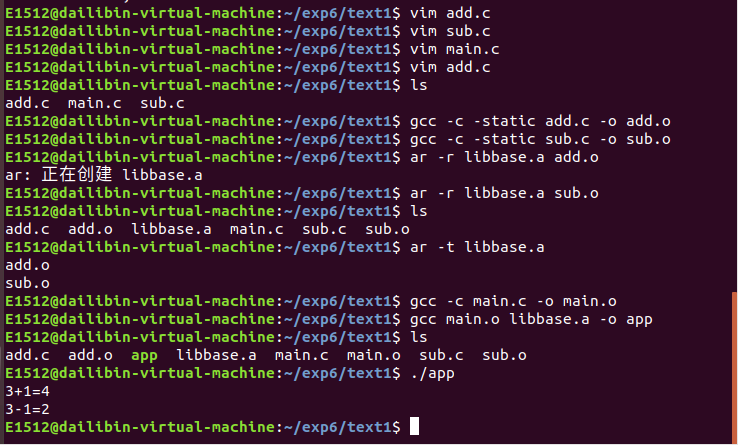
创建静态库及使用步骤:
1.vim add.c /vim sub.c /vim main.c ;创建.c文件
2.gcc -c static add.c -o add.o ;将.c生成.o 文件
3.ar -r lib库名.a add.o ;使用ar工具制作静态库
4.gcc main.o libbase.a -o app ;编译静态库到可执行文件中
5../app ;执行app文件
2.请举例说明共享库的创建与使用。
初始目录

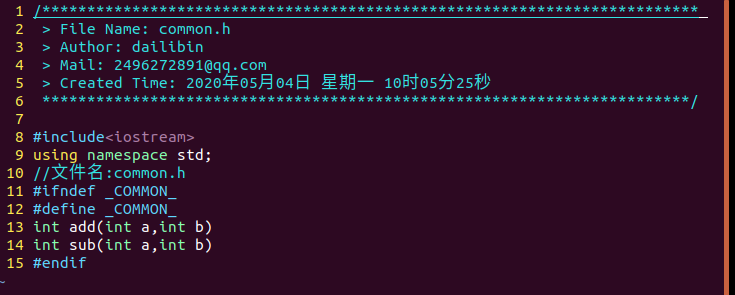
进入src目录,在lib目录下生成libbase.so文件,即创建共享库
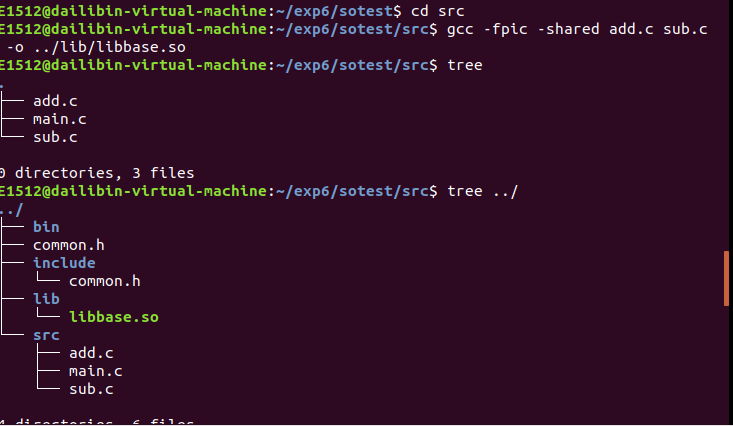
使用自己的共享库
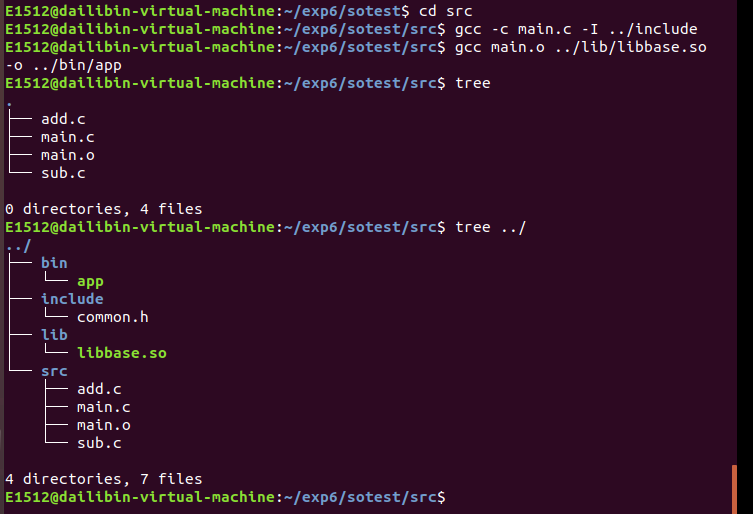
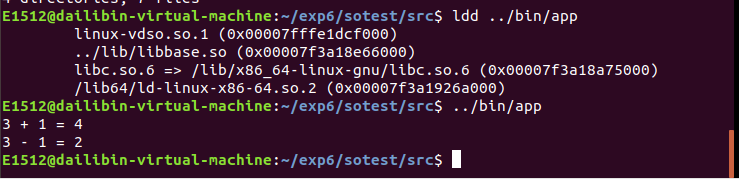
方法一:指定一个相对路径
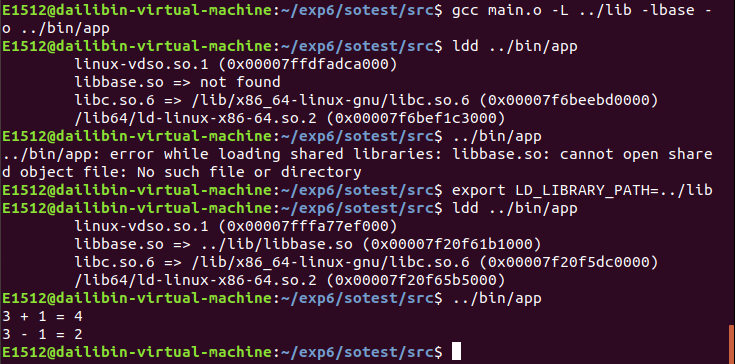
方法二:告诉链接器动态库的名字,添加一个环境变量LD_LIBRARY_PATH=../lib 。 /lib是libbase.so所在路径
3.编程实现一个简单文件复制命令。
i/o文化复制命令代码:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define BUFFERSIZE 4096
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc != 3) {
printf("usage:
mycp src dst
");
return 1;
}
int srcfd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (srcfd == -1) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
int dstfd = open(argv[2], O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0666);
if (dstfd == -1) {
close(srcfd);
perror("open");
return 1;
}
int len = 0;
char buffer[BUFFERSIZE] = {0};
while((len = read(srcfd, buffer, BUFFERSIZE)) > 0) {
if (write(dstfd, buffer, len) != len) {
perror("write error");
return 1;
}
}
if (len < 0) {
perror("read error");
return 1;
}
close(srcfd); // 关闭文件
close(dstfd);
return 0;
}
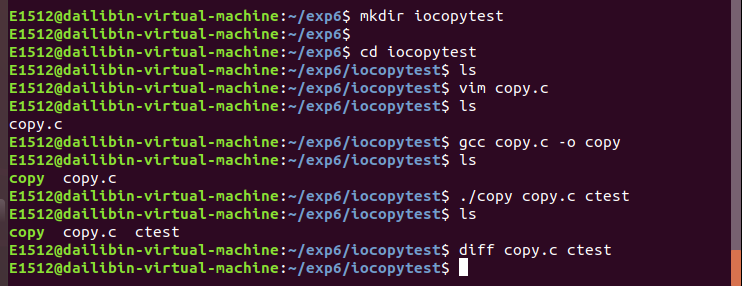
逐行比较copy.c与ctest.c的异同


4.使用 fork 创建一个子进程,进程创建成功后父子进程分别输出不同的内容。
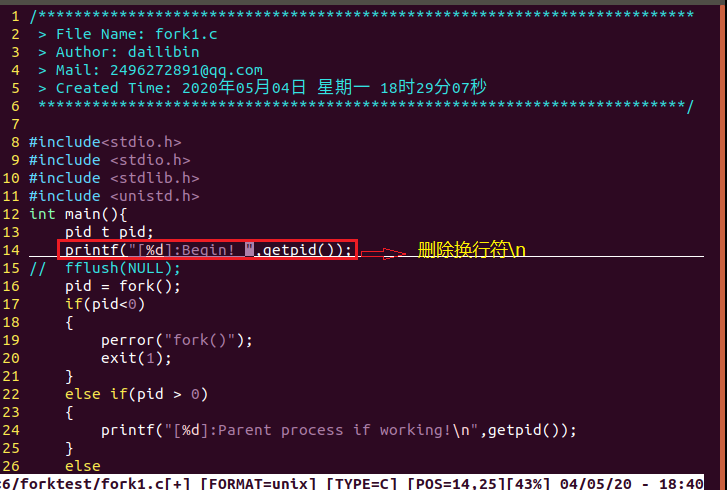
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
pid_t pid;
printf("[%d]:Begin!
",getpid());
fflush(NULL);
pid = fork();
if(pid<0)
{
perror("fork()");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
printf("[%d]:Parent process if working!
",getpid());
}
else
{
printf("[%d]:Child process if working!
",getpid());
}
printf("[%d]:Finish!
",getpid());
return 0;
}
fork函数简介
(1)依赖的头文件 #include <unistd.h>
(2)fork的原理和概念:
fork子进程就是从父进程拷贝一个新的进程出来,子进程和父进程的进程ID不同,但用户数据一样。
(3)父进程和子进程
执行fork函数后有3中情况:
>0 : 本体(调用 fork 的那个进程),这个值,是分身(子进程)的 id 号。
=0:分身(子进程)
=−1:分身失败

全缓冲:
全缓冲指的是系统在填满标准IO缓冲区之后才进行实际的IO操作;
注意,对于驻留在磁盘上的文件来说通常是由标准IO库实施全缓冲。
行缓冲:
在这种情况下,标准IO在输入和输出中遇到换行符时执行IO操作;
注意,当流涉及终端的时候,通常使用的是行缓冲。
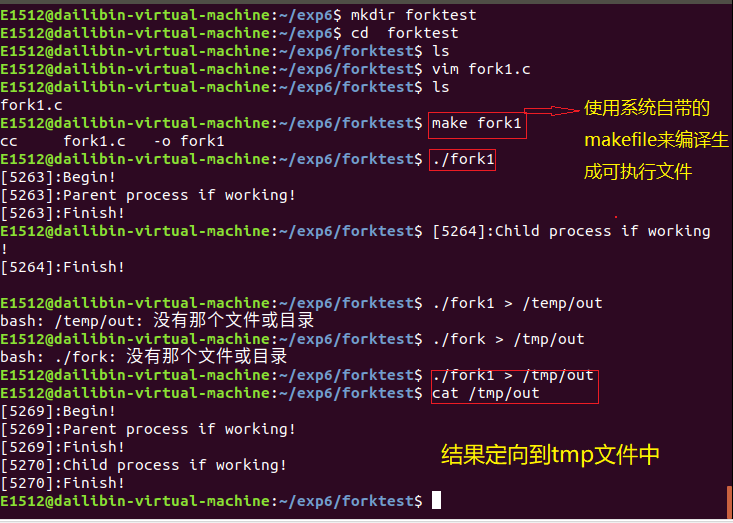
./fork1即结果直接输出在屏幕上,出现了一个Begin,而将结果定向到tmp 文件Begin出现了两次?
解:原因在于 printf 这个函数,它是带缓冲区的!
1.结果没有定向到tem文件时,printf 接收到字符串后,首先把字符串复制到一个 char 数组(缓冲区)里,当这个数组遇到了特定的字符,比如 ‘
’ 字符,回车或者装满等等,就会立即把字符写到屏幕终端上。
2.结果定向到tmp文件时,printf 函数遇到 ‘
’ 字符,并不会立即把字符写到文件里,printf 里的缓冲区数据还没来得及被刷新到 tmp 文件里,就被 fork 函数复制了,同时,printf 的缓冲区也被复制了一模一样的一份出来。



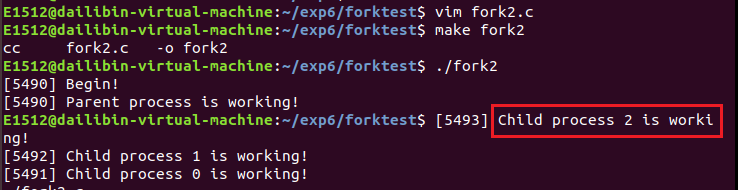
5. 使用fork创建多个子进程。
int i;
pid_t pid;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
pid = fork();
上面代码段会产生多少子进程?
答:2^3-1=7 ;产生7个子进程
代码:
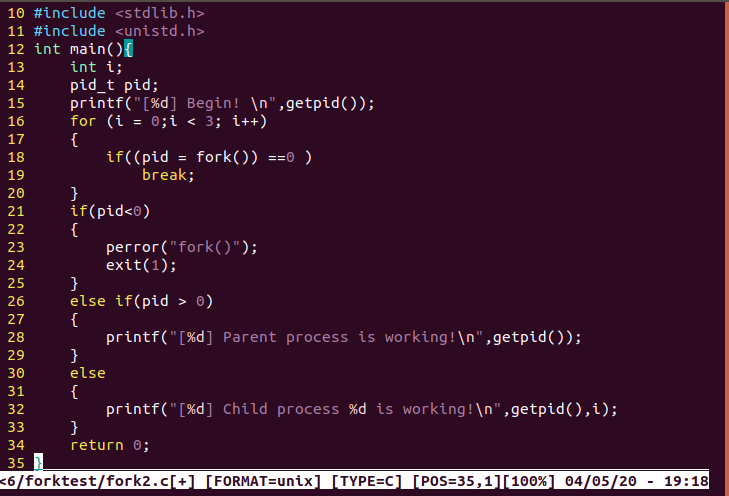
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
int i;
pid_t pid;
printf("[%d] Begin!
",getpid());
for (i = 0;i < 3; i++)
{
if((pid = fork()) ==0 )
break;
}
if(pid<0)
{
perror("fork()");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
printf("[%d] Parent process is working!
",getpid());
}
else
{
printf("[%d] Child process %d is working!
",getpid(),i);
}
return 0;
}
编译生成.o文件
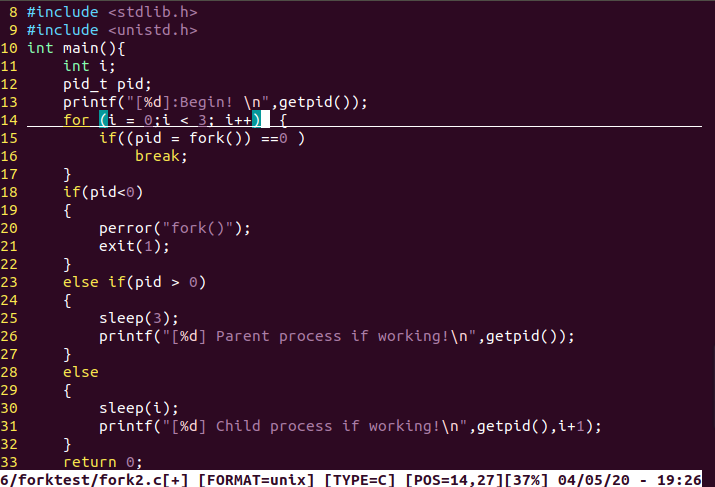
使用sleep函数简单控制进程输出顺序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
int i;
pid_t pid;
printf("[%d]:Begin!
",getpid());
for (i = 0;i < 3; i++)
{
if((pid = fork()) ==0 )
break;
}
if(pid<0)
{
perror("fork()");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
sleep(3);
printf("[%d] Parent process if working!
",getpid());
}
else
{
sleep(i);
printf("[%d] Child process if working!
",getpid(),i+1);
}
return 0;
}

6.在 fork 之前以写的方式创建了一个文件 test.txt。然后 fork 出的子进程立即向文件中写入“world”,然后睡眠5秒。而父进程在 fork 后睡眠3秒后向 test.txt 写入 "hello",并关闭描述符。子进程恢复后,又向 test.txt 文件中写入 "lalala"后关闭描述符,结束。
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int fd = open("test.txt",O_WRONLY | O_CREAT,0664);
if (fd == -1){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
printf("I'm father
");
printf("before fork
");
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid > 0){
sleep(3);
printf("I'm father; I'm writing test.txt...
");
write(fd, "hello", 5);
close(fd);
}
else if (pid ==0){
printf("I'm child; I'm writing test.txt...
");
write(fd, "world", 5);
sleep(5);
write(fd, "lalala", 6);
close(fd);
}
else {
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
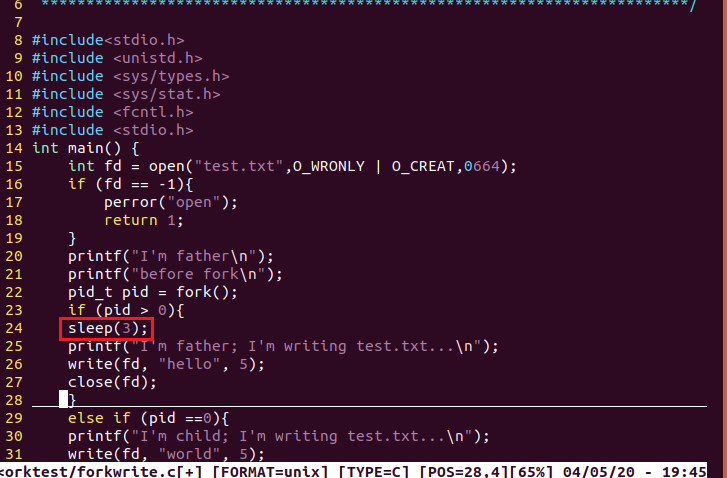
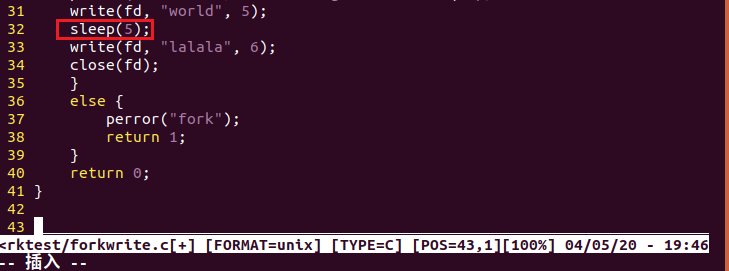
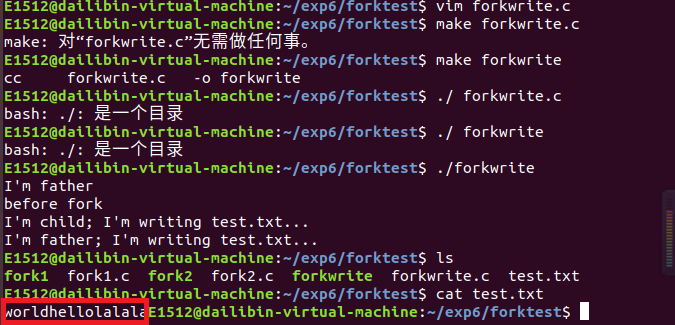
编译forkwrite.c生成.o文件并且运行生成的文件
7.分别在主函数中使用execvp 启动 ls 命令以及使用 fork 函数产生子进程调用 execvp 启动 ls 。
使用execvp启动ls命令代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
char* argv[] = {"ls","-l",NULL};
if (execvp("ls",argv) == -1){
perror("exec");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}

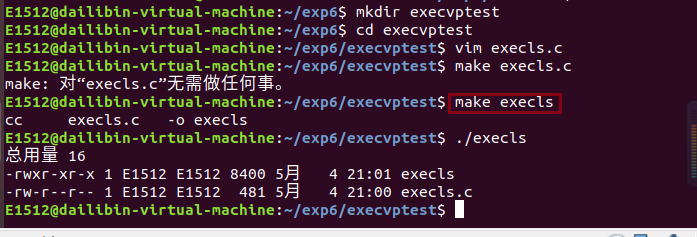
编译execls.c并且运行生成的文件
使用 fork 函数产生子进程调用 execvp 启动 ls :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
char* argv[] = {"ls","-l",NULL};
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid > 0){
printf("I'm father
");
}
else if (pid == 0) {
printf("I'm child
");
if (execvp("ls",argv) == -1){
perror ("exec");
return 1;
}
}
else {
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
编译forkandexec.c并且运行生成的文件


8.创建5个僵尸进程,并在终端通过 ps axf 命令查看僵尸进程信息。
代码:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
printf("before fork
");
pid_t pid, n = 5;
while(n--) {
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0)
break;
else if (pid < 0){
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
}
if (pid == 0) {
printf("hello, I'm child %d; my father is %d
", getpid(),getppid());
//getpid() 获取当前进程的pid
//getppid() 获取当前进程的父进程的pid
return 0;
}
while(1) {
sleep(3);
printf("hello, I'm father %d
", getpid());
}
return 0;
}
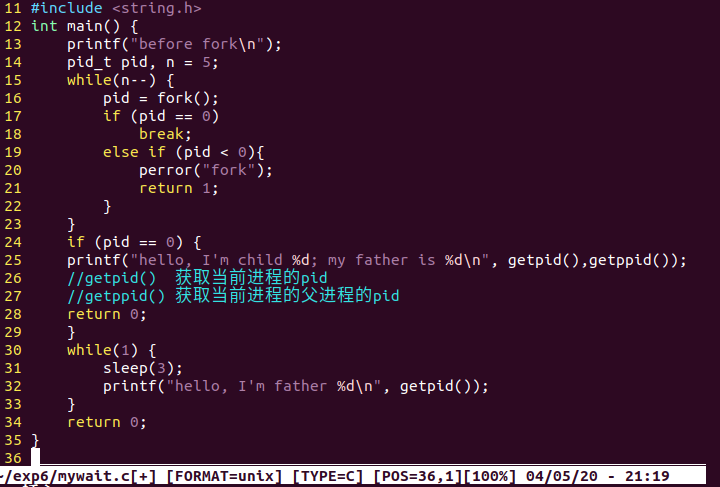
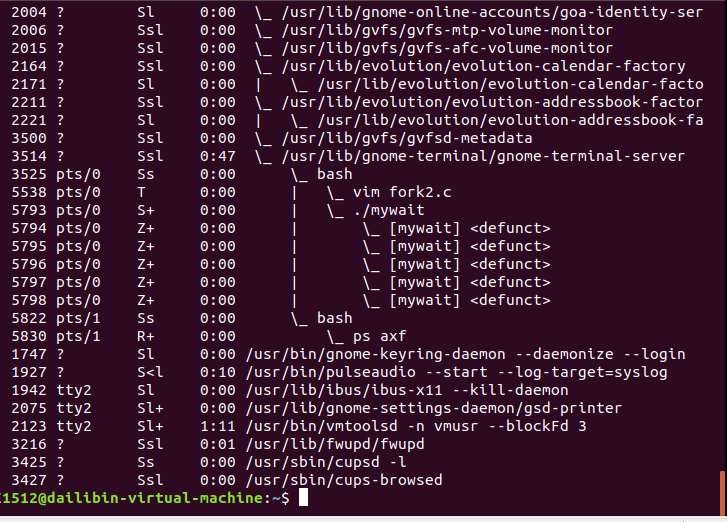
9.通过 wait 来清理僵尸进程。
代码:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main() {
printf("before fork
");
pid_t pid, n = 5;
while(n--) {
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0)
break;
else if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
}
if (pid == 0) {
printf("hello, I'm child %d;my father is %d
",getpid(),getppid());
return 0;
}
while(1) {
sleep(3);
pid = wait(NULL);
if (pid == -1) {
perror("wait");
sleep(10);
printf("I'm father %d;I have wiped out all zombies
",getpid());
return 1;
}
printf("Hello, I'm father %d; child %d exit
",getpid(),pid);
}
return 0;
}
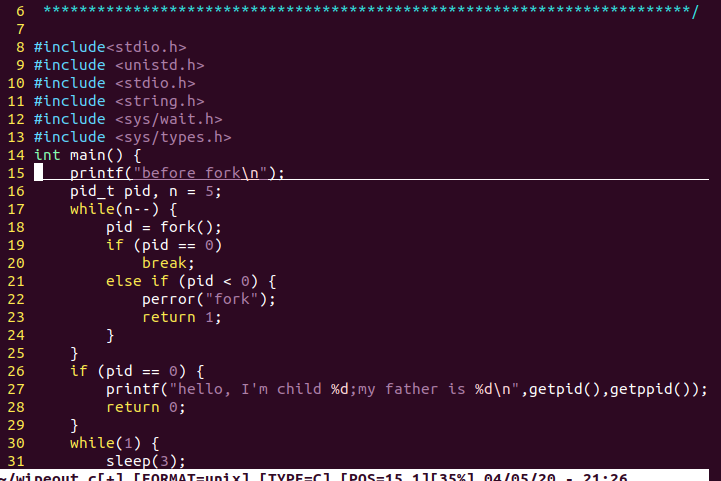
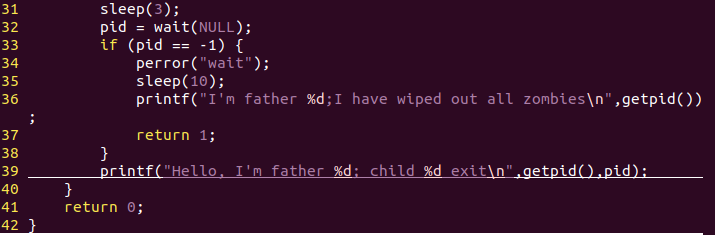
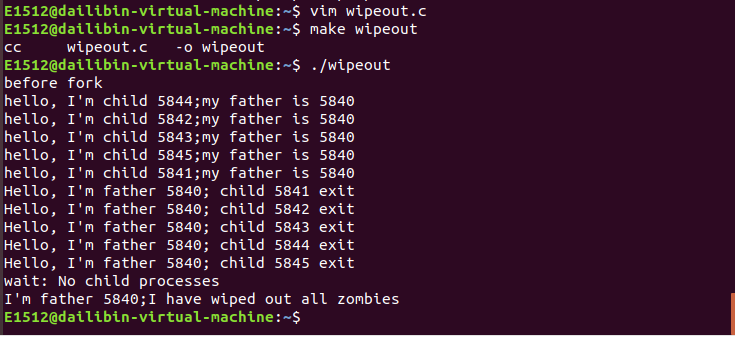
创建文件wipeout并编译运行生成的文件
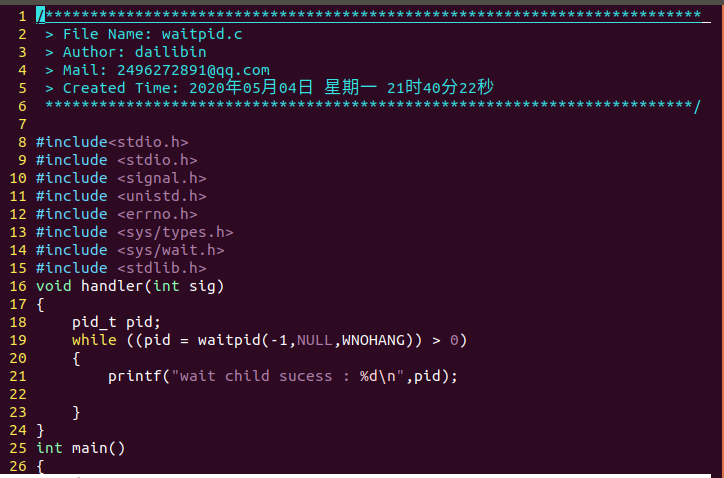
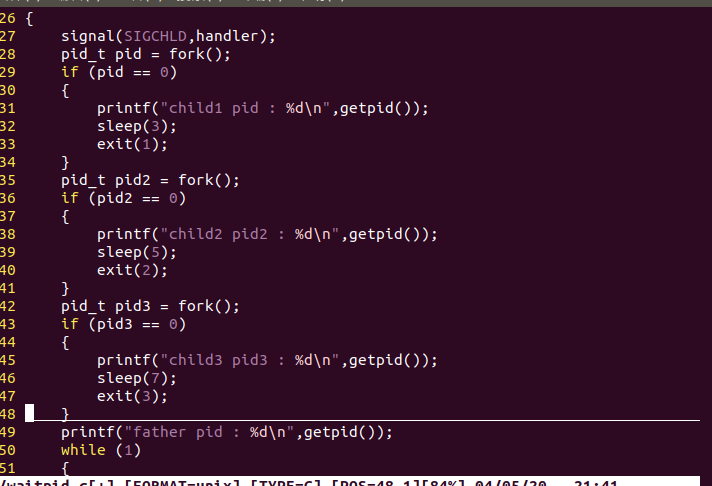
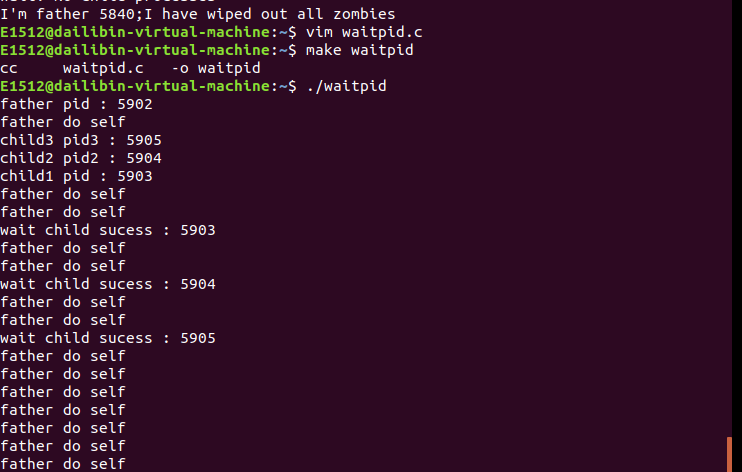
10.父进程通过 waitpid 函数等待特定子进程结束,若该子进程不结束,父进程一直阻塞。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void handler(int sig)
{
pid_t pid;
while ((pid = waitpid(-1,NULL,WNOHANG)) > 0)
{
printf("wait child sucess : %d
",pid);
}
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGCHLD,handler);
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0)
{
printf("child1 pid : %d
",getpid());
sleep(3);
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid2 = fork();
if (pid2 == 0)
{
printf("child2 pid2 : %d
",getpid());
sleep(5);
exit(2);
}
pid_t pid3 = fork();
if (pid3 == 0)
{
printf("child3 pid3 : %d
",getpid());
sleep(7);
exit(3);
}
printf("father pid : %d
",getpid());
while (1)
{
printf("father do self
");
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}