实验八.进程间通信
| 项目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 2020春季Linux系统与应用(南昌航空大学 - 信息工程学院) |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | 作业链接,点这里啦! |
| 学号-姓名 | 17041512-戴利斌 |
| 作业学习目标 | 1、了解进程间通信的常用方式; 2、掌握管道、消息队列、信号量、共享内存实现进程间通信的方法。 |
1.举例说明使用匿名管道进行进程通信。
匿名管道:
当进程使用 pipe 函数,就可以打开位于内核中的这个特殊“文件”。同时 pipe 函数会返回两个描述 符,一个用于读,一个用于写。如果你使用 fstat 函数来测试该描述符,可以发现此文件类型为 FIFO 。而无名管道的无名,指的就是这个虚幻的“文件”,它没有名字
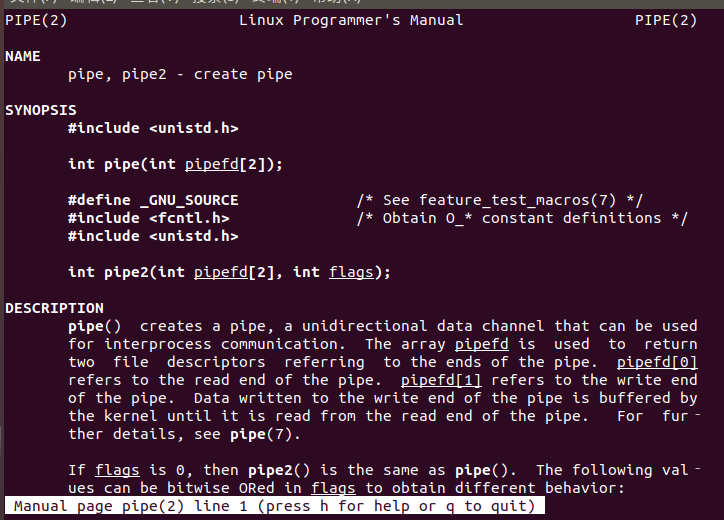
pipe 函数打开的文件描述符是通过参数(数组)传递出来的,而返回值表示打开成功(0)或失败 (-1)。 它的参数是一个大小为 2 的数组。此数组的第 0 个元素用来接收以读的方式打开的描述符,而第 1 个元 素用来接收以写的方式打开的描述符。也就是说, pipefd[0] 是用于读的,而 pipefd[1] 是用于写 的。 打开了文件描述符后,就可以使用 read(pipefd[0]) 和 write(pipefd[1]) 来读写数据了。
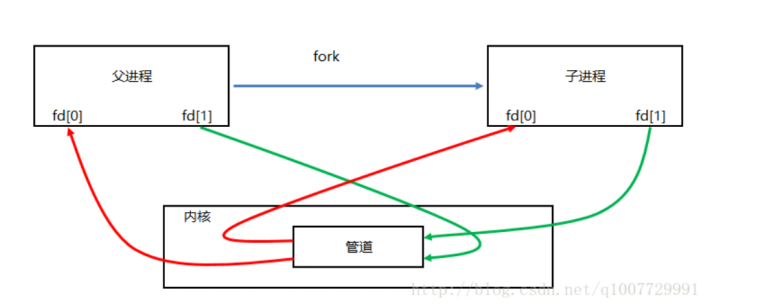
注意事项 :这两个分别用于读写的描述符必须同时打开才行,否则会出问题。
如果关闭读 ( close(pipefd[0]) ) 端保留写端,继续向写端 ( pipefd[1] ) 端写数据( write 函数)的进程会收到 SIGPIPE 信号。
如果关闭写 ( close(pipefd[1]) ) 端保留读端,继续向读端 ( pipefd[0] ) 端读数据( read 函数),read 函数会返回 0.
例题:父进程 fork 出一个子进程,通过无名管道向子进程发送字符,子进程收到数据后将字符串中的 小写字符转换成大写并输出。
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void child(int *fd) {
close(fd[1]); // 子进程关闭写端
char buf[64];
int n = 0,i;
while(1) {
n = read(fd[0], buf, 64);//如果没有数据可读,read会阻塞;如果父进程退出, read 返回 0.
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
putchar(toupper(buf[i]));
if (*buf == 'q') {
close(fd[0]);
exit(0);
}
if (n == 0) {
puts("no data to read!");
sleep(1);
}
}
exit(0);
}
int main() {
int fd[2];//作为传出参数
int n = 0;
char buf[64] = { 0 };
if (pipe(fd) < 0) {
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
child(fd);
}
close(fd[0]);// 父进程关闭读端
while (1) {
n = read(STDIN_FILENO, buf, 64);
write(fd[1], buf, n);
if (*buf == 'q') {
close(fd[1]);
exit(0);
}
}
return 0;
}
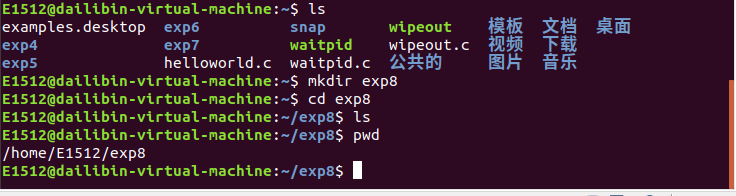
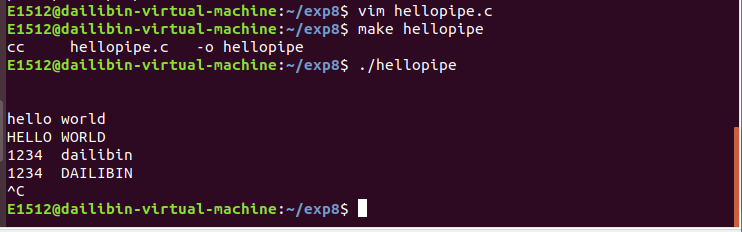
2.举例说明使用 mkfifo 命令创建命名管道以及简单演示管道如何工作。
命名管道
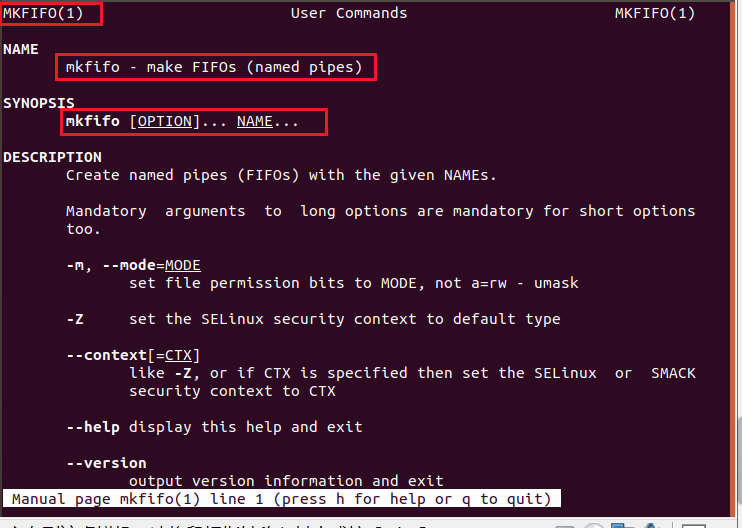
1.通过命令 mkfifo 创建管道
man mkfifo
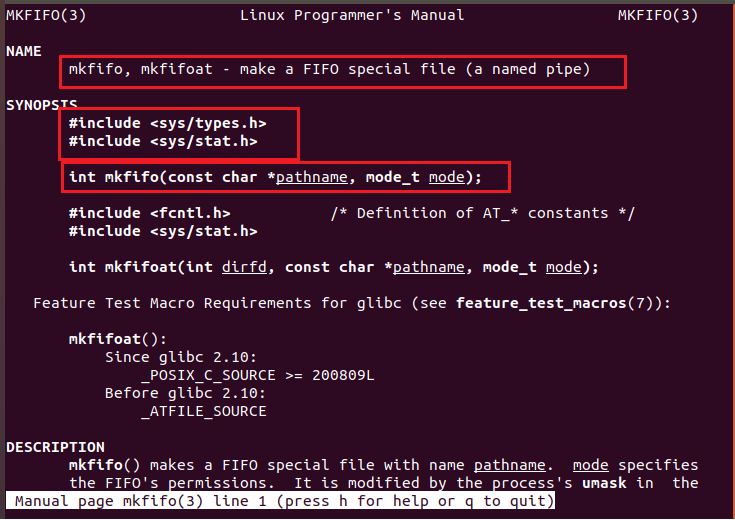
2.通过函数 mkfifo(3) 创建管道
man 3 mkfifo
FIFO文件的特性
a) 查看文件属性
当使用 mkfifo 创建 hello 文件后,查看文件信息如下:

某些版本的系统在 hello 文件后面还会跟着个 | 符号,像这样 hello|
b) 使用 cat 命令打印 hello 文件内容

可以看到cat已经被堵塞了。开启另一个终端,执行

然后你会看到被阻塞的 cat 又继续执行完毕,在屏幕打印 “hello world” 。
如果你反过来执行上面两个命令,会发现先执行的那个总是被阻塞。

c) fifo 文件特性
根据前面两个实验,可以总结:
(1)文件属性前面标注的文件类型是 p ,代表管道
(2)文件大小是 0
(3)fifo 文件需要有读写两端,否则在打开 fifo 文件时会阻塞
如果在 open 的时候,使用了非阻塞方式,肯定是不会阻塞的。
特别地,如果以非阻塞写的方式 open ,同时没有进程为该文件以读的方式打开,会导致 open 返回错误(-1),同时 errno 设置成ENXIO.
3.编写两个程序使用第2题中创建的管道进行通信。
例题:编写两个程序,分别是发送端 pipe_send 和接收端面 pipe_recv 。程序 pipe_send 从标准 输入接收字符,并发送到程序 pipe_recv ,同时 pipe_recv 将接收到的字符打印到屏幕。
// pipe_send.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char buf[64];
int n = 0;
int fd = open("hello", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open fifo");
return -1;
}
puts("has opend fifo");
while((n = read(STDIN_FILENO, buf, 64)) > 0) {
write(fd, buf, n);
if (buf[0] == 'q')
break;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
// pipe_recv.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char buf[64];
int n = 0;
int fd = open("hello", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open fifo");
return -1;
}
puts("has opened fifo");
while((n = read(fd, buf, 64)) > 0) {
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n);
}
if (n == 0) {
puts("remote closed");
}
else {
perror("read fifo");
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}

分别开启两个终端,分别运行pipe_send和pipe_recv:
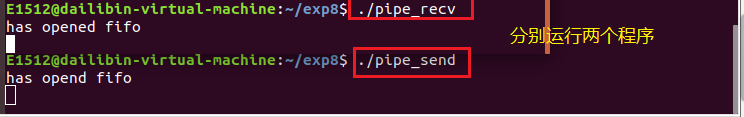
现在两个终端都处于阻塞状态,在运行pipe_send的终端输入数据,然后就可以在运行的pipe_recv的终端看到相应的输出:
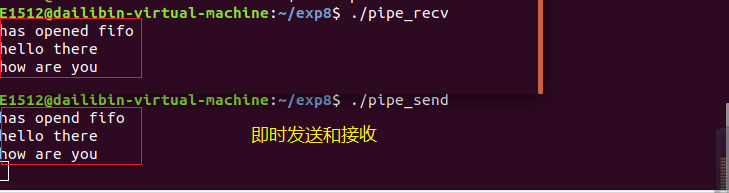
使用组合按键结束上述进程。
4.编写两个程序分别通过指定的键值创建 IPC 内核对象,以及获取该指定键值的 IPC 内核对象。
IPC 内核对象
每个 IPC 内核对象都是位于内核空间中的一个结构体。具体的对于共享内存、消息队列和信号量,他们在内核空间中都有对应的结构体来描述。
当你使用 get 后缀创建内核对象时,内核中就会为它开辟一块内存保存它。只要你不显式删除该内核对象,它就永远位于内核空间中,除非你关机重启。
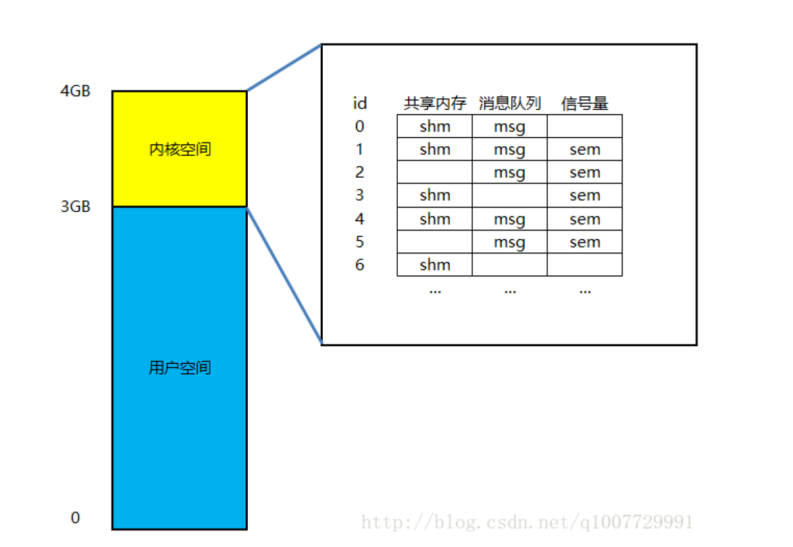
进程空间的高 1G 空间( 3GB-4GB )是内核空间,该空间中保存了所有的 IPC 内核对象。
上图给出不同的 IPC 内核对象在内存中的布局(以数组的方式),实际操作系统的实现并不一定是数组,也可能是链表或者其它数据结构等等。
每个内核对象都有自己的 id 号(数组的索引)。此 id 号可以被用户空间使用。所以只要用户空间知道了内核对象的 id 号,就可以操控内核对象了。
为了能够得到内核对象的 id 号,用户程序需要提供键值—— key ,它的类型是 key_t ( int 整型)。
系统调用函数( shmget , msgget 和 semget )根据 key ,就可以查找到你需要的内核 id号。
在内核创建完成后,就已经有一个唯一的 key 值和它绑定起来了,也就是说 key 和内核对象是一 一对应的关系。(key = 0为特殊的键,它不能用来查找内核对象)
创建 IPC 内核对象
man 2 shmget
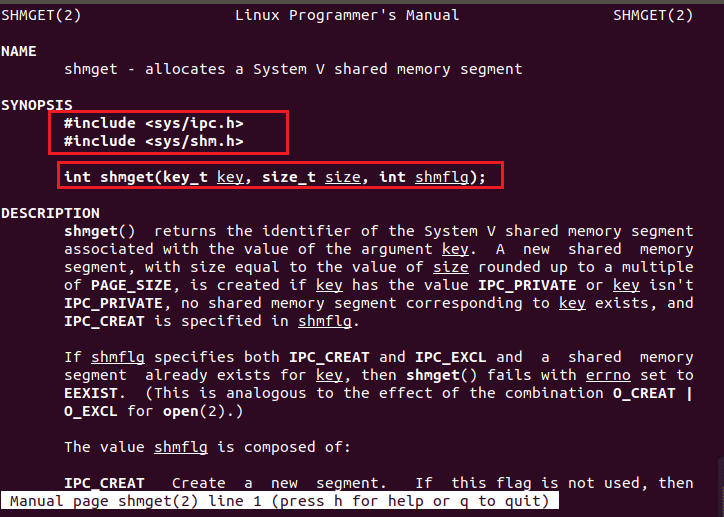
man 2 msgget

man 2 semget

在创建 IPC 内核对象时,用户程序一定需要提供 key 值才行。
实际上,创建 IPC 内核对象的函数和获取内核对象 id 的函数是一样的,都是使用 get 后缀函数。
比如在键值 0x8888 上创建 ipc 内核对象, 并获取其 id ,应该像下面这样:
// 在 0x8888 这个键上创建内核对象,权限为 0644,如果已经存在就返回错误。
int id = shmget(0x8888, 4096, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0644);
int id = msgget(0x8888, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0644);
int id = semget(0x8888, 1, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0644);
// 第二个参数表示创建几个信号量
例题:程序 ipccreate 用于在指定的键值上创建 ipc 内核对象。使用格式为 ./ipccreate ,比如 ./ipccreate 0 0x8888 表示在键值 0x8888 上创建共享内存。
// ipccreate.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 3) {
printf("%s <ipc type> <key>
", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
key_t key = strtoll(argv[2], NULL, 16);//key
char type = argv[1][0];//
char buf[64];
int id;
if (type == '0') {//创建共享内存
id = shmget(key, getpagesize(), IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0644);
strcpy(buf, "share memory");
}
else if (type == '1') {//创建消息队列
id = msgget(key, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0644);
strcpy(buf, "message queue");
}
else if (type == '2') {//创建信号量
id = semget(key, 5, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0644);
strcpy(buf, "semaphore");
}
else {
printf("type must be 0, 1, or 2
");
return -1;
}
if (id < 0) {
perror("get error");
return -1;
}
printf("create %s at 0x%x, id = %d
", buf, key, id);
return 0;
}

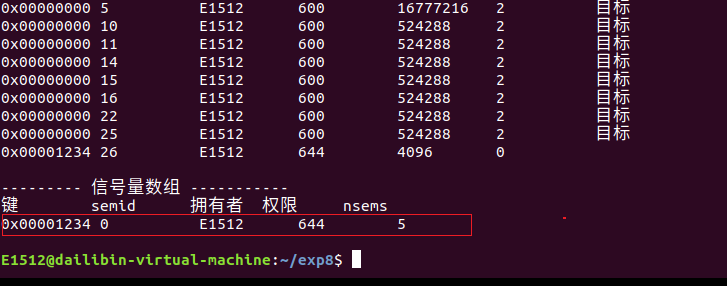
获取 ipc 内核对象
程序 ipcget 用于在指定的键值上获取 ipc 内核对象的 id 号。使用格式为 ./ipcget ,比如./ipcget 0 0x8888 表示获取键值 0x8888 上的共享内存 id 号。
// ipcget.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 3) {
printf("%s <ipc type> <key>
", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
key_t key = strtoll(argv[2], NULL, 16);
char type = argv[1][0];
char buf[64];
int id;
if (type == '0') {
id = shmget(key, 0, 0);
strcpy(buf, "share memory");
}
else if (type == '1') {
id = msgget(key, 0);
strcpy(buf, "message queue");
}
else if (type == '2') {
id = semget(key, 0, 0);
strcpy(buf, "semaphore");
}
else {
printf("type must be 0, 1, or 2
");
return -1;
}
if (id < 0) {
perror("get error");
return -1;
}
printf("get %s at 0x%x, id = %d
", buf, key, id);
return 0;
}

5.编写一个程序可以用来创建、删除内核对象,也可以挂接、卸载共享内存,还可以打印、设置内核对象信息。
共享内存
前面已经知道如何创建内核对象,接下来分别了解三种内核对象的操作:
man 2 shmop
man 2 shmctl
例题:编写一个程序 shmctl 可以用来创建、删除内核对象,也可以挂接、卸载共享内存,还可以打 印、设置内核对象信息。具体使用方法具体见下面的说明:
./shmctl -c : 创建内核对象。
./shmctl -d : 删除内核对象。
./shmctl -v : 显示内核对象信息。
./shmctl -s : 设置内核对象(将权限设置为 0600 )。
./shmctl -a : 挂接和卸载共享内存(挂接 5 秒后,再执行 shmdt ,然后退出)。
// shmctl.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define ASSERT(res) if((res)<0){perror(__FUNCTION__);exit(-1);}
// 打印 ipc_perm
void printPerm(struct ipc_perm *perm) {
printf("euid of owner = %d
", perm->uid);
printf("egid of owner = %d
", perm->gid);
printf("euid of creator = %d
", perm->cuid);
printf("egid of creator = %d
", perm->cgid);
printf("mode = 0%o
", perm->mode);
}
// 打印 ipc 内核对象信息
void printShmid(struct shmid_ds *shmid) {
printPerm(&shmid->shm_perm);
printf("segment size = %d
", shmid->shm_segsz);
printf("last attach time = %s", ctime(&shmid->shm_atime));
printf("last detach time = %s", ctime(&shmid->shm_dtime));
printf("last change time = %s", ctime(&shmid->shm_ctime));
printf("pid of creator = %d
", shmid->shm_cpid);
printf("pid of last shmat/shmdt = %d
", shmid->shm_lpid);
printf("No. of current attaches = %ld
", shmid->shm_nattch);
}
// 创建 ipc 内核对象
void create() {
int id = shmget(0x8888, 123, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0664);
printf("create %d
", id);
ASSERT(id);
}
// IPC_STAT 命令使用,用来获取 ipc 内核对象信息
void show() {
int id = shmget(0x8888, 0, 0);
ASSERT(id);
struct shmid_ds shmid;
ASSERT(shmctl(id, IPC_STAT, &shmid));
printShmid(&shmid);
}
// IPC_SET 命令使用,用来设置 ipc 内核对象信息
void set() {
int id = shmget(0x8888, 123, IPC_CREAT | 0664);
ASSERT(id);
struct shmid_ds shmid;
ASSERT(shmctl(id, IPC_STAT, &shmid));
shmid.shm_perm.mode = 0600;
ASSERT(shmctl(id, IPC_SET, &shmid));
printf("set %d
", id);
}
// IPC_RMID 命令使用,用来删除 ipc 内核对象
void rm() {
int id = shmget(0x8888, 123, IPC_CREAT | 0664);
ASSERT(id);
ASSERT(shmctl(id, IPC_RMID, NULL));
printf("remove %d
", id);
}
// 挂接和卸载
void at_dt() {
int id = shmget(0x8888, 123, IPC_CREAT | 0664);
ASSERT(id);
char *buf = shmat(id, NULL, 0);
if (buf == (char*)-1) ASSERT(-1);
printf("shmat %p
", buf);
sleep(5); // 等待 5 秒后,执行 shmdt
ASSERT(shmdt(buf));
printf("shmdt %p
", buf);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
printf("usage: %s <option -c -v -s -d -a>
", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
printf("I'm %d
", getpid());
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "-c")) {
create();
}
else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "-v")) {
show();
}
else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "-s")) {
set();
}
else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "-d")) {
rm();
}
else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "-a")) {
at_dt();
}
return 0;
}

先在另一个终端执行 ./shmctl -a ,然后在当前终端执行 ./shmctl -v
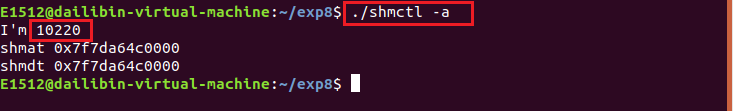
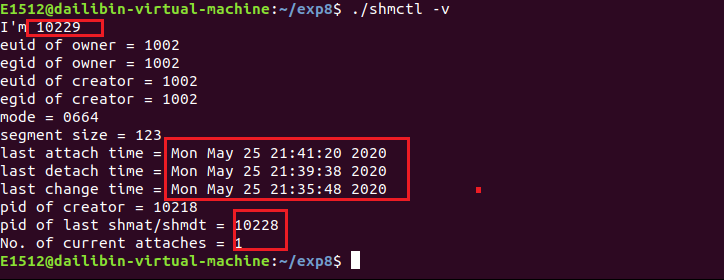
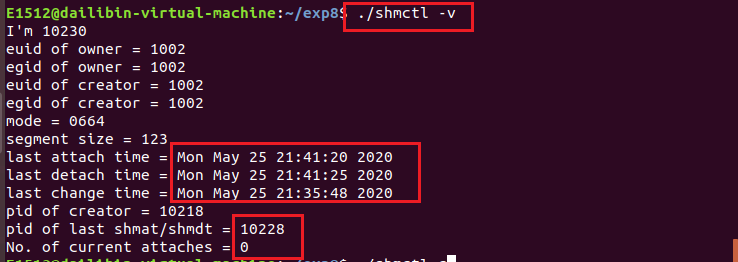
先在另一个终端执行 ./shmctl -a ,运行结束后,然后在当前终端执行 ./shmctl -v
6.编写两程序分别用于向消息队列发送数据和接收数据。 msg_send 程序定义了一个结构体 Msg ,消息正文部分是结构体 Person 。该程序向消息队列发送了 10 条消息。
消息队列
消息队列本质上是位于内核空间的链表,链表的每个节点都是一条消息。
每一条消息都有自己的消息类型,消息类型用整数来表示,
而且必须大于 0.每种类型的消息都被对应的链表所维护,
下图 展示了内核空间的一个消息队列:
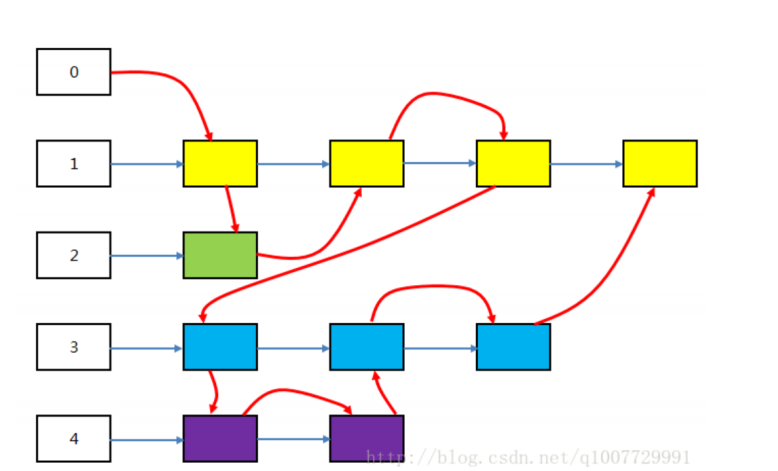
其中数字 1 表示类型为 1 的消息,数字2、3、4 类似。彩色块表示消息数据,它们被挂在对应类型的链表上。
值得注意的是,刚刚说过没有消息类型为 0 的消息,
实际上,消息类型为 0 的链表记录了所有消息加入队列的顺序,其中红色箭头表示消息加入的顺序。
消息队列相关的函数
man 2 msgop

消息数据格式
无论你是发送还是接收消息,消息的格式都必须按照规范来。简单的说,它一般长成下面这个样子:
struct Msg{
long type; // 消息类型。这个是必须的,而且值必须 > 0,这个值被系统使用
// 消息正文,多少字节随你而定
// ...
}
例题:程序 msg_send 和 msg_recv 分别用于向消息队列发送数据和接收数据。 msg_send 程序定义了 一个结构体 Msg ,消息正文部分是结构体 Person 。该程序向消息队列发送了 10 条消息。
// msg_send.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ASSERT(prompt,res) if((res)<0){perror(#prompt);exit(-1);}
typedef struct {
char name[20];
int age;
}Person;
typedef struct {
long type;
Person person;
}Msg;
int main(int argc, char *argv) {
int id = msgget(0x8888, IPC_CREAT | 0664);
ASSERT(msgget, id);
Msg msg[10] = {
{1, {"Luffy", 17}},
{1, {"Zoro", 19}},
{2, {"Nami", 18}},
{2, {"Usopo", 17}},
{1, {"Sanji", 19}},
{3, {"Chopper", 15}},
{4, {"Robin", 28}},
{4, {"Franky", 34}},
{5, {"Brook", 88}},
{6, {"Sunny", 2}}
};
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
int res = msgsnd(id, &msg[i], sizeof(Person), 0);
ASSERT(msgsnd, res);
}
return 0;
}
程序 msg_send 第一次运行完后,内核中的消息队列大概像下面这样:

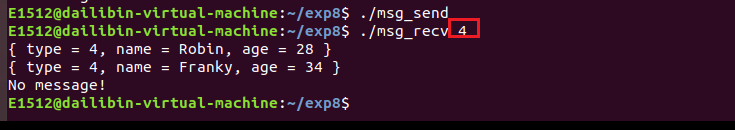
msg_recv 程序接收一个参数,表示接收哪种类型的消息。比如 ./msg_recv 4 表示接收类型为 4 的消息,并打印在屏幕。
// msg_recv.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define ASSERT(prompt,res) if((res)<0){perror(#prompt);exit(-1);}
typedef struct {
char name[20];
int age;
}Person;
typedef struct {
long type;
Person person;
}Msg;
void printMsg(Msg *msg) {
printf("{ type = %ld, name = %s, age = %d }
",
msg->type, msg->person.name, msg->person.age);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
printf("usage: %s <type>
", argv[0]); return -1; }
long type = atol(argv[1]);
int id = msgget(0x8888, 0);
ASSERT(msgget, id);
Msg msg;
int res;
while(1) {
res = msgrcv(id, &msg, sizeof(Person), type, IPC_NOWAIT);
if (res < 0) {
if (errno == ENOMSG) {
printf("No message!
");
break;
}
else {
ASSERT(msgrcv, res);
}
}
printMsg(&msg);
}
return 0;
}
先运行./msg_send,再运行./msg_recv
接收所有消息:

接收类型为 4 的消息,这时要重新运行 ./msg_send :
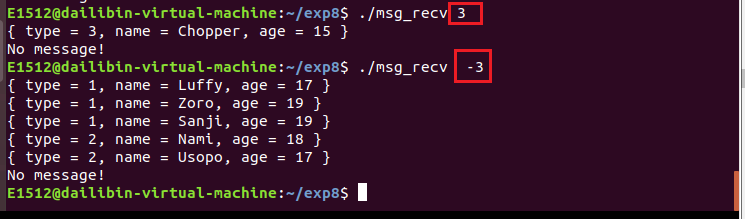
接收类型小于等于 3 的所有消息,这是不用再运行 ./msg_send :
还有一个函数来操作消息队列内核对象的
man 2 msgctl

7.编写程序举例说明信号量如何操作。
信号量
设置和获取信号量值的函数 semctl :
man 2 semctl
请求和释放信号量 semop
man 2 semop
struct sembuf {
unsigned short sem_num; /* semaphore number */
short sem_op; /* semaphore operation */
short sem_flg; /* operation flags */
}
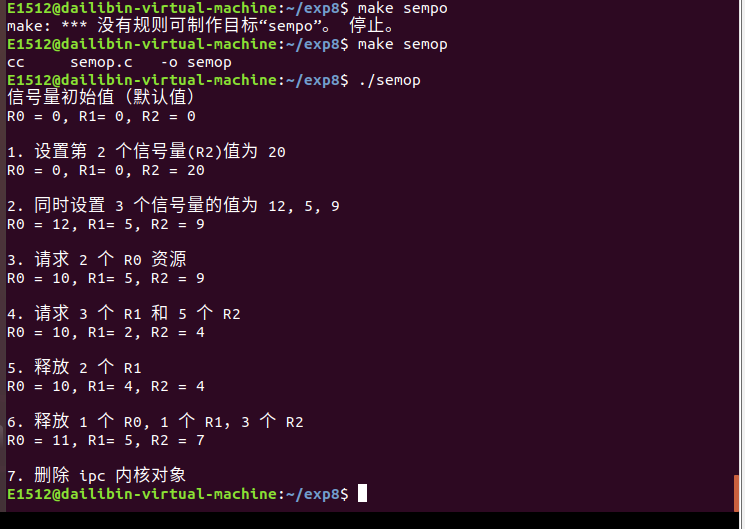
例题:信号量操作 示例
//semop.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define R0 0
#define R1 1
#define R2 2
void printSem(int id) {
unsigned short vals[3] = { 0 };
semctl(id, 3, GETALL, vals);
printf("R0 = %d, R1= %d, R2 = %d
", vals[0], vals[1], vals[2]);
}
int main() {
int id = semget(0x8888, 3, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0664);
// 打印信号量值
puts("信号量初始值(默认值)");
printSem(id);
// 1. 设置第 2 个信号量值
puts("1. 设置第 2 个信号量(R2)值为 20");
semctl(id, 2, SETVAL, 20);
printSem(id);
// 2. 同时设置 3 个信号量的值
puts("2. 同时设置 3 个信号量的值为 12, 5, 9");
unsigned short vals[3] = {12, 5, 9};
semctl(id, 0, SETALL, vals); printSem(id);
// 3. 请求 2 个 R0 资源
puts("3. 请求 2 个 R0 资源");
struct sembuf op1 = {0, -2, 0};
semop(id, &op1, 1);
printSem(id);
// 4. 请求 3 个 R1 和 5 个 R2
puts("4. 请求 3 个 R1 和 5 个 R2");
struct sembuf ops1[2] = { {1, -3, 0}, {2, -5, 0} };
semop(id, ops1, 2);
printSem(id);
// 5. 释放 2 个 R1
puts("5. 释放 2 个 R1");
struct sembuf op2 = {1, 2, 0};
semop(id, &op2, 1);
printSem(id);
// 6. 释放 1 个 R0, 1 个 R1,3 个 R2
puts("6. 释放 1 个 R0, 1 个 R1,3 个 R2");
struct sembuf ops2[3] = { {0, 1, 0}, {1, 1, 0}, {2, 3, 0} };
semop(id, ops2, 3);
printSem(id);
// 7. 删除 ipc 内核对象
puts("7. 删除 ipc 内核对象");
semctl(id, 0, IPC_RMID);
return 0;
}
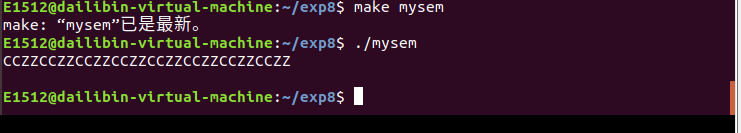
8.编写程序使用信号量实现父子进程之间的同步,防止父子进程抢夺 CPU 。
例题:使用信号量实现父子进程之间的同步,防止父子进程抢夺 CPU 。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/ipc.h>
#include<sys/sem.h>
static int semid;
static void sem_set(){
if(semctl(semid,0,SETVAL,1)==-1)
{
perror("semctl");
exit(1);
}
}
static void sem_p(){
struct sembuf op = {0,-1,0};
if(semop(semid,&op,1) == -1){
perror("semop");
exit(1);
}
}
static void sem_v(){
struct sembuf op = {0,1,0};
if(semop(semid,&op,1) == -1){
perror("semop");
exit(1);
}
}
static void sem_del(){
if(semctl(semid,0,IPC_RMID) == -1){
perror("semctl");
exit(1);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
pid_t pid;
char ch = 'C';
semid = semget((key_t)1000,1,0664|IPC_CREAT);
if(semid == -1){
perror("semget");
exit(1);
}
sem_set();
pid = fork();
if(pid == -1){
sem_del();
exit(1);
}
else if (pid == 0)
ch = 'Z';
else
ch = 'C';
srand((unsigned int)getpid());
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
sem_p();
printf("%c",ch);
fflush(stdout);
sleep(rand()%4);
printf("%c",ch);
fflush(stdout);
sleep(1);
sem_v();
}
if(pid > 0) {
wait(NULL);
sem_del();
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}