代码适中、非常灵活的平衡树。
需要前置:二叉搜索树。
一些基础的函数:
int idx, ch[N][2], cnt[N], sz[N], fa[N];
/*
idx 是节点计数, ch[i][0 / 1] 是 i 节点的左右子树节点
cnt[i] 是 i 节点的数量
sz[i] 是 i 节点子树的大小
fa[i] 是 i 的父亲
*/
// pushup
void inline pushup(int p) {
sz[p] = sz[ch[p][0]] + cnt[p] + sz[ch[p][1]];
}
// 判断 p 是 fa[p] 左儿子还是右儿子 (0 / 1)
bool inline get(int p) {
return p == ch[fa[p]][1];
}
// 清空一个节点
void inline clear(int p) {
ch[p][0] = ch[p][1] = val[p] = cnt[p] = sz[p] = fa[p] = 0;
}
( ext{Pushup}) 要放在旋转的最后。
( ext{Pushdown}) 只要递归就推下去。
旋转的意义:保持中序遍历不变,调整树高。
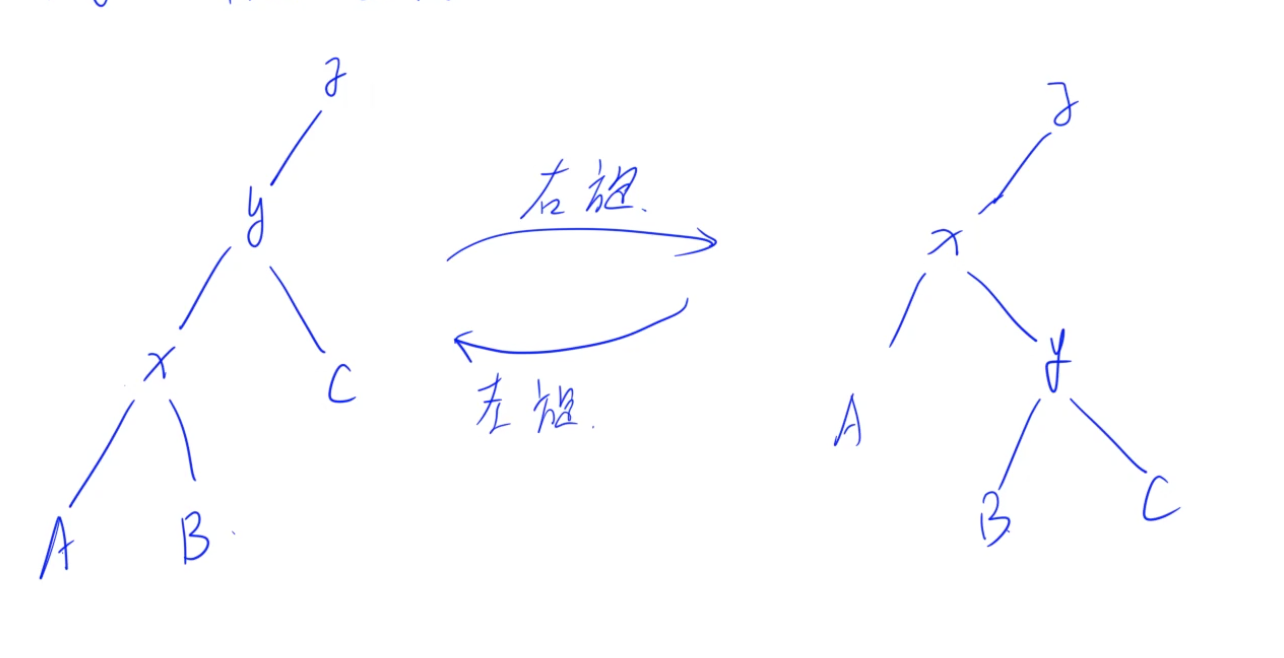
这样旋转后,在改变树形结构的基础上发现中序遍历保持不变。
void inline rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x], z = fa[y], k = get(x);
ch[y][k] = ch[x][!k], fa[ch[x][!k]] = y;
ch[x][!k] = y, fa[y] = x;
fa[x] = z;
if (z) ch[z][y == ch[z][1]] = x;
pushup(y); pushup(x);
}
以下所有介绍的操作都是 Splay 的独特的操作,剩下的二叉搜索树就有了。
复杂度的保持 & 核心思想:
每次操作完的点,均将这个点旋转(Splay)到树根。
感性理解的好处:每一次用到,后面还有可能再用到。
有严谨的证明,结论是若操作 (m) 次,总复杂度是 (O(m log n)),平均意义每次操作都是 (O(log)) 的。
Splay 翻转
定义函数 (splay(x, k)) 表示将点 (x) 旋转至 (k) 下面。
(y = fa_x, z = fa_y)。
迭代:
- 如果 (z) 不存在,转一次 (x) 即可。
- 若 (z, y, x) 是直线,那么先把 (y) 转上去,然后转 (x)
- 否则是折线,就转两次 (x)
只有这么转复杂度才是对的,不能随便转,要背一下)
void inline splay(int p) {
for (int f = fa[p]; f = fa[p]; rotate(p))
if (fa[f]) rotate(get(p) == get(f) ? f : p);
rt = p;
}
以下标为键:将一段序列插入到 y 的后面
- 找到 (y) 的后继 (z)
- 将 (y) 旋转到根 (splay(y, 0))
- 将 (z) 转到 (y) 的下面 (splay(z, y))
这样 (z) 一定没有左子树,直接把一段序列构造好的树节点赋值成 (z) 的左子树就行了。
以下标为键:操作一段
删除序列的 ([l, r])
(splay(kth(l - 1), 0), splay(kth(r+1), l - 1)),这样 ([l, r]) 之间所有的点组成了以 (r + 1) 的左子树,这样直接就可以在 (kth(r + 1)) 的左儿子这个节点打 (tag) 就行了。
板子
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
int n, m, rt;
int idx, ch[N][2], val[N], cnt[N], sz[N], fa[N];
void inline update(int p) {
sz[p] = sz[ch[p][0]] + cnt[p] + sz[ch[p][1]];
}
bool inline get(int p) {
return p == ch[fa[p]][1];
}
void inline clear(int p) {
ch[p][0] = ch[p][1] = val[p] = cnt[p] = sz[p] = fa[p] = 0;
}
void inline rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x], z = fa[y], k = get(x);
ch[y][k] = ch[x][!k], fa[ch[x][!k]] = y;
ch[x][!k] = y, fa[y] = x;
fa[x] = z;
if (z) ch[z][y == ch[z][1]] = x;
update(y); update(x);
}
void inline splay(int p) {
for (int f = fa[p]; f = fa[p]; rotate(p))
if (fa[f]) rotate(get(p) == get(f) ? f : p);
rt = p;
}
void insert(int &p, int x, int f) {
if (!p) {
p = ++idx, sz[p] = cnt[p] = 1, fa[p] = f, val[p] = x;
if (f) ch[f][x > val[f]] = p, update(f), splay(p);
} else if (val[p] == x) cnt[p]++, sz[p]++, update(f), splay(p);
else insert(ch[p][x > val[p]], x, p);
}
int kth(int p, int k) {
if (k <= sz[ch[p][0]]) return kth(ch[p][0], k);
else if (k <= sz[ch[p][0]] + cnt[p]) { splay(p); return val[p]; }
else return kth(ch[p][1], k - sz[ch[p][0]] - cnt[p]);
}
int getRank(int p, int k) {
int res = 0;
if (k < val[p]) return getRank(ch[p][0], k);
else if (k == val[p]) { res = sz[ch[p][0]] + 1; splay(p); return res; }
else { res += sz[ch[p][0]] + cnt[p]; return res + getRank(ch[p][1], k); }
}
int inline pre() {
int p = ch[rt][0];
while (ch[p][1]) p = ch[p][1];
splay(p);
return p;
}
int inline nxt() {
int p = ch[rt][1];
while (ch[p][0]) p = ch[p][0];
splay(p);
return p;
}
void inline del(int k) {
getRank(rt, k);
if (cnt[rt] > 1) cnt[rt]--, sz[rt]--;
else if (!ch[rt][0] && !ch[rt][1]) {
clear(rt), rt = 0;
} else if (!ch[rt][0]) fa[rt = ch[rt][1]] = 0;
else if (!ch[rt][1]) fa[rt = ch[rt][0]] = 0;
else {
int p = rt, x = pre();
splay(x); ch[x][1] = ch[p][1], fa[ch[x][1]] = x;
clear(p); update(rt);
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &m);
while (m--) {
int opt, x; scanf("%d%d", &opt, &x);
if (opt == 1) {
insert(rt, x, 0);
} else if (opt == 2) {
del(x);
} else if (opt == 3) {
insert(rt, x, 0);
printf("%d
", getRank(rt, x));
del(x);
} else if (opt == 4) {
printf("%d
", kth(rt, x));
} else if (opt == 5) {
insert(rt, x, 0);
printf("%d
", val[pre()]);
del(x);
} else if (opt == 6) {
insert(rt, x, 0);
printf("%d
", val[nxt()]);
del(x);
}
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#define ls ch[p][0]
#define rs ch[p][1]
#define get(x) x == ch[fa[x]][1]
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
int n, m, val[N], ch[N][2], sz[N], fa[N], rev[N], rt, idx;
void inline pushup(int p) {
sz[p] = sz[ls] + sz[rs] + 1;
}
void inline reverse(int p) {
swap(ls, rs), rev[p] ^= 1;
}
void inline pushdown(int p) {
if (rev[p]) {
if (ls) reverse(ls);
if (rs) reverse(rs);
rev[p] = 0;
}
}
void inline rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x], z = fa[y], k = get(x);
ch[y][k] = ch[x][!k], fa[ch[x][!k]] = y;
ch[x][!k] = y, fa[y] = x;
fa[x] = z;
if (z) ch[z][y == ch[z][1]] = x;
pushup(y), pushup(x);
}
void inline splay(int x, int k) {
for (int f = fa[x]; (f = fa[x]) != k; rotate(x)) {
if (fa[f]) rotate(get(x) == get(f) ? f : x);
}
if (!k) rt = x;
}
void build(int &p, int l, int r, int f) {
if (l > r) return;
p = ++idx;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1; val[p] = mid, fa[p] = f;
if (l < r) {
build(ch[p][0], l, mid - 1, p);
build(ch[p][1], mid + 1, r, p);
}
pushup(p);
}
void print(int p) {
if (!p) return;
pushdown(p);
print(ch[p][0]);
if (val[p] && val[p] <= n) printf("%d ", val[p]);
print(ch[p][1]);
}
int inline kth(int p, int k) {
pushdown(p);
if (k <= sz[ch[p][0]]) return kth(ch[p][0], k);
else if (k == sz[ch[p][0]] + 1) {
splay(p, 0);
return p;
} else return kth(ch[p][1], k - sz[ch[p][0]] - 1);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
build(rt, 0, n + 1, 0);
while (m--) {
int l, r; scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
int x = kth(rt, l), y = kth(rt, r + 2);
splay(x, 0); splay(y, x);
reverse(ch[y][0]);
}
print(rt);
return 0;
}