Note
Click here to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
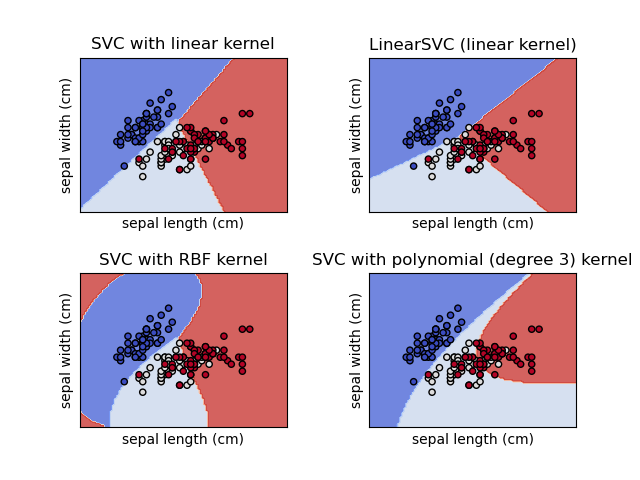
Plot different SVM classifiers in the iris dataset
Comparison of different linear SVM classifiers on a 2D projection of the iris dataset. We only consider the first 2 features of this dataset:
-
Sepal length
-
Sepal width
This example shows how to plot the decision surface for four SVM classifiers with different kernels.
The linear models LinearSVC() and SVC(kernel='linear') yield slightly different decision boundaries. This can be a consequence of the following differences:
-
LinearSVCminimizes the squared hinge loss whileSVCminimizes the regular hinge loss. -
LinearSVCuses the One-vs-All (also known as One-vs-Rest) multiclass reduction whileSVCuses the One-vs-One multiclass reduction.
Both linear models have linear decision boundaries (intersecting hyperplanes) while the non-linear kernel models (polynomial or Gaussian RBF) have more flexible non-linear decision boundaries with shapes that depend on the kind of kernel and its parameters.
Note
while plotting the decision function of classifiers for toy 2D datasets can help get an intuitive understanding of their respective expressive power, be aware that those intuitions don’t always generalize to more realistic high-dimensional problems.
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm, datasets
def make_meshgrid(x, y, h=.02):
"""Create a mesh of points to plot in
Parameters
----------
x: data to base x-axis meshgrid on
y: data to base y-axis meshgrid on
h: stepsize for meshgrid, optional
Returns
-------
xx, yy : ndarray
"""
x_min, x_max = x.min() - 1, x.max() + 1
y_min, y_max = y.min() - 1, y.max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
return xx, yy
def plot_contours(ax, clf, xx, yy, **params):
"""Plot the decision boundaries for a classifier.
Parameters
----------
ax: matplotlib axes object
clf: a classifier
xx: meshgrid ndarray
yy: meshgrid ndarray
params: dictionary of params to pass to contourf, optional
"""
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
out = ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, **params)
return out
# import some data to play with
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# Take the first two features. We could avoid this by using a two-dim dataset
X = iris.data[:, :2]
y = iris.target
# we create an instance of SVM and fit out data. We do not scale our
# data since we want to plot the support vectors
C = 1.0 # SVM regularization parameter
models = (svm.SVC(kernel='linear', C=C),
svm.LinearSVC(C=C, max_iter=10000),
svm.SVC(kernel='rbf', gamma=0.7, C=C),
svm.SVC(kernel='poly', degree=3, gamma='auto', C=C))
models = (clf.fit(