STUN, TURN, and ICE
AnyConnect pioneered the STUN, TURN, and ICE NAT Traversal protocols
Routers create problems
The router remaps your home device IP address to a public IP address typically provided by your internet service provider.
NAT, PAT, and IP masquerading are ubiquitous. They’ve been essential to Internet growth by enabling:
- IP address space expansion
- Network management
- Network security
NAT, PAT and IP Masquerading
I can access a website, but I can’t make a video call.
NATs support device-to-server connections for services like email and web browsing, because email and web servers have public or port-forwarded IP addresses capable of receiving unsolicited packets to initiate connections from devices, and because NATs forward solicited packets to their destinations.
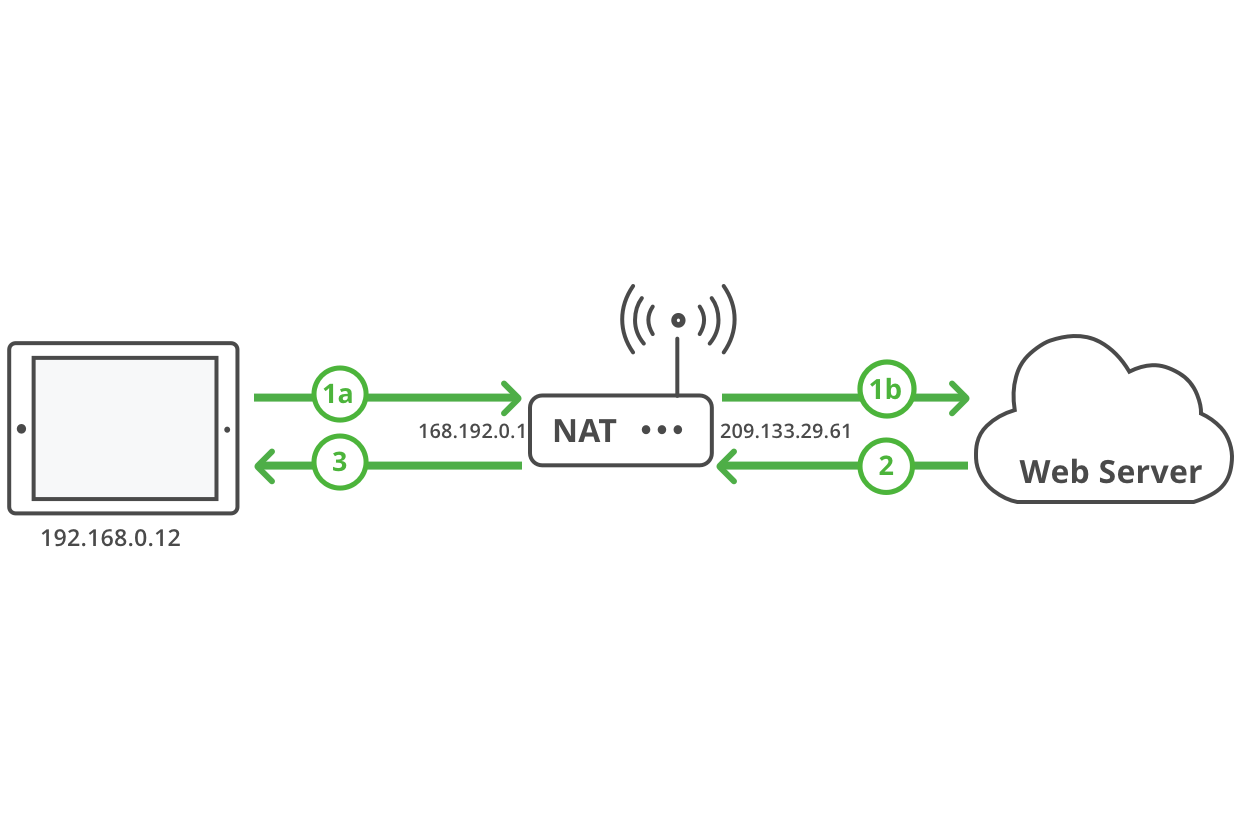
View a web page
| 1a. | Initiate request from behind a NAT. |
| 1b. | NAT maps the device IP address to a public IP address and forwards the request to a public server. |
| 2. | Public server responds with data packets. |
| 3. | NAT forwards the response to the device. |
However, NATs break device-to-device connections for services like IoT, home automation, and video telephony, because when 2 devices are behind different NATs, neither NAT will forward unsolicited packets from the other, which prevents one device from initiating a connection to another.
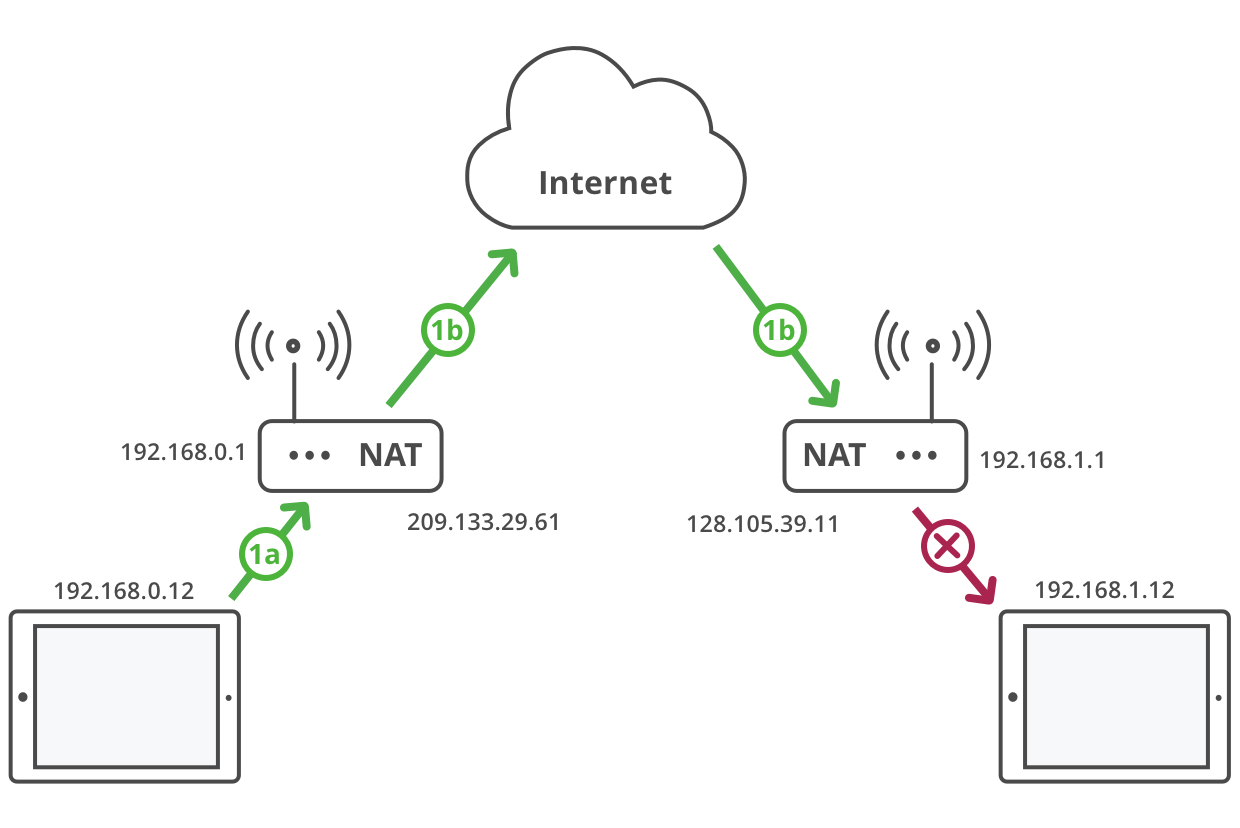
Make a video call
| 1a. | Initiate request from behind a NAT |
| 1b. | NAT maps the device IP address to a public IP address and forwards the request to the peer device. The request hits a NAT at the receiving end. This unsolicited request is blocked by the receiving NAT. |
STUN, TURN, and ICE
In the world of IP communications, devices trying to connect, i.e. make a call over the internet are known as endpoints. Typically, endpoints reside behind NATs and hence it is difficult to discover the public IP addresses of endpoints. The endpoint initiating a call is known as the caller. The endpoint receiving the call is known as the callee.
NAT Traversal
NAT Traversal is a computer networking methodology which establishes and maintains device-to-device connections across routers that implement NAT. NAT Traversal is required for network applications that require device-to-device connections, such as file sharing, VoIP and video telephony, and IoT.
1. STUN binding
2. Caller TURN allocation
3. Caller sends invite
4. Callee TURN allocation
5. Callee answers OK
6. Exchange candidate IP addresses
7a. ICE check for P2P connection
7b. If P2P unsuccessful, make relay connection
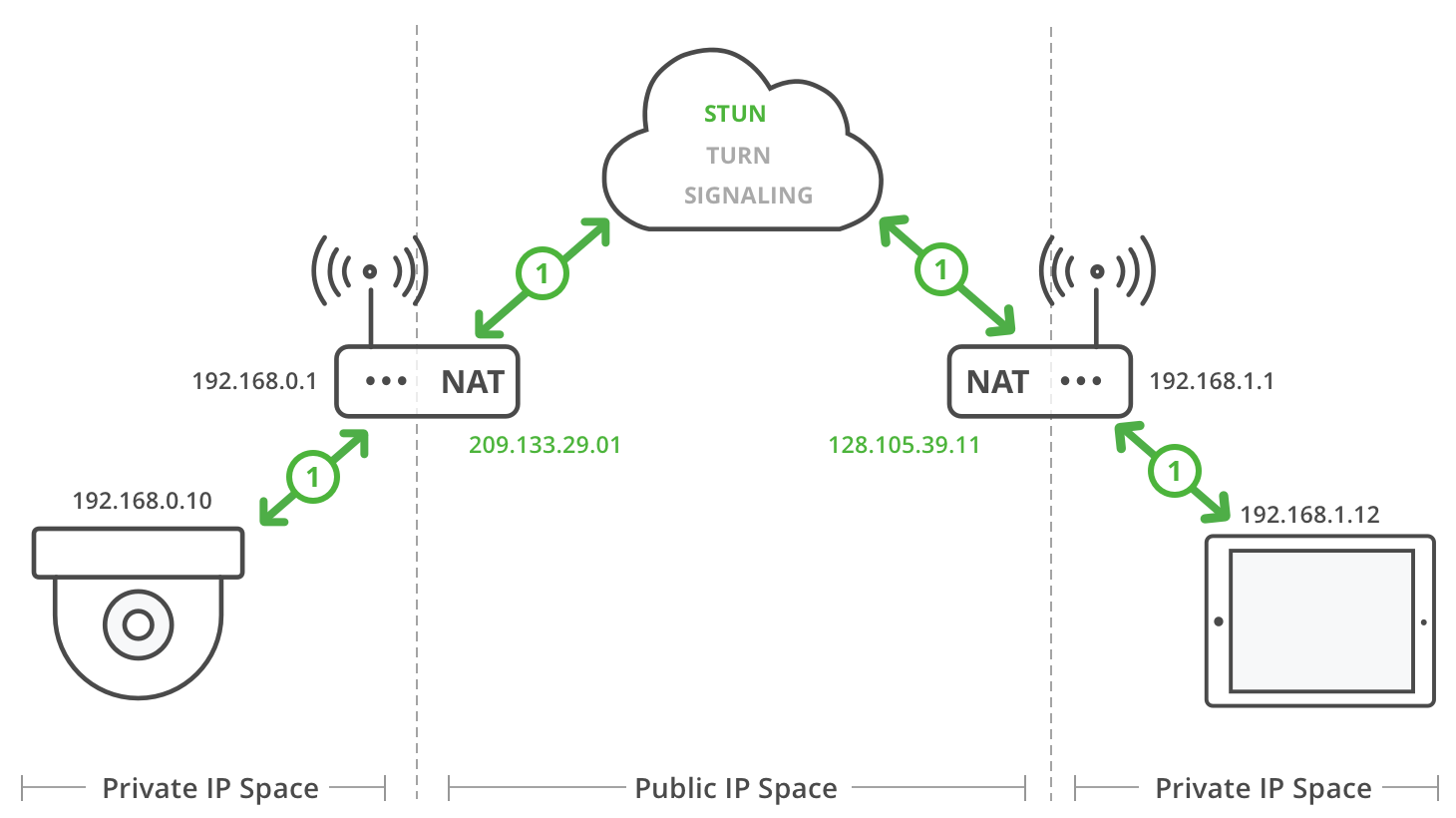
Standard-stun-turn-ice
Following open standard protocols
- RFC 5245 – Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE): A Protocol for Network Address Translator (NAT) Traversal for Offer/Answer Protocols
- RFC 5389 – Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN)
- RFC 5766 – Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN): Relay Extensions to Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN)
- RFC 5768 – Indicating Support for Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE) in the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
- RFC 5928 – Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN) Resolution Mechanism
- RFC 6062 – Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN) Extensions for TCP Allocations
- RFC 6156 – Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN) Extension for IPv6
- RFC 6336 – IANA Registry for Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE) Options
- RFC 6544 – TCP Candidates with Interactive Connectivity Establishment
STUN, TURN, and ICE have been adopted by the following standards bodies:
- IETF – Internet Engineering Task Force
- 3GPP IMS – 3rd Generation Partnership Project IP-Multimedia Subsystem
- Microsoft OCS, Lync, Skype, Skype for Business, Teams
- CableLabs – PacketCable 2.0
- WebRTC – Web Real-Time Communications
Patents in multiple countries
- Canada – 2,476,722 & 2,761,983
- China – ZL02805239.0
- Europe – 1 362 460
- India – 224961
- Japan – 3917076
- Korea – 10-949510
- UK – 1362460
- USA – 7,522,594 & 7,602,784
Copyright