- 多个线程同时操作一个变量
import time
import threading
def addNum():
#在每个线程中都获取这个全局变量
global num
temp = num
time.sleep(0.1)
#对此公共变量进行-1操作
num = temp-1
#设定一个共享变量
num = 100
thread_list = []
for i in range(100):
t = threading.Thread(target=addNum)
t.start()
thread_list.append(t)
#等待所有线程执行完毕
for t in thread_list:
t.join()
print('final num:', num )
输出:
99
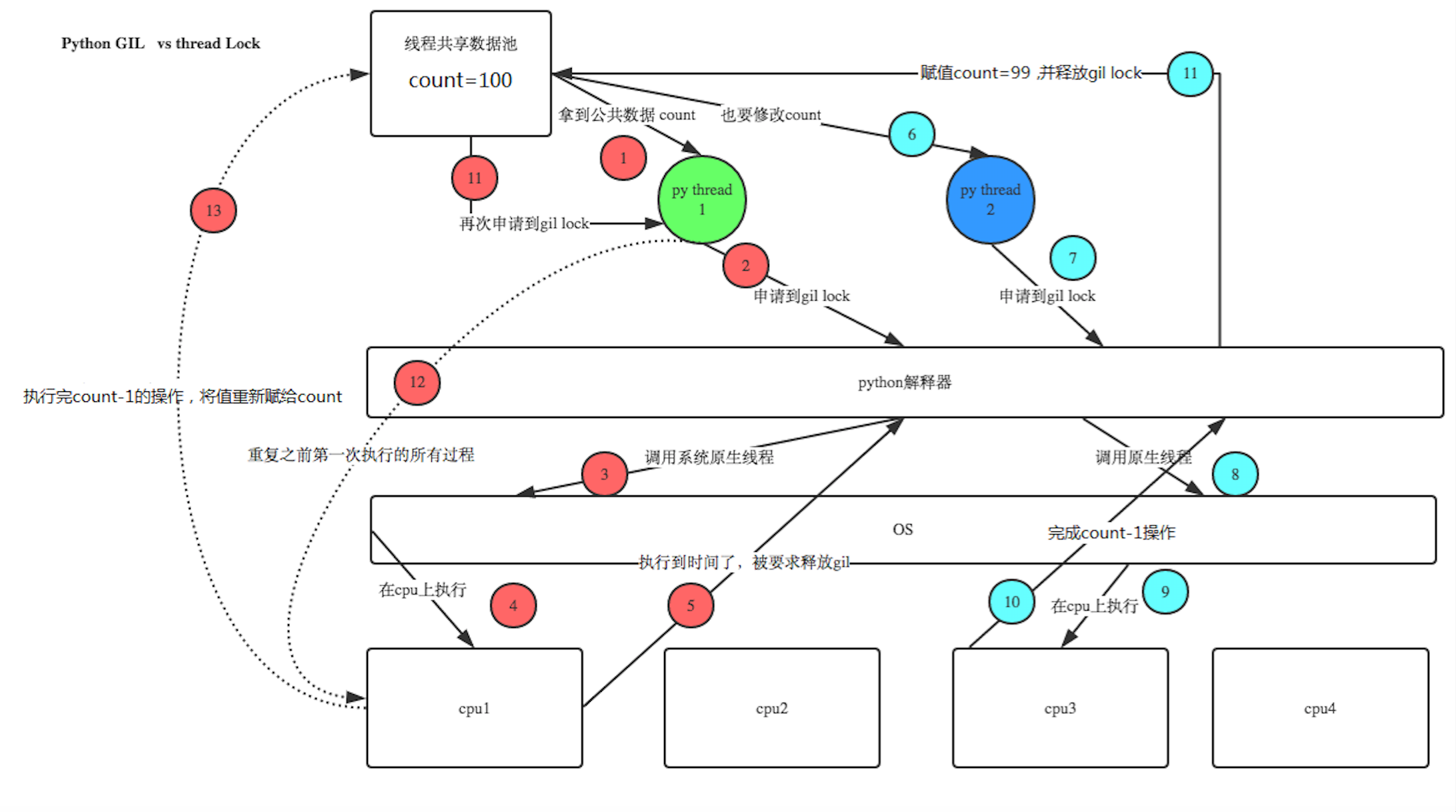
- 同步锁,acquire和release之间的代码,在同一时间只会被一个线程执行
import time
import threading
def addNum():
global num
lock.acquire()
temp = num
time.sleep(0.1)
num = temp-1
lock.release()
num = 100
thread_list = []
lock = threading.Lock()
for i in range(100):
t = threading.Thread(target=addNum)
t.start()
thread_list.append(t)
for t in thread_list:
t.join()
print('final num:', num )
输出:
0
- 死锁
import threading,time
class MyThread(threading.Thread):
def doA(self):
lockA.acquire()
print(self.name, "gotlockA", time.ctime())
time.sleep(3)
lockB.acquire()
print(self.name, "gotlockB", time.ctime())
lockB.release()
lockA.release()
def doB(self):
lockB.acquire()
print(self.name, "gotlockB", time.ctime())
time.sleep(2)
lockA.acquire()
print(self.name, "gotlockA", time.ctime())
lockA.release()
lockB.release()
def run(self):
self.doA()
self.doB()
if __name__ == "__main__":
lockA = threading.Lock()
lockB = threading.Lock()
threads = []
for i in range(5):
threads.append(MyThread())
for t in threads:
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
- 解决死锁 -- RLock
import threading
class Account:
def __init__(self, _id, balance):
self.id = _id
self.balance = balance
self.lock = threading.RLock()
def withdraw(self, amount):
with self.lock:
self.balance -= amount
def deposit(self, amount):
with self.lock:
self.balance += amount
#lock.acquire中嵌套lock.acquire的场景
def drawcash(self, amount):
with self.lock:
interest = 0.05
count = amount+amount*interest
self.withdraw(count)
def transfer(_from, to, amount):
_from.withdraw(amount)
to.deposit(amount)
alex = Account('alex', 1000)
yuan = Account('yuan', 1000)
t1 = threading.Thread(target=transfer, args=(alex, yuan, 100))
t1.start()
t2 = threading.Thread(target=transfer, args=(yuan, alex, 200))
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print('>>>', alex.balance)
print('>>>', yuan.balance)