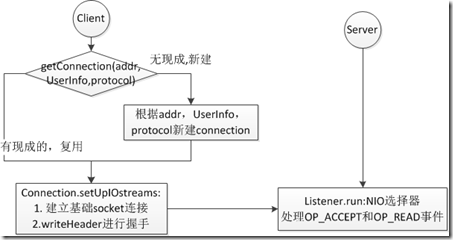
建立IPC连接
IPC Client通过调用getConnection获取IPC连接,具体流程图如下:
服务器端的IPC连接代码分散在Listener和Server.Connection中。
Listener.run() 实现了NIO中的选择器循环。如下代码:
//Listener构造函数 public Listener() throws IOException { address = new InetSocketAddress(bindAddress, port); // Create a new server socket and set to non blocking mode acceptChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); acceptChannel.configureBlocking(false); // Bind the server socket to the local host and port bind(acceptChannel.socket(), address, backlogLength); port = acceptChannel.socket().getLocalPort(); //Could be an ephemeral port // create a selector; selector= Selector.open(); readers = new Reader[readThreads]; readPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(readThreads); for (int i = 0; i < readThreads; i++) { Selector readSelector = Selector.open(); Reader reader = new Reader(readSelector); readers[i] = reader; readPool.execute(reader); }
Listener.run()开启选择器循环,并处理Accept请求,如下:
//Listener运行函数 public void run() { LOG.info(getName() + ": starting"); SERVER.set(Server.this); while (running) { SelectionKey key = null; try { selector.select(); Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) { key = iter.next(); iter.remove(); try { if (key.isValid()) { if (key.isAcceptable()) doAccept(key); } } catch (IOException e) { } key = null; } } catch (OutOfMemoryError e) { // we can run out of memory if we have too many threads // log the event and sleep for a minute and give // some thread(s) a chance to finish LOG.warn("Out of Memory in server select", e); closeCurrentConnection(key, e); cleanupConnections(true); try { Thread.sleep(60000); } catch (Exception ie) {} } catch (Exception e) { closeCurrentConnection(key, e); } cleanupConnections(false); } LOG.info("Stopping " + this.getName()); synchronized (this) { try { acceptChannel.close(); selector.close(); } catch (IOException e) { } selector= null; acceptChannel= null; // clean up all connections while (!connectionList.isEmpty()) { closeConnection(connectionList.remove(0)); } } }
doAccept()中通过server.accpet获取SocketChannel,并获取一个Reader对象,该对象包含一个Selector:readerSelector,通过reader.registerChannel,将SocketChannel注册到readerSelector下.并新建connection对象。
//Do_Accept void doAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException, OutOfMemoryError { Connection c = null; ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); SocketChannel channel; while ((channel = server.accept()) != null) { channel.configureBlocking(false); channel.socket().setTcpNoDelay(tcpNoDelay); Reader reader = getReader(); try { reader.startAdd(); SelectionKey readKey = reader.registerChannel(channel); c = new Connection(readKey, channel, System.currentTimeMillis()); readKey.attach(c); synchronized (connectionList) { connectionList.add(numConnections, c); numConnections++; } if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) LOG.debug("Server connection from " + c.toString() + "; # active connections: " + numConnections + "; # queued calls: " + callQueue.size()); } finally { reader.finishAdd(); } } }
public synchronized SelectionKey registerChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws IOException { return channel.register(readSelector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); }
Listener拥有一个ExecutorService线程池用来运行Reader对象,Reader对象采用轮叫调度(Round Robin Scheduling算法就是以轮叫的方式依次将请求调度不同的服务器),如下:
Reader getReader() { currentReader = (currentReader + 1) % readers.length; return readers[currentReader]; }
Reader对象的startAdd方法和finishAdd方法之间来注册channel和新建conncetion。
以下是Reader对象的run方法,可以看出,当Reader对象调用startAdd方法后,线程从上一次的select阻塞中返回,并循环等待,直到finishAdd方法调用后,adding参数由true转false,跳出循环,再次进入select中。
public void run() { LOG.info("Starting SocketReader"); synchronized (this) { while (running) { SelectionKey key = null; try { readSelector.select(); while (adding) { this.wait(1000); } Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = readSelector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) { key = iter.next(); iter.remove(); if (key.isValid()) { if (key.isReadable()) { doRead(key); } } key = null; } } catch (InterruptedException e) { if (running) { // unexpected -- log it LOG.info(getName() + " caught: " + StringUtils.stringifyException(e)); } } catch (IOException ex) { LOG.error("Error in Reader", ex); } } } }
当有新的数据到来时,调用Listener的doRead方法进行读取数据。
doRead方法主要调用了Server.Connection的readAndProcess方法来读取客户端发送过来的数据并处理。
readAndProcess方法,先读取IPC连接魔数和协议版本号分别在缓冲区dataLengthBuffer和versionBuffer读入。
if (dataLengthBuffer.remaining() > 0) { count = channelRead(channel, dataLengthBuffer); // dataLengthBuffer长度为4byte,第一次循环读取IPC连接魔数hrpc //非第一次循环读取数据data if (count < 0 || dataLengthBuffer.remaining() > 0) return count; } if (!rpcHeaderRead) { //Every connection is expected to send the header. if (rpcHeaderBuffer == null) { rpcHeaderBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(2); } count = channelRead(channel, rpcHeaderBuffer); //rpcHeaderBuffer长度为2byte,读取协议版本号和authMehod if (count < 0 || rpcHeaderBuffer.remaining() > 0) { return count; } int version = rpcHeaderBuffer.get(0);//协议版本号 byte[] method = new byte[] {rpcHeaderBuffer.get(1)};//authMehod authMethod = AuthMethod.read(new DataInputStream( new ByteArrayInputStream(method))); dataLengthBuffer.flip(); if (!HEADER.equals(dataLengthBuffer) || version != CURRENT_VERSION) { //Warning is ok since this is not supposed to happen. LOG.warn("Incorrect header or version mismatch from " + hostAddress + ":" + remotePort + " got version " + version + " expected version " + CURRENT_VERSION); return -1; } dataLengthBuffer.clear(); ……//sasl处理部分,可以忽略
rpcHeaderBuffer = null; rpcHeaderRead = true; continue; }
在接下类的数据处理部分,readAndProcess主要调用了saslReadAndProcess方法,进而调用processOneRpc方法,进而处理processHeader方法和processData方法。processHeader方法如下:
private void processHeader(byte[] buf) throws IOException { DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(buf)); header.readFields(in); try { String protocolClassName = header.getProtocol(); if (protocolClassName != null) { protocol = getProtocolClass(header.getProtocol(), conf); // getProtocolClass只判断Server是否实现了ConnectionHeader中要求的IPC接口 //如果实现,返回Class,否则抛异常。 } } catch (ClassNotFoundException cnfe) { throw new IOException("Unknown protocol: " + header.getProtocol()); } ......//获取用户信息 }
数据分帧和读取
Tcp通信基于字节流,没有消息边界的概念,常用的分帧方法如下:
1. 定长消息:通信双方发送的消息长度为固定的,接收者只需要将数据读入到相应的缓冲区即可。
2. 基于界定符:消息结束由唯一标示(特殊字符序列)指出,这个特殊字符序列不能在传输的消息数据中出现,接收者简单扫描输入信息查找界定符。
3. 显式长度:具体消息前面附加固定大小的字段,用来指示消息包含多少字节。
IPC客户端发送请求采用“显式长度”方法,长度是int类型。如下是服务器端接收数据的相关代码:
if (data == null) { dataLengthBuffer.flip(); dataLength = dataLengthBuffer.getInt();//读取数据长度 //dataLengthBuffer长度为4byte,正好一个int长度。 if (dataLength == Client.PING_CALL_ID) {//心跳消息 if(!useWrap) { //covers the !useSasl too dataLengthBuffer.clear(); return 0; //ping message } } if (dataLength < 0) { LOG.warn("Unexpected data length " + dataLength + "!! from " + getHostAddress()); } data = ByteBuffer.allocate(dataLength); //根据长度,为读取数据分配缓冲区。 } count = channelRead(channel, data); if (data.remaining() == 0) {//读到一个完整的消息 dataLengthBuffer.clear(); data.flip(); if (skipInitialSaslHandshake) { data = null; skipInitialSaslHandshake = false; continue; } boolean isHeaderRead = headerRead; if (useSasl) { saslReadAndProcess(data.array()); } else { processOneRpc(data.array());//处理消息 } data = null; if (!isHeaderRead) { continue; } }
而IPC服务器端到客户端用的是“定长消息”的变种,即利用前面介绍的序列化机制Writable发送响应。双方无需界定符和长度信息,其本质是一种“定长消息”。服务器端往客户端写数据的代码见Server.setupResponse,客户端读数据的代码在Connection.receiveResponse。