一、什么是事务
处理以数据为中心的应用时,另一个重要的话题是事务管理。ADO.NET为事务管理提供了一个非常干净和有效的API。因为EF运行在ADO.NET之上,所以EF可以使用ADO.NET的事务管理功能。
当从数据库角度谈论事务时,它意味着一系列操作被当作一个不可分割的操作。所有的操作要么全部成功,要么全部失败。事务的概念是一个可靠的工作单元,事务中的所有数据库操作应该被看作是一个工作单元。
从应用程序的角度来看,如果我们有多个数据库操作被当作一个工作单元,那么应该将这些操作包裹在一个事务中。为了能够使用事务,应用程序需要执行下面的步骤:
1、开始事务。
2、执行所有的查询,执行所有的数据库操作,这些操作被视为一个工作单元。
3、如果所有的事务成功了,那么提交事务。
4、如果任何一个操作失败,就回滚事务。
二、创建测试环境
提到事务,最经典的例子莫过于银行转账了。我们这里也使用这个例子来理解一下和事务相关的概念。为了简单模拟银行转账的情景,假设银行为不同的账户使用了不同的表,对应地,我们创建了OutputAccount和InputAccount两个实体类,实体类定义如下:
OutputAccount实体类:
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; 4 using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; 5 using System.Linq; 6 using System.Text; 7 using System.Threading.Tasks; 8 9 namespace EFTransactionApp.Model 10 { 11 [Table("OutputAccounts")] 12 public class OutputAccount 13 { 14 public int Id { get; set; } 15 [StringLength(8)] 16 public string Name { get; set; } 17 public decimal Balance { get; set; } 18 19 } 20 }
InputAccount实体类:
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; 4 using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; 5 using System.Linq; 6 using System.Text; 7 using System.Threading.Tasks; 8 9 namespace EFTransactionApp.Model 10 { 11 [Table("InputAccounts")] 12 public class InputAccount 13 { 14 public int Id { get; set; } 15 [StringLength(8)] 16 public string Name { get; set; } 17 public decimal Balance { get; set; } 18 19 } 20 }
2、定义数据上下文类
1 using EFTransactionApp.Model; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Data.Entity; 5 using System.Linq; 6 using System.Text; 7 using System.Threading.Tasks; 8 9 namespace EFTransactionApp.EF 10 { 11 public class EFDbContext:DbContext 12 { 13 public EFDbContext() 14 : base("name=AppConnection") 15 { 16 17 } 18 19 20 public DbSet<OutputAccount> OutputAccounts { get; set; } 21 22 public DbSet<InputAccount> InputAccounts { get; set; } 23 } 24 }
3、使用数据迁移生成数据库,并填充种子数据
1 namespace EFTransactionApp.Migrations 2 { 3 using EFTransactionApp.Model; 4 using System; 5 using System.Data.Entity; 6 using System.Data.Entity.Migrations; 7 using System.Linq; 8 9 internal sealed class Configuration : DbMigrationsConfiguration<EFTransactionApp.EF.EFDbContext> 10 { 11 public Configuration() 12 { 13 AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = false; 14 } 15 16 protected override void Seed(EFTransactionApp.EF.EFDbContext context) 17 { 18 // This method will be called after migrating to the latest version. 19 20 // You can use the DbSet<T>.AddOrUpdate() helper extension method 21 // to avoid creating duplicate seed data. 22 23 // 填充种子数据 24 context.InputAccounts.AddOrUpdate( 25 new InputAccount() 26 { 27 Name = "李四", 28 Balance = 0M 29 } 30 ); 31 32 context.OutputAccounts.AddOrUpdate( 33 new OutputAccount() 34 { 35 Name="张三", 36 Balance=10000M 37 } 38 ); 39 } 40 } 41 }
4、运行程序
从应用程序的角度看,无论何时用户将钱从OutputAccount转入InputAccount,这个操作应该被视为一个工作单元,永远不应该发生OutputAccount的金额扣除了,而InputAccount的金额没有增加。接下来我们就看一下EF如何管理事务。
运行程序前,先查看数据库数据:
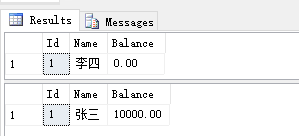
现在,我们尝试使用EF的事务从OutputAccount的张三转入1000给InputAccount的李四。
使用EF默认的事务执行
EF的默认行为是:无论何时执行任何涉及Create,Update或Delete的查询,都会默认创建事务。当DbContext类上的SaveChanges()方法被调用时,事务就会提交。
1 using EFTransactionApp.EF; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace EFTransactionApp 9 { 10 class Program 11 { 12 static void Main(string[] args) 13 { 14 using (var db = new EFDbContext()) 15 { 16 int outputId = 1, inputId = 1; 17 decimal transferAmount = 1000m; 18 //1 检索事务中涉及的账户 19 var outputAccount = db.OutputAccounts.Find(outputId); 20 var inputAccount = db.InputAccounts.Find(inputId); 21 //2 从输出账户上扣除1000 22 outputAccount.Balance -= transferAmount; 23 //3 从输入账户上增加1000 24 inputAccount.Balance += transferAmount; 25 //4 提交事务 26 db.SaveChanges(); 27 } 28 29 } 30 } 31 }
运行程序后,会发现数据库中数据发生了改变:
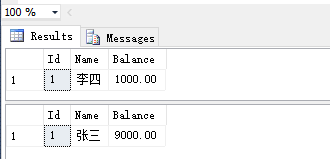
可以看到,用户李四的账户上面多了1000,用户张三的账户上面少了1000。因此,这两个操作有效地被包裹在了一个事务当中,并作为一个工作单元执行。如果任何一个操作失败,数据就不会发生变化。
可能有人会疑惑:上面的程序执行成功了,没有看到事务的效果,能不能修改一下代码让上面的程序执行失败然后可以看到事务的效果呢?答案是肯定可以的,下面将上面的代码进行修改。
通过查看数据库表结构会发现Balance的数据类型是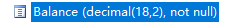 ,意味着Balance列的最大可输入长度是16位(最大长度18位减去2位小数点),如果输入的长度大于16位的话程序就会报错,所以将上面的代码进行如下的修改:
,意味着Balance列的最大可输入长度是16位(最大长度18位减去2位小数点),如果输入的长度大于16位的话程序就会报错,所以将上面的代码进行如下的修改:
1 using EFTransactionApp.EF; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace EFTransactionApp 9 { 10 class Program 11 { 12 static void Main(string[] args) 13 { 14 using (var db = new EFDbContext()) 15 { 16 int outputId = 1, inputId = 1; 17 decimal transferAmount = 1000m; 18 //1 检索事务中涉及的账户 19 var outputAccount = db.OutputAccounts.Find(outputId); 20 var inputAccount = db.InputAccounts.Find(inputId); 21 //2 从输出账户上扣除1000 22 outputAccount.Balance -= transferAmount; 23 //3 从输入账户上增加1000 *3000000000000000倍 24 inputAccount.Balance += transferAmount*3000000000000000; 25 //4 提交事务 26 db.SaveChanges(); 27 } 28 29 } 30 } 31 }
在次运行程序,会发现程序报错了:
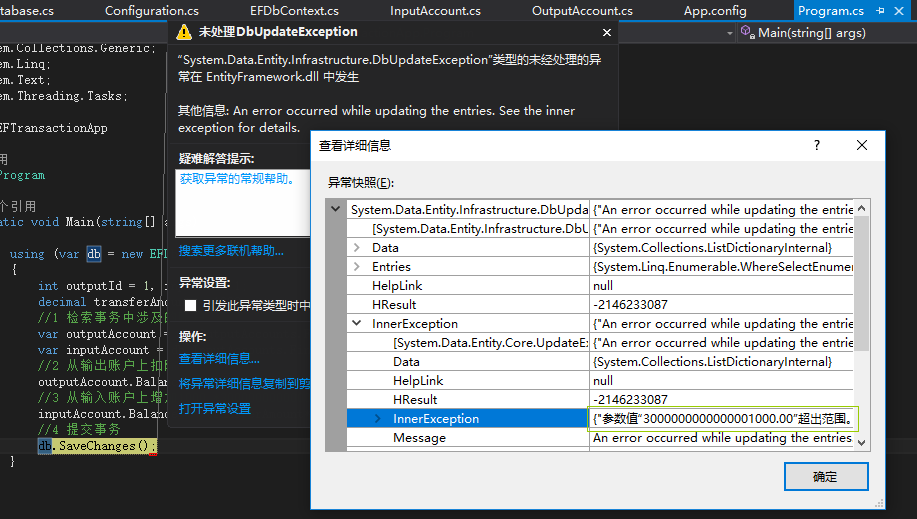
这时在查看数据库,发现用户张三的余额还是9000没有发生变化,说明事务起作用了。
5、使用TransactionScope处理事务
如果有一个场景具有多个DbContext对象,那么我们想将涉及多个DbContext对象的操作关联为一个工作单元,这时,我们需要在TransactionScope对象内部包裹SaveChanges()方法的调用。为了描述这个场景,我们使用DbContext类的两个不同实例来执行扣款和收款,代码如下:
int outputId = 1, inputId = 1; decimal transferAmount = 1000m; using (var ts = new TransactionScope(TransactionScopeOption.Required)) { var db1 = new EFDbContext(); var db2 = new EFDbContext(); //1 检索事务中涉及的账户 var outputAccount = db1.OutputAccounts.Find(outputId); var inputAccount = db2.InputAccounts.Find(inputId); //2 从输出账户上扣除1000 outputAccount.Balance -= transferAmount; //3 从输入账户上增加1000 inputAccount.Balance += transferAmount; db1.SaveChanges(); db2.SaveChanges(); ts.Complete(); }
在上面的代码中,我们使用了两个不同的DbContext实例来执行扣款和收款操作。因此,默认的EF行为不会工作。在调用各自的SaveChanges()方法时,和上下文相关的各个事务不会提交。相反,因为它们都在 TransactionScope对象的内部,所以,当TransactionScope对象的Complete()方法调用时,事务才会提交。如果任何一个操作失败,就会发生异常,TransactionScope就不会调用Complete()方法,从而回滚更改。事务执行失败的案例也可以按照上面的方式进行修改,使Balance列的长度超过最大长度,这里就不在演示了。
三、使用EF6管理事务
从EF6开始,EF在DbContext对象上提供了Database.BeginTransaction()方法,当使用上下文类在事务中执行原生SQL命令时,这个方法特别有用。
接下来看一下如何使用这个新方法管理事务。这里我们使用原生SQL从OutputAccount账户中扣款,使用模型类给InputAccount收款,代码如下:
int outputId = 1, inputId = 1; decimal transferAmount = 1000m; using (var db = new EFDbContext()) { using (var trans = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) { try { var sql = "Update OutputAccounts set Balance=Balance-@amountToDebit where id=@outputId"; db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand(sql, new SqlParameter("@amountToDebit", transferAmount), new SqlParameter("@outputId", outputId)); var inputAccount = db.InputAccounts.Find(inputId); inputAccount.Balance += transferAmount; db.SaveChanges(); trans.Commit(); } catch (Exception ex) { trans.Rollback(); } } }
对上面的代码稍作解释:首先创建了一个DbContext类的实例,然后使用这个实例通过调用Database.BeginTransaction()方法开启了一个事务。该方法给我们返回了一个DbContextTransaction对象的句柄,使用该句柄可以提交或者回滚事务。然后使用原生SQL从OutputAccount账户中扣款,使用模型类给InputAccount收款。调用SaveChanges()方法只会影响第二个操作(在事务提交之后影响),但不会提交事务。如果两个操作都成功了,那么就调用DbContextTransaction对象的Commit()方法,否则,我们就处理异常并调用DbContextTransaction对象的Rollback()方法回滚事务。
四、使用已经存在的事务
有时,我们想在EF的DbContext类中使用一个已经存在的事务。原因可能有这么几个:
1、一些操作可能在应用的不同部分完成。
2、对老项目使用了EF,并且这个老项目使用了一个类库,这个类库给我们提供了事务或者数据库链接的句柄。
对于这些场景,EF允许我们在DbContext类中使用一个和事务相关联的已存在连接。接下来,写一个简单的函数来模拟老项目的类库提供句柄,该函数使用纯粹的ADO.NET执行扣款操作,函数定义如下:
static bool DebitOutputAccount(SqlConnection conn, SqlTransaction trans, int accountId, decimal amountToDebit) { int affectedRows = 0; var command = conn.CreateCommand(); command.Transaction = trans; command.CommandType = CommandType.Text; command.CommandText = "Update OutputAccounts set Balance=Balance-@amountToDebit where id=@accountId"; command.Parameters.AddRange(new SqlParameter[] { new SqlParameter("@amountToDebit",amountToDebit), new SqlParameter("@accountId",accountId) }); try { affectedRows = command.ExecuteNonQuery(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } return affectedRows == 1; }
这种情况,我们不能使用Database.BeginTransaction()方法,因为我们需要将SqlConnection对象和SqlTransaction对象传给该函数,并把该函数放到我们的事务里。这样,我们就需要首先创建一个SqlConnection,然后开始SqlTransaction,代码如下:
int outputId = 2, inputId = 1; decimal transferAmount = 1000m; var connectionString = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["AppConnection"].ConnectionString; using (var conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString)) { conn.Open(); using (var trans = conn.BeginTransaction()) { try { var result = DebitOutputAccount(conn, trans, outputId, transferAmount); if (!result) throw new Exception("不能正常扣款!"); using (var db = new EFDbContext(conn, contextOwnsConnection: false)) { db.Database.UseTransaction(trans); var inputAccount = db.InputAccounts.Find(inputId); inputAccount.Balance += transferAmount; db.SaveChanges(); } trans.Commit(); } catch (Exception ex) { trans.Rollback(); } } }
同时,需要修改数据上下文类,数据库上下文类代码修改如下:
1 using EFTransactionApp.Model; 2 using System; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Data.Common; 5 using System.Data.Entity; 6 using System.Linq; 7 using System.Text; 8 using System.Threading.Tasks; 9 10 namespace EFTransactionApp.EF 11 { 12 //contextOwnsConnection 13 //false:表示上下文和数据库连接没有关系,上下文释放了,数据库连接还没释放; 14 //true:上下文释放了,数据库连接也就释放了。 15 public class EFDbContext:DbContext 16 { 17 //public EFDbContext() 18 // : base("name=AppConnection") 19 //{ 20 21 //} 22 23 public EFDbContext(DbConnection conn, bool contextOwnsConnection) 24 : base(conn, contextOwnsConnection) 25 { 26 27 } 28 29 30 public DbSet<OutputAccount> OutputAccounts { get; set; } 31 32 public DbSet<InputAccount> InputAccounts { get; set; } 33 } 34 }
五、选择合适的事务管理
我们已经知道了好几种使用EF出来事务的方法,下面一一对号入座:
1、如果只有一个DbContext类,那么应该尽力使用EF的默认事务管理。我们总应该将所有的操作组成一个在相同的DbContext对象的作用域中执行的工作单元,SaveChanges()方法会提交处理事务。
2、如果使用了多个DbContext对象,那么管理事务的最佳方法可能就是把调用放到TransactionScope对象的作用域中了。
3、如果要执行原生的SQL命令,并想把这些操作和事务关联起来,那么应该使用EF提供的Database.BeginTransaction()方法。然而这种方法只支持EF6以后的版本,以前的版本不支持。
4、如果想为要求SqlTransaction的老项目使用EF,那么可以使用Database.UseTransaction()方法,在EF6中可用。
示例代码下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1c2wGgSS