一、概要描述
在上篇博文描述了TaskTracker启动一个独立的java进程来执行Map或Reduce任务。在本篇和下篇博文中我们会关注启动的那个入口是org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Child的这个Java进程是如何执行用户定义的map或Reduce任务的。
接上篇文章,TaskRunner线程执行中,会构造一个java –D** Child address port tasked这样第一个java命令,单独启动一个java进程。在Child的main函数中通过TaskUmbilicalProtocol协议,从TaskTracker获得需要执行的Task,并调用Task的run方法来执行,而Task的run方法会通过java反射机制构造Mapper,InputFormat,mapperContext,然后调用构造的mapper的run方法执行mapper操作。
二、 流程描述
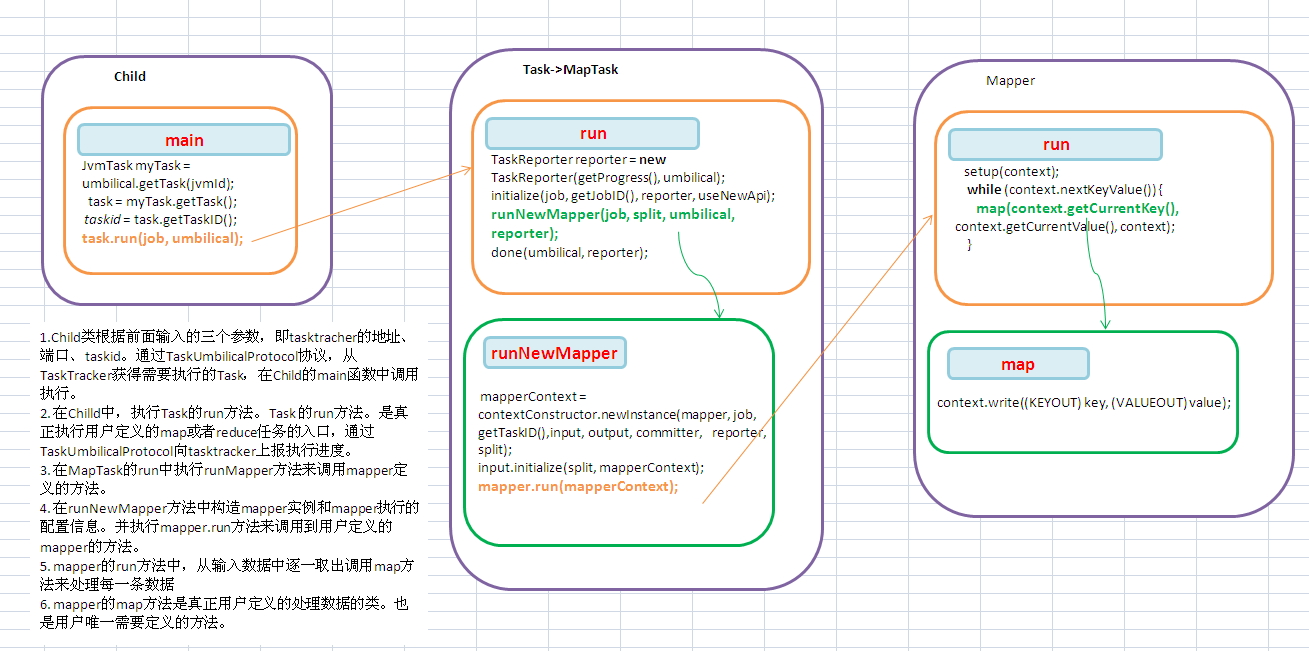
1.Child类根据前面输入的三个参数,即tasktracher的地址、端口、taskid。通过TaskUmbilicalProtocol协议,从TaskTracker获得需要执行的Task,在Child的main函数中调用执行。
2. 在Chilld中,执行Task的run方法。Task 的run方法。是真正执行用户定义的map或者reduce任务的入口,通过TaskUmbilicalProtocol向tasktracker上报执行进度。
3. 在MapTask的run中执行runMapper方法来调用mapper定义的方法。
4. 在runNewMapper方法中构造mapper实例和mapper执行的配置信息。并执行mapper.run方法来调用到用户定义的mapper的方法。
5. mapper的run方法中,从输入数据中逐一取出调用map方法来处理每一条数据
6. mapper的map方法是真正用户定义的处理数据的类。也是用户唯一需要定义的方法。
三、代码详细
1. Child的main方法每个task进程都会被在单独的进程中执行,这个方法就是这些进程的入口方法。观察下载在这个方法中做了哪些事情?
1)从传入的参数中获得tasktracker的地址、从传入的参数中获得tasktracker的地址
2) 根据获取的taskTracker的地址和端口通过RPC方式和tasktracker通信,umbilical是作为tasktracker的代理来执行操作。
3) 根据JvmId从taskTracker查询获取到JvmTask
4) 执行任务
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable { LOG.debug("Child starting"); JobConf defaultConf = new JobConf(); //从传入的参数中获得taskTracker的地址 String host = args[0]; //从传入的参数中获得taskTracker的响应请求的端口。 int port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(host, port); final TaskAttemptID firstTaskid = TaskAttemptID.forName(args[2]); final int SLEEP_LONGER_COUNT = 5; int jvmIdInt = Integer.parseInt(args[3]); JVMId jvmId = new JVMId(firstTaskid.getJobID(),firstTaskid.isMap(),jvmIdInt); //通过RPC方式和tasktracker通信,umbilical是作为tasktracker的代理来执行操作。 TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical = (TaskUmbilicalProtocol)RPC.getProxy(TaskUmbilicalProtocol.class, TaskUmbilicalProtocol.versionID, address, defaultConf); int numTasksToExecute = -1; //-1 signifies "no limit" int numTasksExecuted = 0; //for the memory management, a PID file is written and the PID file //is written once per JVM. We simply symlink the file on a per task //basis later (see below). Long term, we should change the Memory //manager to use JVMId instead of TaskAttemptId Path srcPidPath = null; Path dstPidPath = null; int idleLoopCount = 0; Task task = null; try { while (true) { taskid = null; //根据JvmId从taskTracker查询获取到JvmTask JvmTask myTask = umbilical.getTask(jvmId); if (myTask.shouldDie()) { break; } else { if (myTask.getTask() == null) { taskid = null; if (++idleLoopCount >= SLEEP_LONGER_COUNT) { //we sleep for a bigger interval when we don't receive //tasks for a while Thread.sleep(1500); } else { Thread.sleep(500); } continue; } } idleLoopCount = 0; task = myTask.getTask(); taskid = task.getTaskID(); isCleanup = task.isTaskCleanupTask(); // reset the statistics for the task FileSystem.clearStatistics(); TaskLog.syncLogs(firstTaskid, taskid, isCleanup); JobConf job = new JobConf(task.getJobFile()); if (job.getBoolean("task.memory.mgmt.enabled", false)) { if (srcPidPath == null) { srcPidPath = new Path(task.getPidFile()); } //since the JVM is running multiple tasks potentially, we need //to do symlink stuff only for the subsequent tasks if (!taskid.equals(firstTaskid)) { dstPidPath = new Path(task.getPidFile()); FileUtil.symLink(srcPidPath.toUri().getPath(), dstPidPath.toUri().getPath()); } } //setupWorkDir actually sets up the symlinks for the distributed //cache. After a task exits we wipe the workdir clean, and hence //the symlinks have to be rebuilt. TaskRunner.setupWorkDir(job); numTasksToExecute = job.getNumTasksToExecutePerJvm(); assert(numTasksToExecute != 0); TaskLog.cleanup(job.getInt("mapred.userlog.retain.hours", 24)); task.setConf(job); defaultConf.addResource(new Path(task.getJobFile())); // use job-specified working directory FileSystem.get(job).setWorkingDirectory(job.getWorkingDirectory()); try { //执行任务 task.run(job, umbilical); // run the task } finally { TaskLog.syncLogs(firstTaskid, taskid, isCleanup); if (!taskid.equals(firstTaskid) && job.getBoolean("task.memory.mgmt.enabled", false)) { // delete the pid-file's symlink new File(dstPidPath.toUri().getPath()).delete(); } } if (numTasksToExecute > 0 && ++numTasksExecuted == numTasksToExecute) { break; } } } catch (FSError e) { LOG.fatal("FSError from child", e); umbilical.fsError(taskid, e.getMessage()); } catch (Throwable throwable) { LOG.warn("Error running child", throwable); try { if (task != null) { // do cleanup for the task task.taskCleanup(umbilical); } } catch (Throwable th) { LOG.info("Error cleaning up" + th); } // Report back any failures, for diagnostic purposes ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); throwable.printStackTrace(new PrintStream(baos)); if (taskid != null) { umbilical.reportDiagnosticInfo(taskid, baos.toString()); } } finally { RPC.stopProxy(umbilical); } }
2. TaskTracker 的getTask方法。TaskTracker实现了TaskUmbilicalProtocol接扣。getTask是该接口定义的一个方法。是子进程Child调用的根据jvmId获取task。
public synchronized JvmTask getTask(JVMId jvmId) throws IOException { TaskInProgress tip = jvmManager.getTaskForJvm(jvmId); if (tip == null) { return new JvmTask(null, false); } if (tasks.get(tip.getTask().getTaskID()) != null) { //is task still present LOG.info("JVM with ID: " + jvmId + " given task: " + tip.getTask().getTaskID()); return new JvmTask(tip.getTask(), false); } else { LOG.info("Killing JVM with ID: " + jvmId + " since scheduled task: " + tip.getTask().getTaskID() + " is " + tip.taskStatus.getRunState()); return new JvmTask(null, true); }
3.Task 的run方法。因为map和reduce的执行逻辑大不相同,先看下MapTask中该方法的实现。是真正执行用户定义的map或者reduce任务的入口,通过TaskUmbilicalProtocol向tasktracker上报执行进度。开启线程向TaskTracker上报进度,根据task的不同动作要求执行不同的方法,如jobClean,jobsetup,taskCleanup。对于部分的了解可以产看taskTracker获取Task文章中的 JobTracker的 heartbeat方法处的详细解释。
public void run(final JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException { // 开启线程向TaskTracker上报进度 TaskReporter reporter = new TaskReporter(getProgress(), umbilical); reporter.startCommunicationThread(); boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewMapper(); initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi); // 根据task的不同动作要求执行不同的方法,如jobClean,jobsetup,taskCleanup if (jobCleanup) { runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter); return; } if (jobSetup) { runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter); return; } if (taskCleanup) { runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter); return; } if (useNewApi) { runNewMapper(job, split, umbilical, reporter); } else { runOldMapper(job, split, umbilical, reporter); } done(umbilical, reporter); }
4. TaskReporter的run方法。定时向父进程TaskTracker上报状态和进度。
public void run() { final int MAX_RETRIES = 3; int remainingRetries = MAX_RETRIES; // get current flag value and reset it as well boolean sendProgress = resetProgressFlag(); while (!taskDone.get()) { try { boolean taskFound = true; // whether TT knows about this task // sleep for a bit try { Thread.sleep(PROGRESS_INTERVAL); } break; } if (sendProgress) { // we need to send progress update updateCounters(); taskStatus.statusUpdate(taskProgress.get(), taskProgress.toString(), counters); taskFound = umbilical.statusUpdate(taskId, taskStatus); taskStatus.clearStatus(); } else { // send ping taskFound = umbilical.ping(taskId); } // if Task Tracker is not aware of our task ID (probably because it died and // came back up), kill ourselves if (!taskFound) { LOG.warn("Parent died. Exiting "+taskId); System.exit(66); } sendProgress = resetProgressFlag(); remainingRetries = MAX_RETRIES; } catch (Throwable t) { } } } }
5. Task 的Initialize方法初始化后续要执行的几个重要变量。包括JobContext OutputFormat OutputCommitter等,这些都是后续执行中要用到的属性实例。
public void initialize(JobConf job, JobID id, Reporter reporter, boolean useNewApi) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException { jobContext = new JobContext(job, id, reporter); taskContext = new TaskAttemptContext(job, taskId, reporter); if (getState() == TaskStatus.State.UNASSIGNED) { setState(TaskStatus.State.RUNNING); } if (useNewApi) { LOG.debug("using new api for output committer"); outputFormat = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getOutputFormatClass(), job); committer = outputFormat.getOutputCommitter(taskContext); } else { committer = conf.getOutputCommitter(); } Path outputPath = FileOutputFormat.getOutputPath(conf); if (outputPath != null) { if ((committer instanceof FileOutputCommitter)) { FileOutputFormat.setWorkOutputPath(conf, ((FileOutputCommitter)committer).getTempTaskOutputPath(taskContext)); } else { FileOutputFormat.setWorkOutputPath(conf, outputPath); } } committer.setupTask(taskContext); }
6. Task的 runJobCleanupTask方法。即如果在Task是jobCleanup,则调用OutputCommitter删除输出文件
protected void runJobCleanupTask(TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical, TaskReporter reporter ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // set phase for this task setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.CLEANUP); getProgress().setStatus("cleanup"); statusUpdate(umbilical); // do the cleanup committer.cleanupJob(jobContext); done(umbilical, reporter);
}
7.Task的runJobSetupTask。如果Task是setupTask,则调用OutputCommitter,如创建Task要执行的根目录。
protected void runJobSetupTask(TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical, TaskReporter reporter ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // do the setup getProgress().setStatus("setup"); committer.setupJob(jobContext); done(umbilical, reporter); }
8. Task的runTaskCleanupTask。如果Task是taskCleanup,则调用taskCleanup 方法。最终OutputCommitter方法删除task的工作目录。
protected void runTaskCleanupTask(TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical, TaskReporter reporter) throws IOException, InterruptedException { taskCleanup(umbilical); done(umbilical, reporter); }
9.MapTask的runNewMapper方法是我们要重点关注的方法,是真正执行用户定义的map的方法。
1)根据传入的jobconf构造一个context,包含了job相关的所有配置信息,如后面用到的mapper、inputformat等。
2)根据配置的mapper类创建一个Mapper实例
3)根据配置的inputformat创建一个InputFormat实例。
4)重新够构建InputSplit
5)创建RecordReader,其实使用的是适配器模式适配了inputFormat的Reader。
6)构造输出RecordWriter。当没有Reducer时,output是配置的outputFormat的RecordWriter,即直接写输出。如果ruducer数量不为0,则构造一个NewOutputCollector
7)构造Mapper.Context,封装了刚才配置的所有信息,在map执行时候时候使用。
8)调用mapper的run方法来执行map动作。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>
void runNewMapper(final JobConf job,
final BytesWritable rawSplit,
final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
// 1. 根据传入的jobconf构造一个context,包含了job相关的所有配置信息,如后面用到的mapper、inputformat等。
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext(job, getTaskID());
// 2. 根据配置的mapper类创建一个Mapper实例
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
// 根据配置的input format创建一个InputFormat实例。
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
// 4.重新够构建InputSplit
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null;
DataInputBuffer splitBuffer = new DataInputBuffer();
splitBuffer.reset(rawSplit.getBytes(), 0, rawSplit.getLength());
SerializationFactory factory = new SerializationFactory(job);
Deserializer<? extends org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit>
deserializer =
(Deserializer<? extends org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit>)
factory.getDeserializer(job.getClassByName(splitClass));
deserializer.open(splitBuffer);
split = deserializer.deserialize(null);
//5. 创建RecordReader,其实使用的是适配器模式适配了inputFormat的Reader。
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input =
new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(inputFormat.createRecordReader(split, taskContext), reporter);
job.setBoolean("mapred.skip.on", isSkipping());
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter output = null;
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context
mapperContext = null;
try {
Constructor<org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.Context> contextConstructor =
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.Context.class.getConstructor
(new Class[]{org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.class,
Configuration.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptID.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.OutputCommitter.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.StatusReporter.class,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit.class});
//6. 构造输出RecordWriter。当没有Reducer时,output是配置的outputFormat的RecordWriter,即直接写输出。如果ruducer数量不为0,则构造一个NewOutputCollector
if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
output = outputFormat.getRecordWriter(taskContext);
} else {
output = new NewOutputCollector(job, umbilical, reporter);
}
//7.构造Mapper.Context,封装了刚才配置的所有信息,在map执行时候时候使用。
mapperContext = contextConstructor.newInstance(mapper, job, getTaskID(),
input, output, committer,
reporter, split);
input.initialize(split, mapperContext);
//8. 调用mapper的run方法来执行map动作。
mapper.run(mapperContext);
input.close();
output.close(mapperContext);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IOException("Can't find Context constructor", e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new IOException("Can't create Context", e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new IOException("Can't invoke Context constructor", e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new IOException("Can't invoke Context constructor", e);
}
}
10.Mapper的run方法。即对每一个输入的记录执行map方法。一般不会改变,就是拿出输入记录逐条执行map方法。除非要改变记录的执行方式,(如MultithreadedMapper需要多线程来执行),一般该方法不用override。
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { setup(context); while (context.nextKeyValue()) { map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context); } cleanup(context); } }
11.Mapper的map方法。即对每一个输入的记录执行map方法。这个只是默然的map执行方法,把输入不变的输出即可。用户定义的mapper就是override这个方法来按照自己定义的逻辑来处理数据。
protected void map(KEYIN key, VALUEIN value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value); }
完。
为了转载内容的一致性、可追溯性和保证及时更新纠错,转载时请注明来自:http://www.cnblogs.com/douba/p/hadoop_mapreduce_tasktracker_child_map.html。谢谢!