public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) { Father f = new Father(); Son s = new Son(); System.out.println(f.getInfo()); System.out.println(s.getInfo()); s.test(); System.out.println("-----------------"); s.setInfo("大硅谷"); System.out.println(f.getInfo()); System.out.println(s.getInfo()); s.test(); } } class Father{ private String info = "atguigu"; public void setInfo(String info){ this.info = info; } public String getInfo(){ return info; } } class Son extends Father{ private String info = "尚硅谷"; public void test(){ System.out.println(this.getInfo()); System.out.println(super.getInfo()); } }
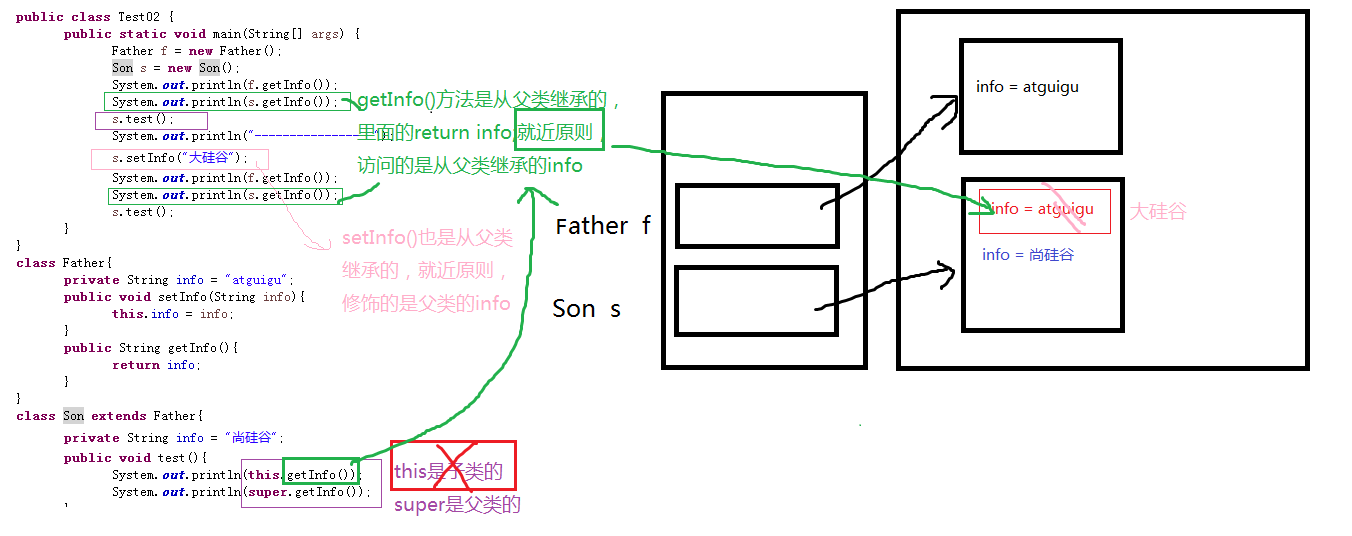
运行结果:
atguigu
atguigu
atguigu
atguigu
-----------------
atguigu
大硅谷
大硅谷
大硅谷
package com.atguigu.homewok.test03; public class Test03 { public static void main(String[] args) { Father f = new Father(); Son s = new Son(); System.out.println(f.getInfo()); System.out.println(s.getInfo()); s.test(); System.out.println("-----------------"); s.setInfo("大硅谷"); System.out.println(f.getInfo()); System.out.println(s.getInfo()); s.test(); } } class Father{ private String info = "atguigu"; public void setInfo(String info){ this.info = info; } public String getInfo(){ return info; } } class Son extends Father{ private String info = "尚硅谷"; public void setInfo(String info){ this.info = info; } public String getInfo(){ return info; } public void test(){ System.out.println(this.getInfo()); System.out.println(super.getInfo()); } }
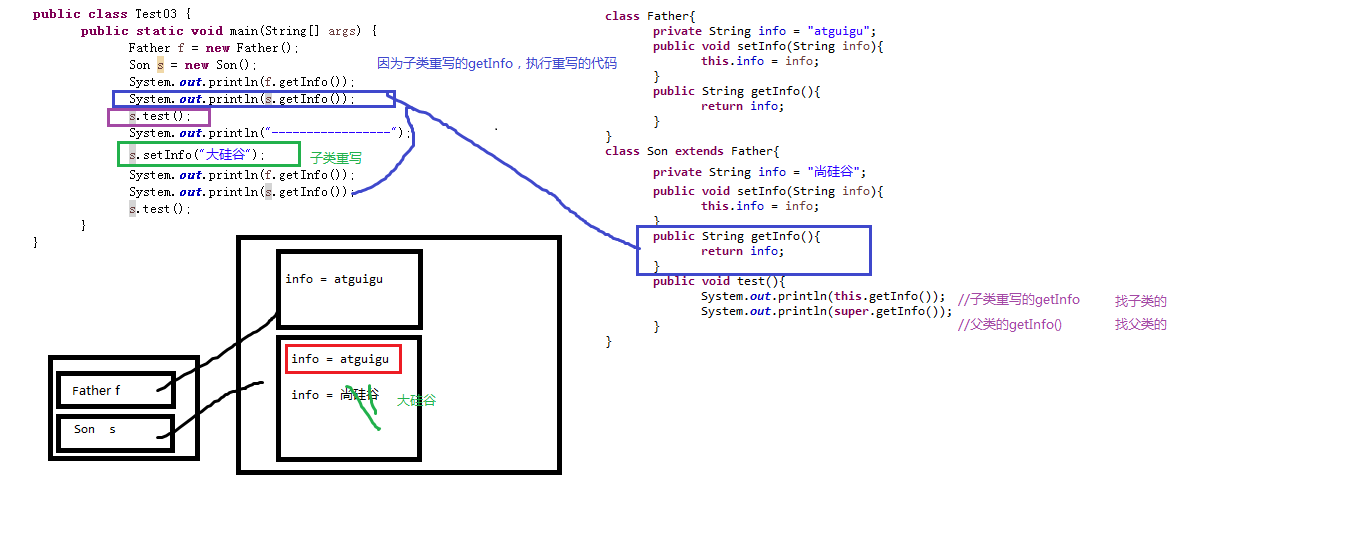
运行结果:
atguigu
尚硅谷
尚硅谷
atguigu
-----------------
atguigu
大硅谷
大硅谷
atguigu
package com.atguigu.homewok.test04; /* * 属性没有多态性。
多态性现象:编译时类型与运行时类型不一致 * 属性都是按照编译时类型处理的。 */ public class Test04 { public static void main(String[] args) { A a = new B(); System.out.println(a.num);//a编译时类型就是A 1 System.out.println(((B)a).num);//编译后,因为a被强制成B类,是B类型 2 System.out.println(((A)((B)a)).num);//编译后,a转成B又转成A,是A类型 1 System.out.println("-------------------"); B b = new B(); System.out.println(b.num);//b编译时类型就是B 2 System.out.println(((A)b).num);//b被强制升级为A类型,按A类型处理, 1 System.out.println(((B)((A)b)).num);//b先转A又转B,最终是B类型 2 } } class A{ int num = 1; } class B extends A{ int num = 2; }
package com.atguigu.homewok.test06; /* * 实例初始化的过程: * (1)父类的实例初始化 * <init>(){ * x = 10;//父类的x * this.print();//子类的print,因为this代表的是正在创建的子类对象,而子类重写了print,所以是子类的print' * System.out.println("Son.x = " + x);//子类的x 没有赋值x=0 x = 20;//父类的x * } * (2)子类的实例初始化 * <init>(){ * x = 30;//子类的x * this.print();//子类的print * System.out.println("Son.x = " + x);//子类的x 已经赋值x=30 x = 40;//子类的x * } */ public class Test06 { public static void main(String[] args) { Father f = new Son(); System.out.println(f.x);//编译时是Father类型,访问Father中的x x=20 } } class Father{ int x = 10; public Father(){ this.print(); x = 20; } public void print(){ System.out.println("Father.x = " + x); } } class Son extends Father{ int x = 30; public Son(){ this.print(); x = 40; } public void print(){ System.out.println("Son.x = " + x); } }
package com.atguigu.homewok.test07; /* * (1)类的初始化 * <clinit>(){ * int x = 5;//局部变量 x--;//局部变量 x=4 * Test07.x--;//静态变量 x = -1 * } * (2)执行main方法 * System.out.println("x=" + x);//静态变量 -1 * z--;//静态变量 z=-1 * method(); * y = z++ + ++z;//静态变量 * ①先加载z的值“-1”②z自增,z=0③z自增 z =1④加载z的值“1” ⑤求和 “-1” + “1” = 0⑥把0赋值给y y=0 * System.out.println("result:" + (z + y + ++z)); * ①加载z的值“1” ②加载y的值"0" ③z自增 z=2 ④加载z的值“2” ⑤求和 “1” + “0” + “2” * */ public class Test07 { static int x, y, z;//类变量,静态变量,成员变量 默认值0 static { int x = 5;//局部变量,因为赋值,所以是局部变量 x--;//局部变量 } static { x--;//静态变量 } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("x=" + x);//静态变量 z--;//静态变量 method(); System.out.println("result:" + (z + y + ++z));//静态变量 } public static void method() { y = z++ + ++z;//静态变量 } }
package com.atguigu.homewok.test08; /* * 1、Base b1 = new Base(); * 父类的实例初始化,和子类无关 * * <init>(){ * method(100); * System.out.println("base : " + i); base:100 * } * * 2、Base b2 = new Sub(); * (1) 父类的实例初始化 * * <init>(){ * method(100);//执行了子类重写的method() * System.out.println("sub : " + j); sub:100 * } * * (2)子类的实例初始化 * <init>(){ * super.method(70); * System.out.println("base : " + i); base:70 * } */ public class Test08 { public static void main(String[] args) { Base b1 = new Base(); Base b2 = new Sub(); } } class Base { Base() { method(100); } public void method(int i) { System.out.println("base : " + i); } } class Sub extends Base { Sub() { super.method(70); } public void method(int j) { System.out.println("sub : " + j); } }
public class Test09 { public static void main(String[] args) { Other o = new Other(); new Test09().addOne(o); System.out.println(o.i); } //o是引用数据类型,实参给形参的是地址值,那么形参修改了属性,实参也会修改 //o变量的值不能修改,不是说i的值不能修改 public void addOne(final Other o){ o.i++; } } class Other{ public int i;//默认值0 }
package com.atguigu.homewok.test02.day10; /* * 实例初始化的过程: * (1)父类的实例初始化 * <init>(){ * System.out.print("1"); * } * (2)子类的实例初始化 * <init>(String name){ * System.out.print("3"); * father = new People(name + " F");//创建了一个父类的对象 * 调用父类的<init>(String name){ * System.out.print("2"); * } * } * */ public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) { new Child("mike"); } } class People { private String name; public People() { System.out.print("1"); } public People(String name) { System.out.print("2"); this.name = name; } } class Child extends People { People father; public Child(String name) { //隐含了super() System.out.print("3"); father = new People(name + " F"); } public Child() { System.out.print("4"); } }
package com.atguigu.homewok.test07.day10; /* * new A(new B()); * (1)new B() * <init>(){ * System.out.println("B"); * } * (2)new A(B的对象) * <init>(B b){ * this(); * System.out.println("A"); * System.out.println("AB"); * } */ public class Test07 { public static void main(String[] args) { new A(new B()); } } class A { public A() { System.out.println("A"); } public A(B b) { this(); System.out.println("AB"); } } class B { public B() { System.out.println("B"); } }