1. 遇到的问题
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <future> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; class Counter { public: void addCount() { m_count++; } int count() const { return m_count; } Counter() : m_count(0) { } private: int m_count; }; int work(int a) { return a + a; } template<class Iter> void realWork(Counter& c, double &totalValue, Iter b, Iter e) { for (; b != e; ++b) { totalValue += work(*b); c.addCount(); } } int main() { unsigned n = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); cout << n << " concurrent threads are support. "; vector<int> vec; double totalValue = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { vec.push_back(rand() % 100); } Counter counter; realWork(counter, totalValue, vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "total times: " << counter.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; totalValue = 0; Counter counter2; auto iter = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3); auto iter2 = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3 * 2); thread b([&counter2, &totalValue, iter, iter2](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter, iter2); }); auto end = vec.end(); thread c([&counter2, &totalValue, iter2, end](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter2, end); }); realWork(counter2, totalValue, vec.begin(), iter); b.join(); c.join(); cout << "total times use multithread: " << counter2.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; return 0; }
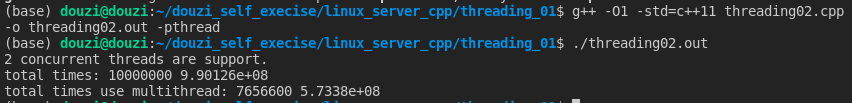
计算结果不一致!三个线程共享一份资源,有的加了有的没加。
2. 解决
2.1 法一:不共享变量
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <future> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; class Counter { public: void addCount() { m_count++; } int count() const { return m_count; } Counter() : m_count(0) { } private: int m_count; }; int work(int a) { return a + a; } template<class Iter> void realWork(Counter& c, double &totalValue, Iter b, Iter e) { for (; b != e; ++b) { totalValue += work(*b); c.addCount(); } } int main() { unsigned n = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); cout << n << " concurrent threads are support. "; vector<int> vec; double totalValue = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { vec.push_back(rand() % 100); } Counter counter; realWork(counter, totalValue, vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "total times: " << counter.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; totalValue = 0; Counter counter2; auto iter = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3); auto iter2 = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3 * 2); double totalC = 0; thread b([&counter2, &totalValue, iter, iter2](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter, iter2); }); auto end = vec.end(); thread c([&counter2, &totalC, iter2, end](){ realWork(counter2, totalC, iter2, end); }); double totalD = 0; realWork(counter2, totalD, vec.begin(), iter); b.join(); c.join(); cout << "total times use multithread: " << counter2.count() << " " << totalValue+totalC+totalD << endl; return 0; }

2.2 法二:原子操作变量类型(复杂,适合简单应用)
b,c 线程共享了变量 counter2, 没有共享变量 totalValue,所以totalValue一样,counter2.count()不一样
count++: 写入寄存器,寄存器+1,写入内存
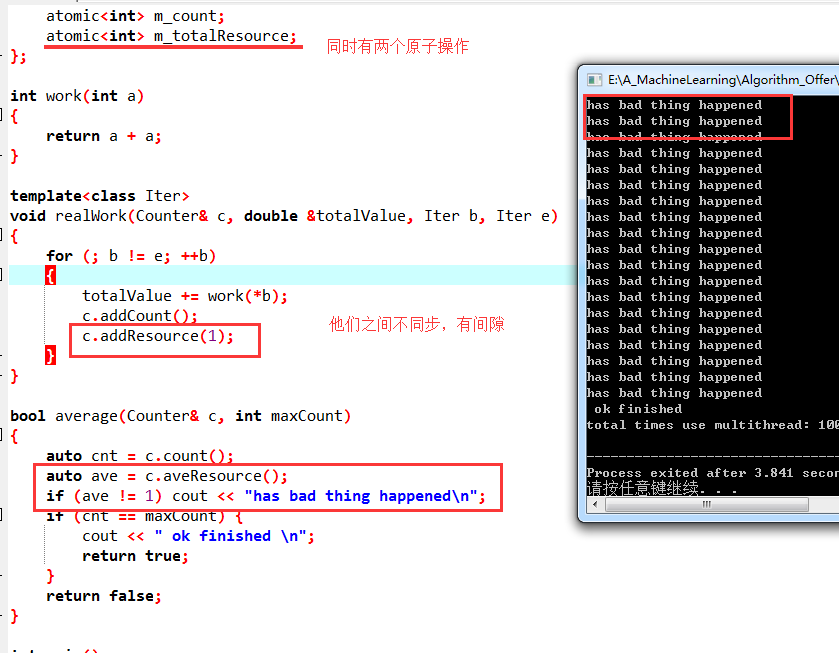
average()函数功能是如果Counter2不等于10000000,程序就不退出,如运行截图,由于共享变量counter2, 导致counter2总是无法等于10000000
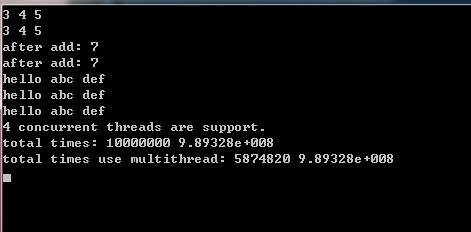
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <future> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <string> using namespace std; class Counter { public: void addCount() { m_count++; } int count() const { return m_count; } Counter() : m_count(0) { } private: int m_count; }; int work(int a) { return a + a; } template<class Iter> void realWork(Counter& c, double &totalValue, Iter b, Iter e) { for (; b != e; ++b) { totalValue += work(*b); c.addCount(); } } void printAll(int a, int b, int c) { cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << endl; } void add(int a, int b, int& c) { c = a + b; } void printString(const string& info, const string& info2) { cout << "hello " << info << " " << info2 << endl; } void testThreadInit() { int a = 3; int b = 4; int c = 5; thread t([=](){ printAll(a, b, c); }); t.join(); thread t2(printAll, a, b, c); t2.join(); thread t3([=, &c](){ add(a, b, c); }); t3.join(); cout << "after add: " << c << endl; // c是引用, 必须用 ref(c) c = 0; thread t4(add, a, b, std::ref(c)); t4.join(); cout << "after add: " << c << endl; string abc("abc"); string def("def"); thread t5([&](){ printString(abc, def); }); t5.join(); // 效率比引用低 thread t6(printString, abc, def); t6.join(); // cref: 常引用 thread t7(printString, cref(abc), cref(def)); t7.join(); } bool average(Counter& c, int maxCount) { auto cnt = c.count(); if (cnt == maxCount) { cout << " ok finished "; return true; } return false; } int main() { testThreadInit(); // (1) 如果没有必要的话,线程间不要共享资源 unsigned n = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); cout << n << " concurrent threads are support. "; vector<int> vec; double totalValue = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { vec.push_back(rand() % 100); } Counter counter; realWork(counter, totalValue, vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "total times: " << counter.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; totalValue = 0; Counter counter2; thread printCount([&counter2](){ while (!average(counter2, 10000000)) { } }); auto iter = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3); auto iter2 = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3 * 2); double totalC = 0; //b,c 线程共享了变量 counter2, 没有共享变量 totalValue,所以totalValue一样,counter2.count()不一样 thread b([&counter2, &totalValue, iter, iter2](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter, iter2); }); auto end = vec.end(); thread c([&counter2, &totalC, iter2, end](){ realWork(counter2, totalC, iter2, end); }); double totalD = 0; realWork(counter2, totalD, vec.begin(), iter); b.join(); c.join(); auto realTotalCount = counter2.count(); totalValue += totalC + totalD; cout << "total times use multithread: " << realTotalCount << " " << totalValue << endl; printCount.join(); // (2) return 0; }
解决:原子操作变量
只需要把int m_count; 改成 atomic<int> m_count; 即可
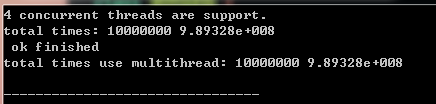
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <future> #include <atomic> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <string> using namespace std; class Counter { public: void addCount() { m_count++; } int count() const { return m_count; } Counter() : m_count(0) { } private: // atomic_int m_count; atomic<int> m_count; }; int work(int a) { return a + a; } template<class Iter> void realWork(Counter& c, double &totalValue, Iter b, Iter e) { for (; b != e; ++b) { totalValue += work(*b); c.addCount(); } } bool average(Counter& c, int maxCount) { auto cnt = c.count(); if (cnt == maxCount) { cout << " ok finished "; return true; } return false; } int main() { // (1) 如果没有必要的话,线程间不要共享资源 unsigned n = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); cout << n << " concurrent threads are support. "; vector<int> vec; double totalValue = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { vec.push_back(rand() % 100); } Counter counter; realWork(counter, totalValue, vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "total times: " << counter.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; totalValue = 0; Counter counter2; thread printCount([&counter2](){ while (!average(counter2, 10000000)) { } }); auto iter = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3); auto iter2 = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3 * 2); double totalC = 0; //b,c 线程共享了变量 counter2, 没有共享变量 totalValue,所以totalValue一样,counter2.count()不一样 thread b([&counter2, &totalValue, iter, iter2](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter, iter2); }); auto end = vec.end(); thread c([&counter2, &totalC, iter2, end](){ realWork(counter2, totalC, iter2, end); }); double totalD = 0; realWork(counter2, totalD, vec.begin(), iter); b.join(); c.join(); auto realTotalCount = counter2.count(); totalValue += totalC + totalD; cout << "total times use multithread: " << realTotalCount << " " << totalValue << endl; printCount.join(); return 0; }
3. 新需求
两个变量,其中第一个变量变化,另一个还没来得及变化,另一个线程又变化了第一个变量
4. 解决:临界区--mutex
4.1 核心部分
void lockMutex() { m_mutex.lock(); } void unlockMutex() { m_mutex.unlock(); }
c.lockMutex();
c.addCount(); c.addResource(1); c.unlockMutex();
完整代码:(不是非常好的写法)
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <future> #include <atomic> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <string> #include <mutex> using namespace std; class Counter { public: void addCount() { m_count++; } int count() const { return m_count; } Counter() : m_count(0) { } void addResource(int a) { m_totalResource++; } int aveResource() { if (m_count == 0) return 1; return m_totalResource / m_count; } void lockMutex() { m_mutex.lock(); } void unlockMutex() { m_mutex.unlock(); } private: // atomic_int m_count; atomic<int> m_count; atomic<int> m_totalResource; mutex m_mutex; }; int work(int a) { return a + a; } template<class Iter> void realWork(Counter& c, double &totalValue, Iter b, Iter e) { for (; b != e; ++b) { totalValue += work(*b); c.lockMutex(); c.addCount(); c.addResource(1); c.unlockMutex(); } } bool average(Counter& c, int maxCount) { auto cnt = c.count(); c.lockMutex(); auto ave = c.aveResource(); if (ave != 1) cout << "has bad thing happened "; c.unlockMutex(); if (cnt == maxCount) { cout << " ok finished "; return true; } return false; } int main() { // (1) 如果没有必要的话,线程间不要共享资源 unsigned n = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); cout << n << " concurrent threads are support. "; vector<int> vec; double totalValue = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { vec.push_back(rand() % 100); } Counter counter; realWork(counter, totalValue, vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "total times: " << counter.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; totalValue = 0; Counter counter2; thread printCount([&counter2](){ while (!average(counter2, 10000000)) { } }); auto iter = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3); auto iter2 = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3 * 2); double totalC = 0; //b,c 线程共享了变量 counter2, 没有共享变量 totalValue,所以totalValue一样,counter2.count()不一样 thread b([&counter2, &totalValue, iter, iter2](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter, iter2); }); auto end = vec.end(); thread c([&counter2, &totalC, iter2, end](){ realWork(counter2, totalC, iter2, end); }); double totalD = 0; realWork(counter2, totalD, vec.begin(), iter); b.join(); c.join(); auto realTotalCount = counter2.count(); totalValue += totalC + totalD; cout << "total times use multithread: " << realTotalCount << " " << totalValue << endl; printCount.join(); return 0; }
注意:使用临界区,可能会发生死锁
4.2 将锁写到接口里
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <future> #include <atomic> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <string> #include <mutex> using namespace std; class Counter { public: Counter() : m_count(0), m_totalResource(0) {} int count() { m_mutex.lock(); auto r = m_count; m_mutex.unlock(); return r; } int aveResource() { m_mutex.lock(); if (m_count == 0) { m_mutex.unlock(); return 1; } auto r = m_totalResource / m_count; m_mutex.unlock(); return r; } void addCoundAndResouce(int r) { m_mutex.lock(); addCount(); addResource(r); m_mutex.unlock(); } private: // atomic_int m_count; void addResource(int a) { m_totalResource++; } void addCount() { m_count++; } int m_count; int m_totalResource; mutex m_mutex; }; int work(int a) { return a + a; } template<class Iter> void realWork(Counter& c, double &totalValue, Iter b, Iter e) { for (; b != e; ++b) { totalValue += work(*b); c.addCoundAndResouce(1); } } bool average(Counter& c, int maxCount) { auto cnt = c.count(); auto ave = c.aveResource(); if (ave != 1) cout << "has bad thing happened "; if (cnt == maxCount) { cout << " ok finished "; return true; } return false; } int main() { // (1) 如果没有必要的话,线程间不要共享资源 unsigned n = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); cout << n << " concurrent threads are support. "; vector<int> vec; double totalValue = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { vec.push_back(rand() % 100); } Counter counter; realWork(counter, totalValue, vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "total times: " << counter.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; totalValue = 0; Counter counter2; thread printCount([&counter2](){ while (!average(counter2, 10000000)) { } }); auto iter = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3); auto iter2 = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3 * 2); double totalC = 0; //b,c 线程共享了变量 counter2, 没有共享变量 totalValue,所以totalValue一样,counter2.count()不一样 thread b([&counter2, &totalValue, iter, iter2](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter, iter2); }); auto end = vec.end(); thread c([&counter2, &totalC, iter2, end](){ realWork(counter2, totalC, iter2, end); }); double totalD = 0; realWork(counter2, totalD, vec.begin(), iter); b.join(); c.join(); auto realTotalCount = counter2.count(); totalValue += totalC + totalD; cout << "total times use multithread: " << realTotalCount << " " << totalValue << endl; printCount.join(); return 0; }
如果要把 count()设置成const
class Counter { public: Counter() : m_count(0), m_totalResource(0) {} int count() const { m_mutex.lock(); auto r = m_count; m_mutex.unlock(); return r; } int aveResource() { m_mutex.lock(); if (m_count == 0) { m_mutex.unlock(); return 1; } auto r = m_totalResource / m_count; m_mutex.unlock(); return r; } void addCoundAndResouce(int r) { m_mutex.lock(); addCount(); addResource(r); m_mutex.unlock(); } private: // atomic_int m_count; void addResource(int a) { m_totalResource++; } void addCount() { m_count++; } int m_count; int m_totalResource; mutable mutex m_mutex; };
将mutex设置成mutable类型
4.3 自定义lock类
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <chrono> #include <future> #include <atomic> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <cstdlib> #include <string> #include <mutex> using namespace std; template<typename T> class Lock{ public: Lock(T& mutex) : m_mutex(mutex) { m_mutex.lock(); } ~Lock() { m_mutex.unlock(); } private: T& m_mutex; }; class Counter { public: Counter() : m_count(0), m_totalResource(0) {} int count() const { Lock<mutex> lock(m_mutex); return m_count; } int aveResource() { Lock<mutex> lock(m_mutex); if (m_count == 0) { return 1; } return m_totalResource / m_count; } void addCoundAndResouce(int r) { Lock<mutex> lock(m_mutex); addCount(); addResource(r); m_mutex.unlock(); } private: // atomic_int m_count; void addResource(int a) { m_totalResource++; } void addCount() { m_count++; } int m_count; int m_totalResource; mutable mutex m_mutex; }; int work(int a) { return a + a; } template<class Iter> void realWork(Counter& c, double &totalValue, Iter b, Iter e) { for (; b != e; ++b) { totalValue += work(*b); c.addCoundAndResouce(1); } } bool average(Counter& c, int maxCount) { auto cnt = c.count(); auto ave = c.aveResource(); if (ave != 1) cout << "has bad thing happened "; if (cnt == maxCount) { cout << " ok finished "; return true; } return false; } int main() { // (1) 如果没有必要的话,线程间不要共享资源 unsigned n = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); cout << n << " concurrent threads are support. "; vector<int> vec; double totalValue = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { vec.push_back(rand() % 100); } Counter counter; realWork(counter, totalValue, vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "total times: " << counter.count() << " " << totalValue << endl; totalValue = 0; Counter counter2; thread printCount([&counter2](){ while (!average(counter2, 100000)) { } }); auto iter = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3); auto iter2 = vec.begin() + (vec.size() / 3 * 2); double totalC = 0; //b,c 线程共享了变量 counter2, 没有共享变量 totalValue,所以totalValue一样,counter2.count()不一样 thread b([&counter2, &totalValue, iter, iter2](){ realWork(counter2, totalValue, iter, iter2); }); auto end = vec.end(); thread c([&counter2, &totalC, iter2, end](){ realWork(counter2, totalC, iter2, end); }); double totalD = 0; realWork(counter2, totalD, vec.begin(), iter); b.join(); c.join(); auto realTotalCount = counter2.count(); totalValue += totalC + totalD; cout << "total times use multithread: " << realTotalCount << " " << totalValue << endl; printCount.join(); return 0; }
4.4 STL中的lock_guard
-
上述自定义lock换成lock_guard
-
lock_guard更灵活
class Counter { public: Counter() : m_count(0), m_totalResource(0) {} int count() const { lock_guard<mutex> lock(m_mutex); return m_count; } int aveResource() { lock_guard<mutex> lock(m_mutex); if (m_count == 0) { return 1; } return m_totalResource / m_count; } void addCoundAndResouce(int r) { lock_guard<mutex> lock(m_mutex); addCount(); addResource(r); m_mutex.unlock(); } private: // atomic_int m_count; void addResource(int a) { m_totalResource++; } void addCount() { m_count++; } int m_count; int m_totalResource; mutable mutex m_mutex; };
4.5 死锁
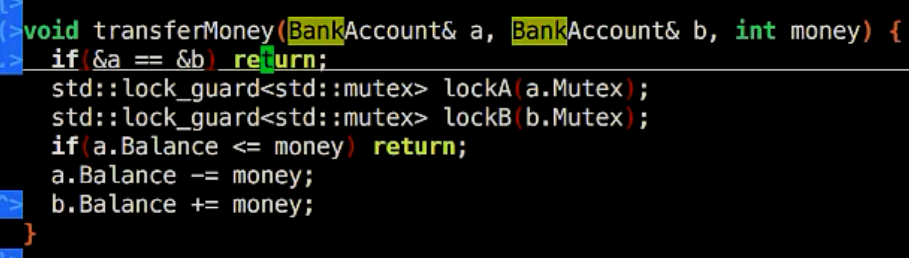
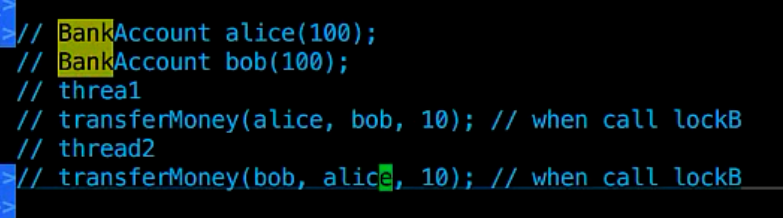
alice往bob账户转钱,线程1被锁;同时bob也往alice账户转钱,线程2被锁 ===》产生死锁
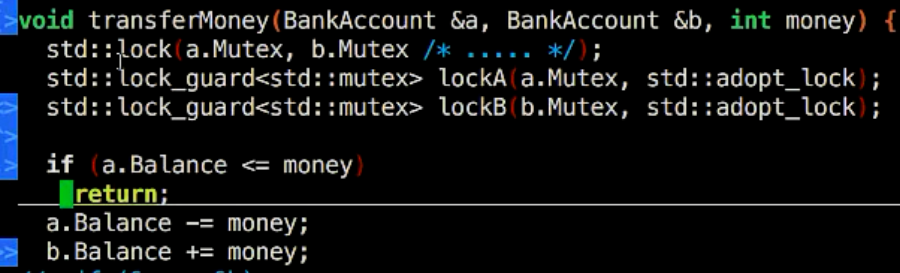
4.6 lock_guard解决死锁方案
- lock(.....): 一口气将里面的临界体mutex都锁住
- lock_guard<mutex> locka(a.mutex, adopt_lock): 告诉已经锁住了,只需要析构的时候解锁一下