概述
本章从下面几个方面来分析AOP的增强获取:
1、继续关系
2、增强的获取
3、增强的应用
继承关系
从之前的入口一节介绍过,AOP的核心为AnnotationAwareAspectAutoProxyCreator,接下来来分析一下这个类,首先看继承关系:
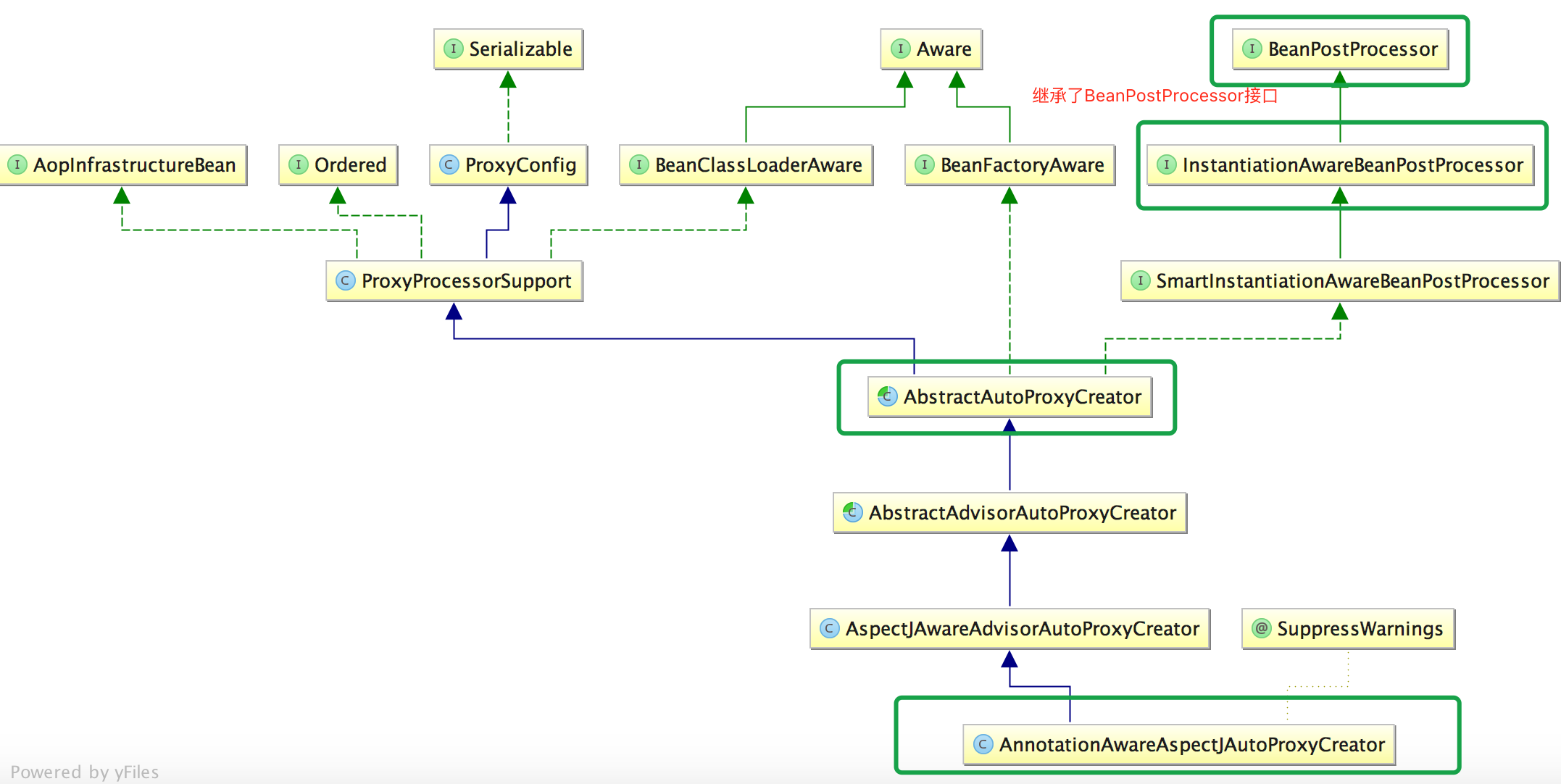
再看下类的层次关系,继承的类AbstractAutoProxyCreator,而AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了BeanPostProcessor接口:
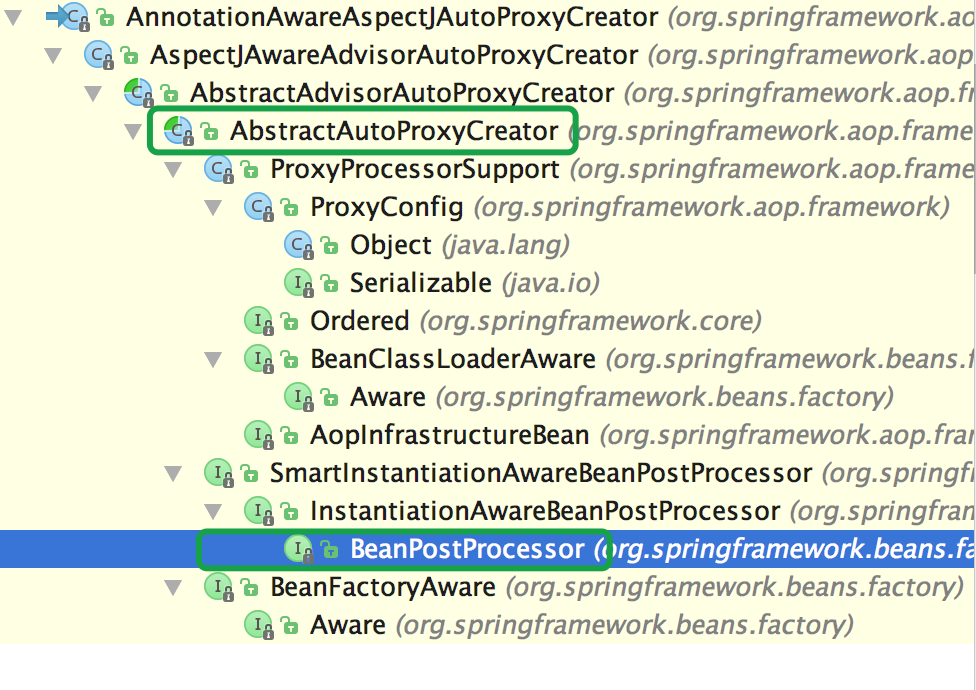
BeanPostProcessor接口是干什么的呢?
如果我们想在bean实例化或其他配置初始化之前或之后要添加一些自己的处理,则如下定义一个实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类,然后注册到Ioc容器中:
看下BeanPostProcessor的接口:
public interface BeanPostProcessor { Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
在AOP中,AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了该接口,且实现了接口中的方法:
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean != null) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); //根据给定的bean和className构建cacheKey,形式为beanClassName_beanName if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); //判断是否需要代理 } } return bean; } /** * Build a cache key for the given bean class and bean name. * @param beanClass the bean class * @param beanName the bean name * @return the cache key for the given class and name */ protected Object getCacheKey(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { return beanClass.getName() + "_" + beanName; } /** * Wrap the given bean if necessary, i.e. if it is eligible for being proxied. * @param bean the raw bean instance * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param cacheKey the cache key for metadata access * @return a proxy wrapping the bean, or the raw bean instance as-is */ protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { //是否被处理过 return bean; } if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { //无需增强 return bean; } if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { //是否为基础设施类,是否指定了不需要代理? this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } // Create proxy if we have advice. Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); //获取增强 if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { //如果获取了增强,则需要去创建代理 this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
从上面代码看,增强的获取是从getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法开始的,而AbstractAutoProxyCreator中的方法为抽象类,我们看具体的实现AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类:
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) { List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray(); } /** * Find all eligible Advisors for auto-proxying this class. * @param beanClass the clazz to find advisors for * @param beanName the name of the currently proxied bean * @return the empty List, not {@code null}, * if there are no pointcuts or interceptors * @see #findCandidateAdvisors * @see #sortAdvisors * @see #extendAdvisors */ protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//最终为这两个方法 List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); //获取所有的增强 List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); //增强中适用于bean的增强并应用 extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
findCandidateAdvisors(),寻找advisors,
AOP的配置
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true"> <aop:aspect ref="audience"> <aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(* com.spring.test.action1.Performer.perform(..))"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="takeSeats"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="turnOffCellPhones"/> <aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="performance" method="applaud"/> <aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="performance" method="demandRefund"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() { // Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already. String[] advisorNames = null; synchronized (this) { advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames; if (advisorNames == null) { // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the auto-proxy creator apply to them! advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( //获取所有的bean this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false); this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames; } } if (advisorNames.length == 0) { return new LinkedList<Advisor>(); } List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>(); for (String name : advisorNames) { if (isEligibleBean(name)) { //是否为合法的bean if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'"); } } else { try { advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class)); } catch (BeanCreationException ex) { Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause(); if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) { BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause; if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bce.getBeanName())) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping advisor '" + name + "' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage()); } // Ignore: indicates a reference back to the bean we're trying to advise. // We want to find advisors other than the currently created bean itself. continue; } } throw ex; } } } } return advisors; }
findAdvisorsThatCanApply()
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) { if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) { return candidateAdvisors; } List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { // already processed continue; } if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } return eligibleAdvisors; }
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass); } else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { //PointCut类型的advisor PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions); } else { // It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies. return true; } }
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null"); if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) { return false; } MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher(); IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null; if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) { introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher; } Set<Class<?>> classes = new HashSet<Class<?>>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass)); classes.add(targetClass); for (Class<?> clazz : classes) { Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null && introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) || methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) { return true; } } } return false; }
这个方法其实就是拿当前Advisor对应的expression做了两层判断:
- 目标类必须满足expression的匹配规则
- 目标类中的方法必须满足expression的匹配规则,当然这里方法不是全部需要满足expression的匹配规则,有一个方法满足即可
如果以上两条都满足,那么容器则会判断该<bean>满足条件,需要被生成代理对象,具体方式为返回一个数组对象,该数组对象中存储的是<bean>对应的Advisor。
获取增强的方法就到这里,接下来就是要处理createProxy了。下一节介绍