模型视图详解
在doDispatch中,SpringMVC会调用HandlerAdapter的handler方法获取ModelAndView对象,最后进行视图解析,视图渲染,都跟这个对象有着密切的关联。
/**
* Holder for both Model and View in the web MVC framework.
* Note that these are entirely distinct. This class merely holds
* both to make it possible for a controller to return both model
* and view in a single return value.
*
* <p>Represents a model and view returned by a handler, to be resolved
* by a DispatcherServlet. The view can take the form of a String
* view name which will need to be resolved by a ViewResolver object;
* alternatively a View object can be specified directly. The model
* is a Map, allowing the use of multiple objects keyed by name.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @see DispatcherServlet
* @see ViewResolver
* @see HandlerAdapter#handle
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller#handleRequest
*/
public class ModelAndView {
/** View instance or view name String */
private Object view;
/** Model Map */
private ModelMap model;
/** Optional HTTP status for the response */
private HttpStatus status;
/** Indicates whether or not this instance has been cleared with a call to {@link #clear()} */
private boolean cleared = false;
}
doDispatch中获取ModelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
下面,我将详细分析模型视图,其间将会看到常见ModelAttribute,参数解析,返回值转换等SpringMVC的主要内容。
1. 全局初始化:@ControllerAdvice
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean
透过RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的实现,我们知道RequestMappingHandlerAdapter是实现InitializingBean的,明显在初始化完成后会调用afterPropertiesSet方法,在afterPropertiesSet会调用initControllerAdviceCache()方法。
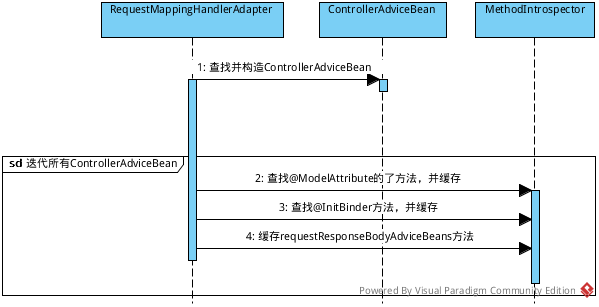
- 查找并构造ControllerAdviceBean
会从Bean容器中查找带有@ControllerAdvice注解的bean
public static List<ControllerAdviceBean> findAnnotatedBeans(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
List<ControllerAdviceBean> beans = new ArrayList<ControllerAdviceBean>();
for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, Object.class)) {
if (applicationContext.findAnnotationOnBean(name, ControllerAdvice.class) != null) {
beans.add(new ControllerAdviceBean(name, applicationContext));
}
}
return beans;
}
- 查找所有@ModelAttribute注解的方法
会选择不包含@RequestMapping但包汉@ModelAttribute注解的方法
public static final MethodFilter MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS = new MethodFilter() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method) {
return ((AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class) == null) &&
(AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, ModelAttribute.class) != null));
}
};
- 查找@InitBinder方法
public static final MethodFilter INIT_BINDER_METHODS = new MethodFilter() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method) {
return AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, InitBinder.class) != null;
}
};
- 缓存所有的requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans
if (RequestBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(bean.getBeanType())) {
requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.add(bean);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected RequestBodyAdvice bean in " + bean);
}
}
if (ResponseBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(bean.getBeanType())) {
requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.add(bean);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected ResponseBodyAdvice bean in " + bean);
}
}
}
if (!requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.requestResponseBodyAdvice.addAll(0, requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans);
}
2. 模型那些事
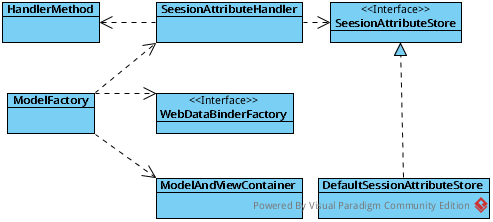
- 相关类图Overview
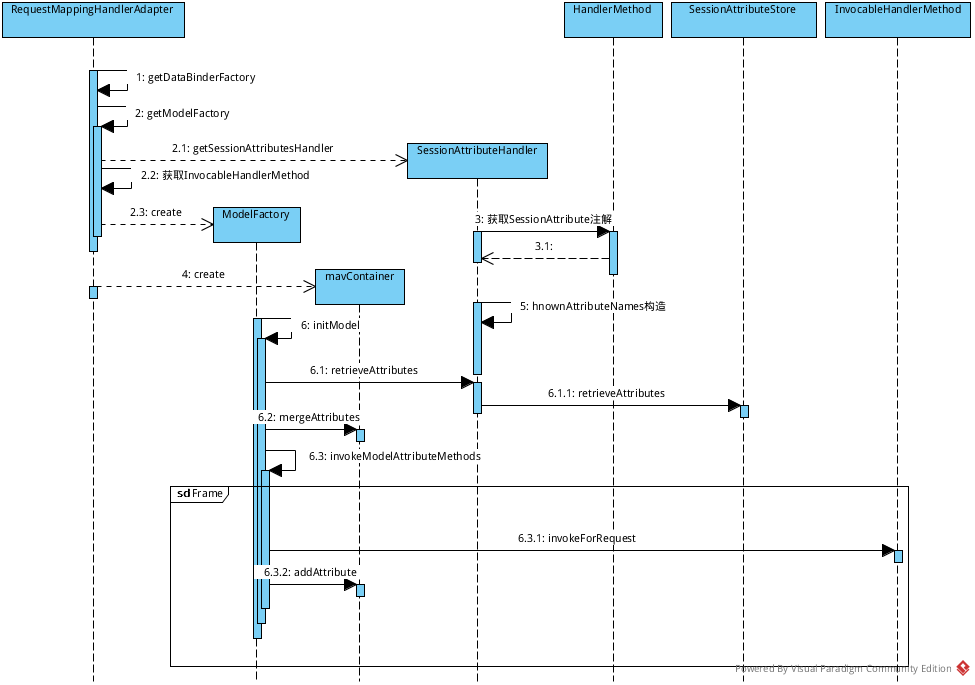
- 序列图Overview
- 浅谈SessionAttributeHandler
由前面的类图可知,SeesionAttibuteHandler代理了SessionAttibuteStore。而SessionAttibuteStore提供了简化从request的作用域中存取对象的操作,默认的DefaultSessionAttributeStore则是从session作用域中存取。
public interface SessionAttributeStore {
/**
* Store the supplied attribute in the backend session.
* <p>Can be called for new attributes as well as for existing attributes.
* In the latter case, this signals that the attribute value may have been modified.
* @param request the current request
* @param attributeName the name of the attribute
* @param attributeValue the attribute value to store
*/
void storeAttribute(WebRequest request, String attributeName, Object attributeValue);
/**
* Retrieve the specified attribute from the backend session.
* <p>This will typically be called with the expectation that the
* attribute is already present, with an exception to be thrown
* if this method returns {@code null}.
* @param request the current request
* @param attributeName the name of the attribute
* @return the current attribute value, or {@code null} if none
*/
Object retrieveAttribute(WebRequest request, String attributeName);
/**
* Clean up the specified attribute in the backend session.
* <p>Indicates that the attribute name will not be used anymore.
* @param request the current request
* @param attributeName the name of the attribute
*/
void cleanupAttribute(WebRequest request, String attributeName);
}
DefaultSessionAttributeStore中的实现,我们一其中一个实现一窥究竟。
@Override
public void storeAttribute(WebRequest request, String attributeName, Object attributeValue) {
Assert.notNull(request, "WebRequest must not be null");
Assert.notNull(attributeName, "Attribute name must not be null");
Assert.notNull(attributeValue, "Attribute value must not be null");
String storeAttributeName = getAttributeNameInSession(request, attributeName);
request.setAttribute(storeAttributeName, attributeValue, WebRequest.SCOPE_SESSION);
}
在构造SessionAttributeHandler时,会构造绑定到Session作用域的对象名称,通过@SessionAttributes注解来定义。
public SessionAttributesHandler(Class<?> handlerType, SessionAttributeStore sessionAttributeStore) {
Assert.notNull(sessionAttributeStore, "SessionAttributeStore may not be null");
this.sessionAttributeStore = sessionAttributeStore;
SessionAttributes annotation =
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(handlerType, SessionAttributes.class);
if (annotation != null) {
this.attributeNames.addAll(Arrays.asList(annotation.names()));
this.attributeTypes.addAll(Arrays.asList(annotation.types()));
}
for (String attributeName : this.attributeNames) {
this.knownAttributeNames.add(attributeName);
}
}
在调用完成所有@ModelAttribute注解的方法后,会解析HandlerMethod方法的参数中带有@ModelAttribute注解的参数,如果在ModelAndViewContainer容器中没有包含此ModelAttribute,则会从Session作用域中查找该值,如果不存在,直接抛出异常,交给框架顶层处理。
for (String name : findSessionAttributeArguments(handlerMethod)) {
if (!container.containsAttribute(name)) {
Object value = this.sessionAttributesHandler.retrieveAttribute(request, name);
if (value == null) {
throw new HttpSessionRequiredException("Expected session attribute '" + name + "'", name);
}
container.addAttribute(name, value);
}
}
private List<String> findSessionAttributeArguments(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
for (MethodParameter parameter : handlerMethod.getMethodParameters()) {
if (parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class)) {
String name = getNameForParameter(parameter);
Class<?> paramType = parameter.getParameterType();
if (this.sessionAttributesHandler.isHandlerSessionAttribute(name, paramType)) {
result.add(name);
}
}
}
return result;
}
- 浅谈@ModelAttibute
前面在@ControllerAdvice一节中,有提过,afterPropertiesSet中会全局缓存@ModelAttibute方法至modelAttributeAdviceCache中。注意@ModelAttibute注解,不仅可以出现先全局的@ControllerAdvice定义的bean中,还可以出现在@Controller注解的普通Controller中。所以在查询并构造@ModelAttibute方法时,会首先从全局缓存的@ControllerAdvice的bean中查找,然后从Controller中查找带有@ModelAttibute的方法。
private ModelFactory getModelFactory(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) {
SessionAttributesHandler sessionAttrHandler = getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod);
Class<?> handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
Set<Method> methods = this.modelAttributeCache.get(handlerType);
if (methods == null) {
methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS);
this.modelAttributeCache.put(handlerType, methods);
}
List<InvocableHandlerMethod> attrMethods = new ArrayList<InvocableHandlerMethod>();
// Global methods first
for (Entry<ControllerAdviceBean, Set<Method>> entry : this.modelAttributeAdviceCache.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
Object bean = entry.getKey().resolveBean();
for (Method method : entry.getValue()) {
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
}
}
for (Method method : methods) {
Object bean = handlerMethod.getBean();
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
return new ModelFactory(attrMethods, binderFactory, sessionAttrHandler);
}
private InvocableHandlerMethod createModelAttributeMethod(WebDataBinderFactory factory, Object bean, Method method) {
InvocableHandlerMethod attrMethod = new InvocableHandlerMethod(bean, method);
attrMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
attrMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
attrMethod.setDataBinderFactory(factory);
return attrMethod;
}
注意,@ModelAttribute方法同样支持@ModelAttribute参数,此为强依赖关系。所有的@ModelAttribute方法,最后都是缓存在ModelFactory的modelMethods中的。
public ModelFactory(List<InvocableHandlerMethod> handlerMethods,WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory, SessionAttributesHandler attributeHandler) {
if (handlerMethods != null) {
for (InvocableHandlerMethod handlerMethod : handlerMethods) {
this.modelMethods.add(new ModelMethod(handlerMethod));
}
}
this.dataBinderFactory = binderFactory;
this.sessionAttributesHandler = attributeHandler;
}
ModelFactory的initModel中,获取完session作用域的对象后,会钓鱼嗯invokModelAttributeMethods方法,会依次调用所的@ModelAttribute方法。在请求的时候可以拿到request对象,很明显可以解析大量的参数,对@ModelAttribute方法的参数赋值。
private void invokeModelAttributeMethods(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer container) throws Exception {
while (!this.modelMethods.isEmpty()) {
InvocableHandlerMethod modelMethod = getNextModelMethod(container).getHandlerMethod();
ModelAttribute ann = modelMethod.getMethodAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
if (container.containsAttribute(ann.name())) {
if (!ann.binding()) {
container.setBindingDisabled(ann.name());
}
continue;
}
Object returnValue = modelMethod.invokeForRequest(request, container);
if (!modelMethod.isVoid()){
String returnValueName = getNameForReturnValue(returnValue, modelMethod.getReturnType());
if (!ann.binding()) {
container.setBindingDisabled(returnValueName);
}
if (!container.containsAttribute(returnValueName)) {
container.addAttribute(returnValueName, returnValue);
}
}
}
}
顺便提一下,SpringMvc调用handlerMethod和ModelAttribute方法获取结果基本是一致的方式,只是handlerMethod方法需要再进行结果集的进一步加工,而ModelAttibute方法会将结果保存在ModelAndViewContainer中。
3. 参数解析
- 类图
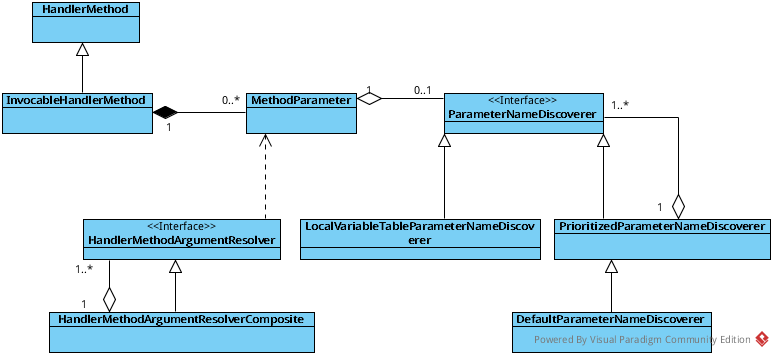
注意这边使用了两个组合模式,parameterNameDiscoverer族和handlerMethodArgumentResolver族 -
模型视图详解
在doDispatch中,SpringMVC会调用HandlerAdapter的handler方法获取ModelAndView对象,最后进行视图解析,视图渲染,都跟这个对象有着密切的关联。
/**
* Holder for both Model and View in the web MVC framework.
* Note that these are entirely distinct. This class merely holds
* both to make it possible for a controller to return both model
* and view in a single return value.
*
* <p>Represents a model and view returned by a handler, to be resolved
* by a DispatcherServlet. The view can take the form of a String
* view name which will need to be resolved by a ViewResolver object;
* alternatively a View object can be specified directly. The model
* is a Map, allowing the use of multiple objects keyed by name.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @see DispatcherServlet
* @see ViewResolver
* @see HandlerAdapter#handle
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller#handleRequest
*/
public class ModelAndView {
/** View instance or view name String */
private Object view;
/** Model Map */
private ModelMap model;
/** Optional HTTP status for the response */
private HttpStatus status;
/** Indicates whether or not this instance has been cleared with a call to {@link #clear()} */
private boolean cleared = false;
}
doDispatch中获取ModelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
下面,我将详细分析模型视图,其间将会看到常见ModelAttribute,参数解析,返回值转换等SpringMVC的主要内容。
1. 全局初始化:@ControllerAdvice
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean
透过RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的实现,我们知道RequestMappingHandlerAdapter是实现InitializingBean的,明显在初始化完成后会调用afterPropertiesSet方法,在afterPropertiesSet会调用initControllerAdviceCache()方法。

- 查找并构造ControllerAdviceBean
会从Bean容器中查找带有@ControllerAdvice注解的bean
public static List<ControllerAdviceBean> findAnnotatedBeans(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
List<ControllerAdviceBean> beans = new ArrayList<ControllerAdviceBean>();
for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, Object.class)) {
if (applicationContext.findAnnotationOnBean(name, ControllerAdvice.class) != null) {
beans.add(new ControllerAdviceBean(name, applicationContext));
}
}
return beans;
}
- 查找所有@ModelAttribute注解的方法
会选择不包含@RequestMapping但包汉@ModelAttribute注解的方法
public static final MethodFilter MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS = new MethodFilter() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method) {
return ((AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class) == null) &&
(AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, ModelAttribute.class) != null));
}
};
- 查找@InitBinder方法
public static final MethodFilter INIT_BINDER_METHODS = new MethodFilter() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method) {
return AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, InitBinder.class) != null;
}
};
- 缓存所有的requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans
if (RequestBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(bean.getBeanType())) {
requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.add(bean);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected RequestBodyAdvice bean in " + bean);
}
}
if (ResponseBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(bean.getBeanType())) {
requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.add(bean);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Detected ResponseBodyAdvice bean in " + bean);
}
}
}
if (!requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.requestResponseBodyAdvice.addAll(0, requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans);
}
2. 模型那些事
- 相关类图Overview

- 序列图Overview

- 浅谈SessionAttributeHandler
由前面的类图可知,SeesionAttibuteHandler代理了SessionAttibuteStore。而SessionAttibuteStore提供了简化从request的作用域中存取对象的操作,默认的DefaultSessionAttributeStore则是从session作用域中存取。
public interface SessionAttributeStore {
/**
* Store the supplied attribute in the backend session.
* <p>Can be called for new attributes as well as for existing attributes.
* In the latter case, this signals that the attribute value may have been modified.
* @param request the current request
* @param attributeName the name of the attribute
* @param attributeValue the attribute value to store
*/
void storeAttribute(WebRequest request, String attributeName, Object attributeValue);
/**
* Retrieve the specified attribute from the backend session.
* <p>This will typically be called with the expectation that the
* attribute is already present, with an exception to be thrown
* if this method returns {@code null}.
* @param request the current request
* @param attributeName the name of the attribute
* @return the current attribute value, or {@code null} if none
*/
Object retrieveAttribute(WebRequest request, String attributeName);
/**
* Clean up the specified attribute in the backend session.
* <p>Indicates that the attribute name will not be used anymore.
* @param request the current request
* @param attributeName the name of the attribute
*/
void cleanupAttribute(WebRequest request, String attributeName);
}
DefaultSessionAttributeStore中的实现,我们一其中一个实现一窥究竟。
@Override
public void storeAttribute(WebRequest request, String attributeName, Object attributeValue) {
Assert.notNull(request, "WebRequest must not be null");
Assert.notNull(attributeName, "Attribute name must not be null");
Assert.notNull(attributeValue, "Attribute value must not be null");
String storeAttributeName = getAttributeNameInSession(request, attributeName);
request.setAttribute(storeAttributeName, attributeValue, WebRequest.SCOPE_SESSION);
}
在构造SessionAttributeHandler时,会构造绑定到Session作用域的对象名称,通过@SessionAttributes注解来定义。
public SessionAttributesHandler(Class<?> handlerType, SessionAttributeStore sessionAttributeStore) {
Assert.notNull(sessionAttributeStore, "SessionAttributeStore may not be null");
this.sessionAttributeStore = sessionAttributeStore;
SessionAttributes annotation =
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(handlerType, SessionAttributes.class);
if (annotation != null) {
this.attributeNames.addAll(Arrays.asList(annotation.names()));
this.attributeTypes.addAll(Arrays.asList(annotation.types()));
}
for (String attributeName : this.attributeNames) {
this.knownAttributeNames.add(attributeName);
}
}
在调用完成所有@ModelAttribute注解的方法后,会解析HandlerMethod方法的参数中带有@ModelAttribute注解的参数,如果在ModelAndViewContainer容器中没有包含此ModelAttribute,则会从Session作用域中查找该值,如果不存在,直接抛出异常,交给框架顶层处理。
for (String name : findSessionAttributeArguments(handlerMethod)) {
if (!container.containsAttribute(name)) {
Object value = this.sessionAttributesHandler.retrieveAttribute(request, name);
if (value == null) {
throw new HttpSessionRequiredException("Expected session attribute '" + name + "'", name);
}
container.addAttribute(name, value);
}
}
private List<String> findSessionAttributeArguments(HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
for (MethodParameter parameter : handlerMethod.getMethodParameters()) {
if (parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class)) {
String name = getNameForParameter(parameter);
Class<?> paramType = parameter.getParameterType();
if (this.sessionAttributesHandler.isHandlerSessionAttribute(name, paramType)) {
result.add(name);
}
}
}
return result;
}
- 浅谈@ModelAttibute
前面在@ControllerAdvice一节中,有提过,afterPropertiesSet中会全局缓存@ModelAttibute方法至modelAttributeAdviceCache中。注意@ModelAttibute注解,不仅可以出现先全局的@ControllerAdvice定义的bean中,还可以出现在@Controller注解的普通Controller中。所以在查询并构造@ModelAttibute方法时,会首先从全局缓存的@ControllerAdvice的bean中查找,然后从Controller中查找带有@ModelAttibute的方法。
private ModelFactory getModelFactory(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) {
SessionAttributesHandler sessionAttrHandler = getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod);
Class<?> handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
Set<Method> methods = this.modelAttributeCache.get(handlerType);
if (methods == null) {
methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS);
this.modelAttributeCache.put(handlerType, methods);
}
List<InvocableHandlerMethod> attrMethods = new ArrayList<InvocableHandlerMethod>();
// Global methods first
for (Entry<ControllerAdviceBean, Set<Method>> entry : this.modelAttributeAdviceCache.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
Object bean = entry.getKey().resolveBean();
for (Method method : entry.getValue()) {
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
}
}
for (Method method : methods) {
Object bean = handlerMethod.getBean();
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
return new ModelFactory(attrMethods, binderFactory, sessionAttrHandler);
}
private InvocableHandlerMethod createModelAttributeMethod(WebDataBinderFactory factory, Object bean, Method method) {
InvocableHandlerMethod attrMethod = new InvocableHandlerMethod(bean, method);
attrMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
attrMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
attrMethod.setDataBinderFactory(factory);
return attrMethod;
}
注意,@ModelAttribute方法同样支持@ModelAttribute参数,此为强依赖关系。所有的@ModelAttribute方法,最后都是缓存在ModelFactory的modelMethods中的。
public ModelFactory(List<InvocableHandlerMethod> handlerMethods,WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory, SessionAttributesHandler attributeHandler) {
if (handlerMethods != null) {
for (InvocableHandlerMethod handlerMethod : handlerMethods) {
this.modelMethods.add(new ModelMethod(handlerMethod));
}
}
this.dataBinderFactory = binderFactory;
this.sessionAttributesHandler = attributeHandler;
}
ModelFactory的initModel中,获取完session作用域的对象后,会钓鱼嗯invokModelAttributeMethods方法,会依次调用所的@ModelAttribute方法。在请求的时候可以拿到request对象,很明显可以解析大量的参数,对@ModelAttribute方法的参数赋值。
private void invokeModelAttributeMethods(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer container) throws Exception {
while (!this.modelMethods.isEmpty()) {
InvocableHandlerMethod modelMethod = getNextModelMethod(container).getHandlerMethod();
ModelAttribute ann = modelMethod.getMethodAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
if (container.containsAttribute(ann.name())) {
if (!ann.binding()) {
container.setBindingDisabled(ann.name());
}
continue;
}
Object returnValue = modelMethod.invokeForRequest(request, container);
if (!modelMethod.isVoid()){
String returnValueName = getNameForReturnValue(returnValue, modelMethod.getReturnType());
if (!ann.binding()) {
container.setBindingDisabled(returnValueName);
}
if (!container.containsAttribute(returnValueName)) {
container.addAttribute(returnValueName, returnValue);
}
}
}
}
顺便提一下,SpringMvc调用handlerMethod和ModelAttribute方法获取结果基本是一致的方式,只是handlerMethod方法需要再进行结果集的进一步加工,而ModelAttibute方法会将结果保存在ModelAndViewContainer中。
3. 参数解析
- 类图

注意这边使用了两个组合模式,parameterNameDiscover族和handlerMethodArgumentResolver族。 - parameterNameDiscover族,默认使用的是DefaultParameterNameDiscover。parameterNameDiscover只有两个方法,故名思议,不做过多解释
public interface ParameterNameDiscoverer {
String[] getParameterNames(Method method);
String[] getParameterNames(Constructor<?> ctor);
}
public DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer() {
if (standardReflectionAvailable) {
addDiscoverer(new StandardReflectionParameterNameDiscoverer());
}
addDiscoverer(new LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer());
}
默认的实现最终是使用LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer。
/**
*Implementation of {@link ParameterNameDiscoverer} that uses the LocalVariableTable
*information in the method attributes to discover parameter names. Returns
*{@code null} if the class file was compiled without debug information.
*<p>Uses ObjectWeb's ASM library for analyzing class files. Each discoverer instance
*caches the ASM discovered information for each introspected Class, in a thread-safe
*manner. It is recommended to reuse ParameterNameDiscoverer instances as far as possible.
*@author Adrian Colyer
*@author Costin Leau
*@author Juergen Hoeller
*@author Chris Beams
*@since 2.0
*/
public class LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer implements ParameterNameDiscoverer {
LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer的实现会通过ASM分析.class文件,如果.class中不包含调式信息,是没办法知道参数名称,编译的时候会将本地变量重新编码优化,这地方确实是有点坑。好在SpringMVC中首先会从参数的注解中获取name,如果没有定义,才会使用变量名作为参数来解析。应当尽量在注解中定义参数名称,这样可以省去不少麻烦。
- HandlerMethodArgumentResolver族:
public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter);
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception;
}
只有两个方法,第一个方法supportsParameter的功能是判断该解析器是否支持传入的参数的解析,如果不支持会去下一个解析器来判断,知道找到合适的解析器,第二个才是真实的解析参数的方法。在RequestMappingHandlerAdapter初始化完成后的afterPropertiesSet方法会添加框架支持的参数解析器列表。
if (this.argumentResolvers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultArgumentResolvers();
this.argumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
if (this.argumentResolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
try {
args[i] = this.argumentResolvers.resolveArgument(
parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);
continue;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(getArgumentResolutionErrorMessage("Error resolving argument", i), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
本文先把目光聚焦到框架的实现上,以后在来详细分析每一个参数解析器的具体实现。HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite是一个合成对象,里面包含所有的参数解析器。
3. 返回值处理
- 类图
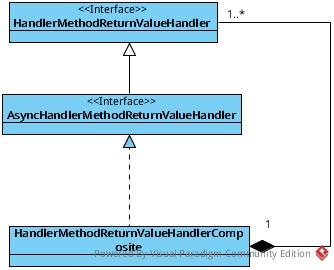
- SpringMVC对返回值的处理跟参数解析实现类似都是使用组合模式,关键方法也是类似的两个方法,同样本文不作详细分析,后面笔者会详细分析每一中返回值的解析。
public interface HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType);
void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception;
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers = getDefaultReturnValueHandlers();
this.returnValueHandlers = new HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite().addHandlers(handlers);
}
4. 返回ModelAndView
private ModelAndView getModelAndView(ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
ModelFactory modelFactory, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
modelFactory.updateModel(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
return null;
}
ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel();
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, mavContainer.getStatus());
if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) {
mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView());
}
if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes) {
Map<String, ?> flashAttributes = ((RedirectAttributes) model).getFlashAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = webRequest.getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class);
RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes);
}
return mav;
}