安装nc-vsock
https://github.com/stefanha/nc-vsock
root@ubuntu:~# git clone https://github.com/stefanha/nc-vsock.git git clone https://github.com/stefanha/nc-vsock.git Cloning into 'nc-vsock'... remote: Enumerating objects: 16, done. remote: Total 16 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 16 Unpacking objects: 100% (16/16), done. root@ubuntu:~# ls ls build-aarch64 firecracker.sh go install_kata.sh nc-vsock rootfs start_fire_vm.sh firecracker get_vm.sh install_docker_ce.sh kata network.sh sock.sh v.sock root@ubuntu:~# cd nc-vsock/ cd nc-vsock/ root@ubuntu:~/nc-vsock# ls ls LICENSE Makefile nc-vsock.c nc-vsock.spec root@ubuntu:~/nc-vsock# make make cc nc-vsock.c -o nc-vsock root@ubuntu:~/nc-vsock# ls ls LICENSE Makefile nc-vsock nc-vsock.c nc-vsock.spec root@ubuntu:~/nc-vsock# ldd nc-vsock ldd nc-vsock linux-vdso.so.1 (0x0000ffff8d6a3000) libc.so.6 => /lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 (0x0000ffff8d50b000) /lib/ld-linux-aarch64.so.1 (0x0000ffff8d678000) root@ubuntu:~/nc-vsock# ls /tmp/my-rootfs/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/lib libc-2.27.so libc.so.6 libdl-2.27.so libdl.so.2 libtinfo.so.5 libtinfo.so.5.9 root@ubuntu:~/nc-vsock# ls /tmp/my-rootfs/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 ls /tmp/my-rootfs/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 /tmp/my-rootfs/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 root@ubuntu:~/nc-vsock# ls /tmp/my-rootfs/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 -l ls /tmp/my-rootfs/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 -l lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 12 Jun 5 01:25 /tmp/my-rootfs/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 -> libc-2.27.so root@ubuntu:~/nc-vsock#
ubuntu@ubuntu:~$ lsmod | grep vhost_vsock vhost_vsock 24576 0 vmw_vsock_virtio_transport_common 36864 1 vhost_vsock vsock 45056 2 vmw_vsock_virtio_transport_common,vhost_vsock vhost 57344 2 vhost_vsock,vhost_net ubuntu@ubuntu:~$
ubuntu@ubuntu:~$ nc -vsock -l 52 nc: getaddrinfo: Temporary failure in name resolution ubuntu@ubuntu:~$ sudo su [sudo] password for ubuntu: root@ubuntu:/home/ubuntu# nc -vsock -l 52 nc: getaddrinfo: Name or service not known root@ubuntu:/home/ubuntu#

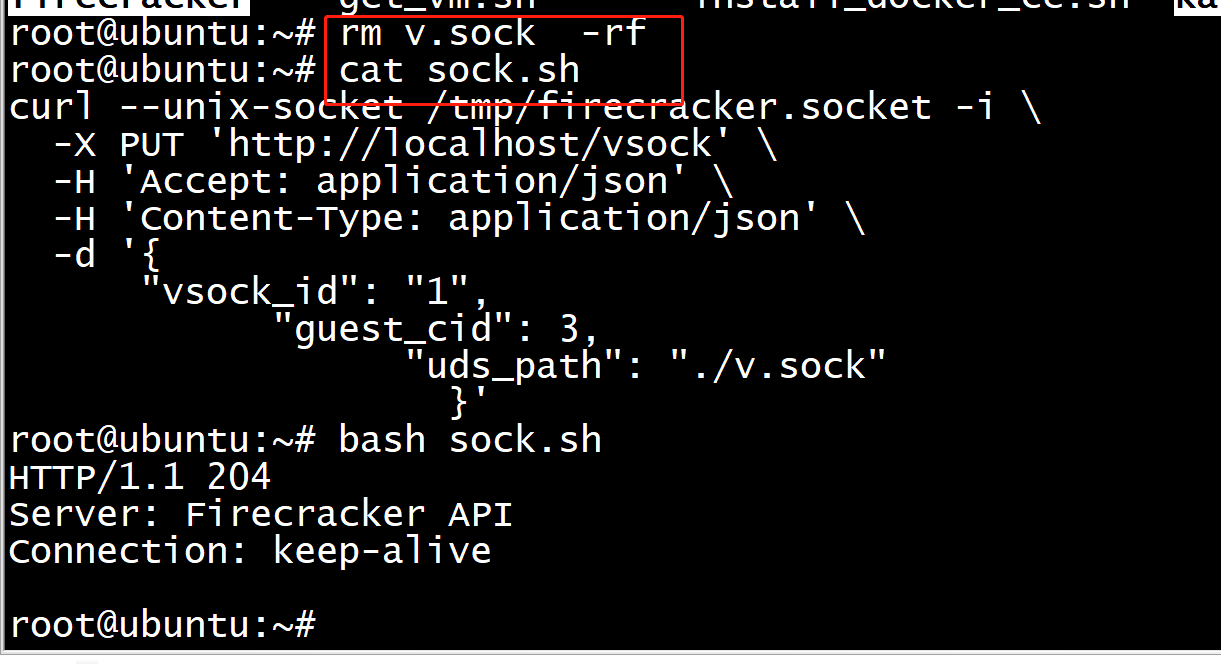
curl --unix-socket /tmp/firecracker.socket -i -X PUT 'http://localhost/vsock' -H 'Accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "vsock_id": "1", "guest_cid": 3, "uds_path": "./v.sock" }'
curl --unix-socket /tmp/firecracker.socket -i -X PUT 'http://localhost/vsock' -H 'Accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "vsock_id": "1", "guest_cid": 3, "uds_path": "./v.sock" }' root@ubuntu:~#
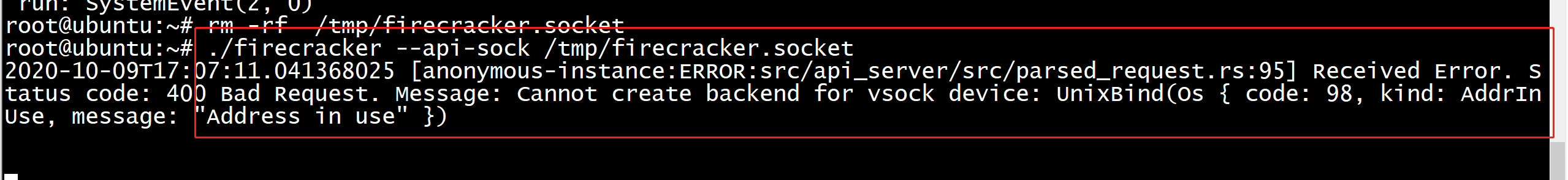
{"fault_message":"Cannot create backend for vsock device: UnixBind(Os { code: 98, kind: AddrInUse, message: "Address in use" })"}

Using the Firecracker Virtio-vsock Device
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
This document assumes the reader is familiar with running Firecracker and issuing API commands over its API socket. For a more details on how to run Firecracker, check out the getting started guide.
Familiarity with socket programming, in particular Unix sockets, is also assumed.
Firecracker Virtio-vsock Design
The Firecracker vsock device aims to provide full virtio-vsock support to software running inside the guest VM, while bypassing vhost kernel code on the host. To that end, Firecracker implements the virtio-vsock device model, and mediates communication between AF_UNIX sockets (on the host end) and AF_VSOCK sockets (on the guest end).
In order to provide channel multiplexing the guest AF_VSOCK ports are mapped 1:1 to AF_UNIX sockets on the host. The virtio-vsock device must be configured with a path to an AF_UNIX socket on the host (e.g. /path/to/v.sock). There are two scenarios to be considered, depending on where the connection is initiated.
Host-Initiated Connections
When a microvm having a vsock device attached is started, Firecracker will begin listening on an AF_UNIX socket (e.g. /path/to/v.sock). When the host needs to initiate a connection, it should connect to that Unix socket, then send a connect command, in text form, specifying the destination AF_VSOCK port: "CONNECT PORT
". Where PORT is the decimal port number, and "
" is EOL (ASCII 0x0A). Following that, the same connection will be forwarded by Firecracker to the guest software listening on that port, thus establishing the requested channel. If the connection has been established, Firecracker will send an acknowledgement message to the connecting end (host-side), in the form "OK PORT
", where PORT is the vsock port number assigned to the host end. If no one is listening, Firecracker will terminate the host connection.
Client A initiates connection to Server A in figure below:
- Host: At VM configuration time, add a virtio-vsock device, with some path specified in
uds_path; - Guest: create an AF_VSOCK socket and
listen()on<port_num>; - Host:
connect()to AF_UNIX atuds_path. - Host:
send()"CONNECT <port_num> ". - Guest:
accept()the new connection. - Host:
read()"OK <assigned_hostside_port> ".
The channel is established between the sockets obtained at steps 3 (host) and 5 (guest).
Guest-Initiated Connections
When the virtio-vsock device model in Firecracker detects a connection request coming from the guest (a VIRTIO_VSOCK_OP_REQUEST packet), it tries to forward the connection to an AF_UNIX socket listening on the host, at /path/to/v.sock_PORT (or whatever path was configured via the uds_path property of the vsock device), where PORT is the destination port (in decimal), as specified in the connection request packet. If no such socket exists, or no one is listening on it, a connection cannot be established, and a VIRTIO_VSOCK_OP_RST packet will be sent back to the guest.
Client B initiates connection to Server B in figure below:
- Host: At VM configuration time, add a virtio-vsock device, with some
uds_path(e.g./path/to/v.sock). - Host: create and listen on an AF_UNIX socket at
/path/to/v.sock_PORT. - Guest: create an AF_VSOCK socket and connect to
HOST_CID(i.e. integer value 2) andPORT; - Host:
accept()the new connection.
The channel is established between the sockets obtained at steps 4 (host) and 3 (guest).

Setting up the virtio-vsock device
The virtio-vsock device will require an ID, a CID, and the path to a backing AF_UNIX socket:
curl --unix-socket /tmp/firecracker.socket -i
-X PUT 'http://localhost/vsock'
-H 'Accept: application/json'
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
-d '{
"vsock_id": "1",
"guest_cid": 3,
"uds_path": "./v.sock"
}'
Once the microvm is started, Firecracker will create and start listening on the AF_UNIX socket at uds_path. Incoming connections will get forwarded to the guest microvm, and translated to AF_VSOCK. The destination port is expected to be specified by sending the text command "CONNECT <port_num>
", immediately after the AF_UNIX connection is established. Connections initiated from within the guest will be forwarded to AF_UNIX sockets expected to be listening at ./v.sock_<port_num>. I.e. a guest connection to port 52 will get forwarded to ./v.sock_52.
Examples
The examples below assume a running microvm, with a vsock device configured as shown above.
Using External Socket Tools (nc-vsock and socat)
Connecting From Host to Guest
First, make sure the vsock port is bound and listened to on the guest side. Say, port 52:
$ nc-vsock -l 52
On the host side, connect to ./v.sock and issue a connection request to that port:
$ socat - UNIX-CONNECT:./v.sock
CONNECT 52
socat will display the connection acknowledgement message:
OK 1073741824
The connection should now be established (in the above example, between nc-vsock on the guest side, and socat on the host side).
Connecting From Guest To Host
First make sure the AF_UNIX corresponding to your desired port is listened to on the host side:
$ socat - UNIX-LISTEN:./v.sock_52
On the guest side, create an AF_VSOCK socket and connect it to the previously chosen port on the host (CID=2):
$ nc-vsock 2 52