client
第一次发送给server 50000
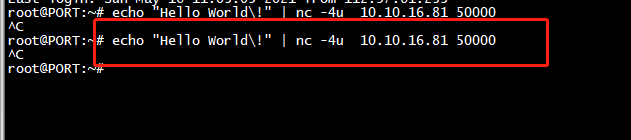
root@ubuntu:~/c++# echo "Hello World!" | nc -4u 10.10.16.81 50000
client
第二次发送给server 50003 (不是服务器的端口)
root@ubuntu:~/c++# echo "Hello World!" | nc -4u 10.10.16.81 50000 root@ubuntu:~/c++# echo "Hello World!" | nc -4u 10.10.16.81 50003 root@ubuntu:~/c++# echo "Hello World!" | nc -4u 10.10.16.81 50003 root@ubuntu:~/c++#
server
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <linux/udp.h> #include <signal.h> #include <errno.h> #include <linux/ip.h> struct sockaddr_in *servaddr = NULL, *client_addr = NULL; int sock_fd; #define PORT 50000 #define PORT_CLIENT 50001 #define SERVER_ADDR "10.10.16.81" #define CLIENT_ADDR "10.10.16.82" /* structure to calculate UDP checksum * The below members are part of the IP header * which do not change from the UDP layer and hence * are used as a part of the UDP checksum */ struct pseudo_iphdr { unsigned int source_ip_addr; unsigned int dest_ip_addr; unsigned char fixed; unsigned char protocol; unsigned short udp_len; }; /* checksum code to calculate TCP/UDP checksum * Code taken from Unix network programming – Richard stevens*/ unsigned short in_cksum (uint16_t * addr, int len) { int nleft = len; unsigned int sum = 0; unsigned short *w = addr; unsigned short answer = 0; /* Our algorithm is simple, using a 32 bit accumulator (sum), we add * sequential 16 bit words to it, and at the end, fold back all the * carry bits from the top 16 bits into the lower 16 bits. */ while (nleft > 1) { sum += *w++; nleft -= 2; } /* mop up an odd byte, if necessary */ if (nleft == 1) { *(unsigned char *) (&answer) = * (unsigned char *) w; sum += answer; } /* add back carry outs from top 16 bits to low 16 bits */ sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff); /* add hi 16 to low 16 */ sum += (sum >> 16); /* add carry */ answer = (unsigned short) ~sum; /* truncate to 16 bits */ return (answer); } /* Interrupt_handler – so that CTRL + C can be used to * exit the program */ void interrupt_handler (int signum) { close(sock_fd); free(client_addr); exit(0); } #if DEBUG /* print the IP and UDP headers */ void dumpmsg(unsigned char *recvbuffer, int length) { int count_per_length = 28, i = 0; for (i = 0; i < count_per_length; i++) { printf("%02x ", recvbuffer[i]); } printf(" "); } #endif int main () { char buffer[1024] = {0}; unsigned char recvbuffer[1024] = {0}; int length; char *string = "Hello client"; struct udphdr *udp_hdr = NULL; char *string_data = NULL; char *recv_string_data = NULL; char *csum_buffer = NULL; struct pseudo_iphdr csum_hdr; int error; signal (SIGINT, interrupt_handler); signal (SIGTERM, interrupt_handler); /* Part 1: create the socket */ sock_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_UDP); if(0 > sock_fd) { printf("unable to create socket "); exit(0); } servaddr = (struct sockaddr_in *)malloc(sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); if (servaddr == NULL) { printf("could not allocate memory "); goto end; } servaddr->sin_family = AF_INET; servaddr->sin_port = PORT; servaddr->sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERVER_ADDR); /* Part 2 – fill data structure and bind to socket */ if (0 != (bind(sock_fd, (struct sockaddr *)servaddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)))) { printf("could not bind server socket to address "); goto end1; } /* part 3: read and write data */ client_addr = (struct sockaddr_in *)malloc(sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); if (client_addr == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory to client address socket "); goto end2; } client_addr->sin_family = AF_INET; client_addr->sin_port = PORT_CLIENT; client_addr->sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(CLIENT_ADDR); error = connect(sock_fd, (struct sockaddr *)client_addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); if (error != 0) { printf("error %d", errno); printf("connect returned error "); goto end2; } /* copy the data after the UDP header */ string_data = (char *) (buffer + sizeof(struct udphdr)); strncpy(string_data, string, strlen(string)); /* Modify some parameters to send to client in UDP hdr */ udp_hdr = (struct udphdr *)buffer; udp_hdr->source = htons(PORT); udp_hdr->dest = htons(PORT_CLIENT); udp_hdr->len = htons(sizeof(struct udphdr)); /* calculate the UDP checksum – based on wikipedia * pseudo IP header + UDP HDR + * UDP data- check sum is calculated. * create a buffer to calculate CSUM and calculate CSUM*/ csum_buffer = (char *)calloc((sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr) + sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data)), sizeof(char)); if (csum_buffer == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate csum buffer "); goto end1; } csum_hdr.source_ip_addr = inet_addr(SERVER_ADDR); csum_hdr.dest_ip_addr = inet_addr(CLIENT_ADDR); csum_hdr.fixed = 0; csum_hdr.protocol = IPPROTO_UDP; /* UDP protocol */ csum_hdr.udp_len = htons(sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data) + 1); memcpy(csum_buffer, (char *)&csum_hdr, sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr)); memcpy(csum_buffer + sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr), buffer, (sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data) + 1)); udp_hdr->check = (in_cksum((unsigned short *) csum_buffer, (sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr)+ sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data) + 1))); printf("checksum is %x ", udp_hdr->check); /* since we are resending the same packet over and over again * free the csum buffer here */ free (csum_buffer); while (1) { memset(recvbuffer, 0, sizeof(recvbuffer)); read(sock_fd, recvbuffer, sizeof(recvbuffer)); udp_hdr = (struct udphdr *)(recvbuffer + sizeof (struct iphdr)); recv_string_data = (char *) (recvbuffer + sizeof (struct iphdr) + sizeof (struct udphdr)); #if DEBUG dumpmsg((unsigned char *)&recvbuffer, (sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct udphdr)+ strlen(string_data) + 1)); #endif //if (PORT == ntohs(udp_hdr->dest)) { // printf("udp data received from port : %d ",ntohs(udp_hdr->source)); // printf("data received at server from client is: %s ", recv_string_data); //} printf("udp data received from port : %d ",ntohs(udp_hdr->source)); printf("data received at server from client is: %s ", recv_string_data); write(sock_fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)); } end2: free(client_addr); end1: free(servaddr); end: close(sock_fd); return 0; }
server端tcpdump
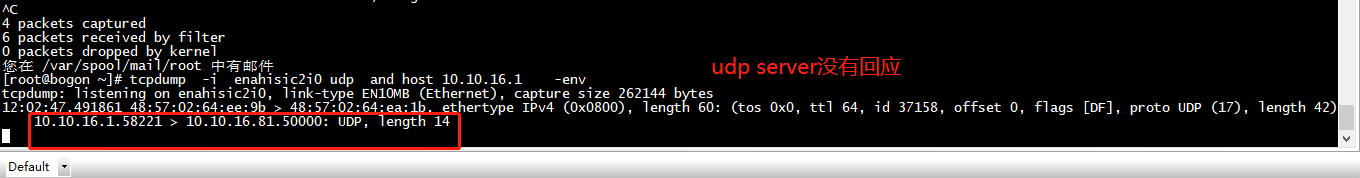
用了 connect t 和bind 定义了port 也能收到其他报文的


换个client ip
clien发送
server 抓包
server 本地访问

udp raw client
[root@bogon raw-sockets-example]# cat raw_udp_client.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <signal.h> #include <errno.h> #include <linux/ip.h> #include <linux/udp.h> struct sockaddr_in *serveraddr = NULL, *clientaddr; int sockfd; #define PORT 50001 #define SERVER_PORT 50000 #define SERVER_ADDR "10.10.16.81" #define CLIENT_ADDR "10.10.16.82" /* structure to calculate UDP checksum * The below members are part of the IP header * which do not change from the UDP layer and hence * are used as a part of the UDP checksum */ struct pseudo_iphdr { unsigned int source_ip_addr; unsigned int dest_ip_addr; unsigned char fixed; unsigned char protocol; unsigned short udp_len; }; /* checksum code to calculate UDP checksum * Code taken from Unix network programming – Richard stevens*/ unsigned short in_cksum (uint16_t * addr, int len) { int nleft = len; unsigned int sum = 0; unsigned short *w = addr; unsigned short answer = 0; /* Our algorithm is simple, using a 32 bit accumulator (sum), we add * sequential 16 bit words to it, and at the end, fold back all the * carry bits from the top 16 bits into the lower 16 bits. */ while (nleft > 1) { sum += *w++; nleft -= 2; } /* mop up an odd byte, if necessary */ if (nleft == 1) { *(unsigned char *) (&answer) = * (unsigned char *) w; sum += answer; } /* add back carry outs from top 16 bits to low 16 bits */ sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff); /* add hi 16 to low 16 */ sum += (sum >> 16); /* add carry */ answer = (unsigned short) ~sum; /* truncate to 16 bits */ return (answer); } /* Interrupt_handler – so that CTRL + C can be used to * exit the program */ void interrupt_handler (int signum) { close(sockfd); free(clientaddr); exit(0); } #if DEBUG /* print the IP and UDP headers */ void dumpmsg(unsigned char *recvbuffer, int length) { int count_per_length = 28, i = 0; for (i = 0; i < count_per_length; i++) { printf("%02x ", recvbuffer[i]); } printf(" "); } #endif int main () { char buffer[1024] = {0}; unsigned char recvbuffer[1024] = {0}; int length; char *string = "Hello UDP server"; struct udphdr *udp_hdr = NULL; char *string_data = NULL; char *recv_string_data = NULL; char *csum_buffer = NULL; struct pseudo_iphdr csum_hdr; int error; signal (SIGINT, interrupt_handler); signal (SIGTERM, interrupt_handler); /* Part 1: create the socket */ sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_UDP); if(0 > sockfd) { printf("unable to create socket "); exit(0); } clientaddr = (struct sockaddr_in *)malloc(sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); if (clientaddr == NULL) { printf("could not allocate memory "); goto end; } clientaddr->sin_family = AF_INET; clientaddr->sin_port = PORT; clientaddr->sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(CLIENT_ADDR); /* Part 2 – fill data structure and bind to socket */ if (0 != (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)clientaddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)))) { printf("could not bind server socket to address "); goto end1; } /* part 3: read and write data */ serveraddr = (struct sockaddr_in *)malloc(sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); if (serveraddr == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory to server address socket "); goto end2; } serveraddr->sin_family = AF_INET; serveraddr->sin_port = SERVER_PORT; serveraddr->sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERVER_ADDR); error = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)serveraddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); if (error != 0) { printf("error %d", errno); printf("connect returned error "); goto end2; } /* copy the data after the UDP header */ string_data = (char *) (buffer + sizeof(struct udphdr)); strncpy(string_data, string, strlen(string)); /* Modify some parameters to send to client in UDP hdr */ udp_hdr = (struct udphdr *)buffer; udp_hdr->source = htons(PORT); udp_hdr->dest = htons(SERVER_PORT); udp_hdr->len = htons(sizeof(struct udphdr)); csum_buffer = (char *)calloc((sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr) + sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data)), sizeof(char)); if (csum_buffer == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate csum buffer "); goto end1; } csum_hdr.source_ip_addr = inet_addr(CLIENT_ADDR); csum_hdr.dest_ip_addr = inet_addr(SERVER_ADDR); csum_hdr.fixed = 0; csum_hdr.protocol = IPPROTO_UDP; /* UDP protocol */ csum_hdr.udp_len = htons(sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data) + 1); memcpy(csum_buffer, (char *)&csum_hdr, sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr)); memcpy(csum_buffer + sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr), buffer, (sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data) + 1)); /* since we are resending the same packet over and over again * free the csum buffer here */ free (csum_buffer); while (1) { write(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)); memset(recvbuffer, 0, sizeof(recvbuffer)); read(sockfd, recvbuffer, sizeof(recvbuffer)); udp_hdr = (struct udphdr *)(recvbuffer + sizeof (struct iphdr)); recv_string_data = (char *) (recvbuffer + sizeof (struct iphdr) + sizeof (struct udphdr)); #if DEBUG dumpmsg((unsigned char *)&recvbuffer, (sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct udphdr)+ strlen(string_data) + 1)); #endif if (PORT == ntohs(udp_hdr->dest)) { printf("udp packet received from port %d ",ntohs(udp_hdr->source)); printf("data received from server is : %s ", recv_string_data); } } end2: free(serveraddr); end1: free(clientaddr); end: close(sockfd); return 0; }
bind的作用
给网卡配一个ip
2: enahisic2i0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 48:57:02:64:ea:1b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.10.16.81/24 scope global enahisic2i0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet 10.10.16.250/24 scope global secondary enahisic2i0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever

0 packets dropped by kernel [root@bogon raw-sockets-example]# tcpdump -i enahisic2i0 udp and port 50000 or port 60000 -nnvvv tcpdump: listening on enahisic2i0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 16:39:50.370938 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 17467, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 42) 10.10.16.82.33094 > 10.10.16.250.50000: [udp sum ok] UDP, length 14 16:39:54.069681 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 18218, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 42) 10.10.16.82.47607 > 10.10.16.250.60000: [udp sum ok] UDP, length 14 16:39:59.408240 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 53492, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 42) 10.10.16.82.59967 > 10.10.16.81.60000: [udp sum ok] UDP, length 14 16:39:59.408368 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 28064, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 1044) 10.10.16.81.50000 > 10.10.16.82.50001: [bad udp cksum 0xe53f -> 0x4485!] UDP, length 0 16:40:02.810879 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 53725, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 42) 10.10.16.82.44298 > 10.10.16.81.50000: [udp sum ok] UDP, length 14 16:40:02.811002 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 28125, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 1044) 10.10.16.81.50000 > 10.10.16.82.50001: [bad udp cksum 0xe53f -> 0x4485!] UDP, length 0
从82节点访问
root@ubuntu:~/c++# echo "Hello World!" | nc -4u 10.10.16.250 50000 root@ubuntu:~/c++# echo "Hello World!" | nc -4u 10.10.16.250 60000 root@ubuntu:~/c++# echo "Hello World!" | nc -4u 10.10.16.81 60000 root@ubuntu:~/c++# echo "Hello World!" | nc -4u 10.10.16.81 50000 root@ubuntu:~/c++# ping 10.10.16.250 PING 10.10.16.250 (10.10.16.250) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.10.16.250: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.904 ms 64 bytes from 10.10.16.250: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.097 ms ^C --- 10.10.16.250 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1028ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.097/0.500/0.904/0.404 ms root@ubuntu:~/c++#
raw_udp_server.c
[root@bogon raw-sockets-example]# cat raw_udp_server.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <linux/udp.h> #include <signal.h> #include <errno.h> //#include <linux/ip.h> #include <netinet/ip.h> struct sockaddr_in *servaddr = NULL, *client_addr = NULL; int sock_fd; #define PORT 50000 #define PORT_CLIENT 50001 #define SERVER_ADDR "10.10.16.81" #define CLIENT_ADDR "10.10.16.82" /* structure to calculate UDP checksum * The below members are part of the IP header * which do not change from the UDP layer and hence * are used as a part of the UDP checksum */ struct pseudo_iphdr { unsigned int source_ip_addr; unsigned int dest_ip_addr; unsigned char fixed; unsigned char protocol; unsigned short udp_len; }; /* checksum code to calculate TCP/UDP checksum * Code taken from Unix network programming – Richard stevens*/ unsigned short in_cksum (uint16_t * addr, int len) { int nleft = len; unsigned int sum = 0; unsigned short *w = addr; unsigned short answer = 0; /* Our algorithm is simple, using a 32 bit accumulator (sum), we add * sequential 16 bit words to it, and at the end, fold back all the * carry bits from the top 16 bits into the lower 16 bits. */ while (nleft > 1) { sum += *w++; nleft -= 2; } /* mop up an odd byte, if necessary */ if (nleft == 1) { *(unsigned char *) (&answer) = * (unsigned char *) w; sum += answer; } /* add back carry outs from top 16 bits to low 16 bits */ sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff); /* add hi 16 to low 16 */ sum += (sum >> 16); /* add carry */ answer = (unsigned short) ~sum; /* truncate to 16 bits */ return (answer); } /* Interrupt_handler – so that CTRL + C can be used to * exit the program */ void interrupt_handler (int signum) { close(sock_fd); free(client_addr); exit(0); } #if DEBUG /* print the IP and UDP headers */ void dumpmsg(unsigned char *recvbuffer, int length) { int count_per_length = 28, i = 0; for (i = 0; i < count_per_length; i++) { printf("%02x ", recvbuffer[i]); } printf(" "); } #endif int main () { char buffer[1024] = {0}; unsigned char recvbuffer[1024] = {0}; int length; char *string = "Hello client"; struct udphdr *udp_hdr = NULL; char *string_data = NULL; char *recv_string_data = NULL; char *csum_buffer = NULL; struct pseudo_iphdr csum_hdr; int error; signal (SIGINT, interrupt_handler); signal (SIGTERM, interrupt_handler); /* Part 1: create the socket */ sock_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_UDP); if(0 > sock_fd) { printf("unable to create socket "); exit(0); } servaddr = (struct sockaddr_in *)malloc(sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); if (servaddr == NULL) { printf("could not allocate memory "); goto end; } servaddr->sin_family = AF_INET; servaddr->sin_port = PORT; servaddr->sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERVER_ADDR); /* Part 2 – fill data structure and bind to socket */ if (0 != (bind(sock_fd, (struct sockaddr *)servaddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)))) { printf("could not bind server socket to address "); goto end1; } /* part 3: read and write data */ client_addr = (struct sockaddr_in *)malloc(sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); if (client_addr == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate memory to client address socket "); goto end2; } client_addr->sin_family = AF_INET; client_addr->sin_port = PORT_CLIENT; client_addr->sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(CLIENT_ADDR); error = connect(sock_fd, (struct sockaddr *)client_addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)); if (error != 0) { printf("error %d", errno); printf("connect returned error "); goto end2; } /* copy the data after the UDP header */ string_data = (char *) (buffer + sizeof(struct udphdr)); strncpy(string_data, string, strlen(string)); /* Modify some parameters to send to client in UDP hdr */ udp_hdr = (struct udphdr *)buffer; udp_hdr->source = htons(PORT); udp_hdr->dest = htons(PORT_CLIENT); udp_hdr->len = htons(sizeof(struct udphdr)); /* calculate the UDP checksum – based on wikipedia * pseudo IP header + UDP HDR + * UDP data- check sum is calculated. * create a buffer to calculate CSUM and calculate CSUM*/ csum_buffer = (char *)calloc((sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr) + sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data)), sizeof(char)); if (csum_buffer == NULL) { printf("Unable to allocate csum buffer "); goto end1; } csum_hdr.source_ip_addr = inet_addr(SERVER_ADDR); csum_hdr.dest_ip_addr = inet_addr(CLIENT_ADDR); csum_hdr.fixed = 0; csum_hdr.protocol = IPPROTO_UDP; /* UDP protocol */ csum_hdr.udp_len = htons(sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data) + 1); memcpy(csum_buffer, (char *)&csum_hdr, sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr)); memcpy(csum_buffer + sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr), buffer, (sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data) + 1)); udp_hdr->check = (in_cksum((unsigned short *) csum_buffer, (sizeof(struct pseudo_iphdr)+ sizeof(struct udphdr) + strlen(string_data) + 1))); printf("checksum is %x ", udp_hdr->check); /* since we are resending the same packet over and over again * free the csum buffer here */ free (csum_buffer); while (1) { memset(recvbuffer, 0, sizeof(recvbuffer)); read(sock_fd, recvbuffer, sizeof(recvbuffer)); udp_hdr = (struct udphdr *)(recvbuffer + sizeof (struct iphdr)); recv_string_data = (char *) (recvbuffer + sizeof (struct iphdr) + sizeof (struct udphdr)); #if DEBUG dumpmsg((unsigned char *)&recvbuffer, (sizeof(struct iphdr) + sizeof(struct udphdr)+ strlen(string_data) + 1)); #endif //if (PORT == ntohs(udp_hdr->dest)) { // printf("udp data received from port : %d ",ntohs(udp_hdr->source)); // printf("data received at server from client is: %s ", recv_string_data); //} struct ip *ip = (struct ip*)recvbuffer; printf(" %20s",inet_ntoa(ip->ip_src)); printf("%20s %5d %5d ",inet_ntoa(ip->ip_dst),ip->ip_p,ntohs(ip->ip_len)); printf(" "); printf("udp data received from port : %d ",ntohs(udp_hdr->source)); printf("data received at server from client is: %s ", recv_string_data); write(sock_fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)); } end2: free(client_addr); end1: free(servaddr); end: close(sock_fd); return 0; }