线程和进程的区别是什么?进程是一个正在运行的软件程序,打开资源管理器可以看到好多正在运行的进程,而线程则是程序中的顺序控制流,只能使用分配给程序的资源和环境。一个进程至少存在一个线程(主线程)。
在java中有两种创建线程的方式:继承Thread类和实现Runnable接口。
线程有以下几种状态,创建状态->就绪状态(start)->运行状态(执行run方法)->阻塞状态(暂时停止执行)->终止状态
1. 先来看下线程的实现:
package com.javaTestDemo;
public class JavaThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.继承Thread
// MyThread t1 = new MyThread("A");
// MyThread t2 = new MyThread("B");
//
// t1.start();
// t2.start();
//2.实现runnable接口
MyRunnable r1 = new MyRunnable("A");
MyRunnable r2 = new MyRunnable("B");
Thread t1 = new Thread(r1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(r2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
/**
* 继承Thread
* @author newtouch
*
*/
class MyThread extends Thread
{
String name;
public MyThread(String name)
{
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.run();
for(int i=0;i<20;i++)
{
System.out.println("线程"+name+i);
}
}
}
/**
* 实现runnable接口
* @author newtouch
*
*/
class MyRunnable implements Runnable
{
String name;
public MyRunnable(String name)
{
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<20;i++)
{
System.out.println("线程"+name+i);
}
}
}
可以看到线程输出AB是并发执行的:

2.线程的常用方法
写过自动化测试脚本的同学肯定对这个方法不陌生
Thread.sleep(); 线程休眠
还有哪些常用方法呢?
①取得线程名称 getName()
②取得当前线程对象 currentThread()
③判断线程是否启动 isAlive()
④线程的强行运行 join()
⑤线程礼让 yield()
来看下join()方法和yield()方法:
MyRunnable r1 = new MyRunnable("A");
// MyRunnable r2 = new MyRunnable("B");
Thread t1 = new Thread(r1);
// Thread t2 = new Thread(r2);
//
t1.start();
// t2.start();
//join()方法
for(int i=0;i<30;i++)
{
if(i==5)
{
try {
t1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("主线程:"+i);
}
当主线程执行到i=5的时候,强行让t1线程执行:
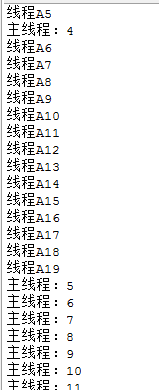
class MyRunnable implements Runnable
{
String name;
public MyRunnable(String name)
{
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<50;i++)
{
System.out.println("线程"+name+i);
if(i==10)
{
System.out.println("礼让");
Thread.yield();
}
}
}
}
当i=10的时候,线程礼让查看输出:
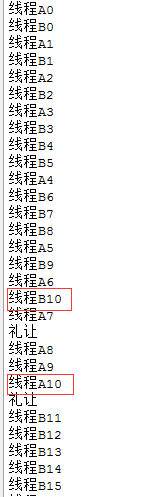
可以看到当两个线程到10的时候都礼让让另一个线程执行
3.线程的同步
举个例子,好几个窗口一同往外卖票,虽然都是并发执行的,但是票数是一定的是共有的,票数是随着多个窗口往外卖而同步减少的,这样的话我们就需要线程同步。
①同步代码块,在代码块加上 synchronized 关键字,则此代码块就被称为同步代码块
格式:
synchronized(同步对象){
需要同步的代码;
}
②同步方法
synchronized void 方法名称(){}
同步代码块:
package com.javaTestDemo; public class JavaThreadDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub MyThreadDemo2 mt = new MyThreadDemo2(); Thread t1 = new Thread(mt); Thread t2 = new Thread(mt); Thread t3 = new Thread(mt); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } } class MyThreadDemo2 implements Runnable { private int ticket = 50; @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<50;i++) { synchronized (this) { if(ticket>0) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"车票:"+ticket--); } } } } }
可以看到输出:
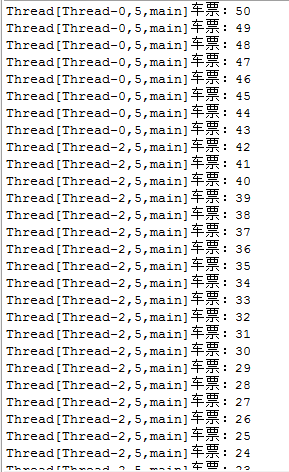
也可以同步方法:
class MyThreadDemo2 implements Runnable { private int ticket = 150; @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<150;i++) { sell(); } } public synchronized void sell(){ if(ticket>0) { try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"车票:"+ticket--); } } }
查看输出:
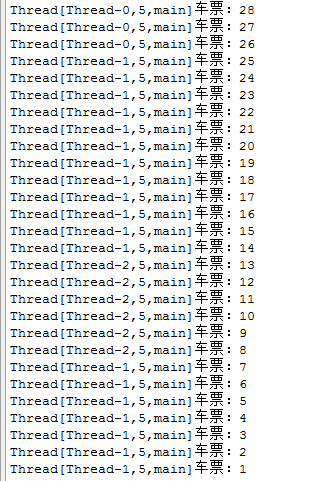
简单记录下线程的入门学习,以后再深入学习理解关于线程的更多知识。