它既是 DispatcherServlet 的 (WebApplicationContext)默认策略,又是 ContextLoaderListener 创建 root WebApplicationContext(根容器,同时也是 DispatcherServlet 的 WebApplicationContext 的父容器)的默认策略。
继承体系
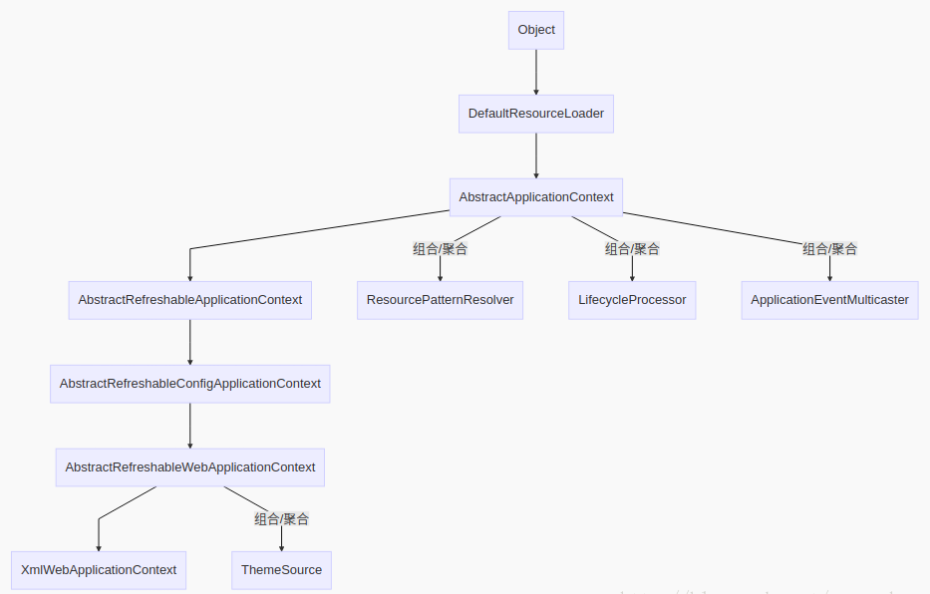
一、XmlWebApplicationContext实例化过程
spring的配置文件加载是以监听的方式加载的xml配置文件
spring-web-4.3.14.RELEASE.jar中的org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.java类,通过ContextLoader初始化和销毁Spring Web上下文的过程。
1、ContextLoader类中有一个静态代码块,这个静态代码块就是从配置中读取到“XmlWebApplicationContext”类
static { // Load default strategy implementations from properties file. // This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized // by application developers. try { //DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties",即加载的是contextLoader.properties的配置文件了 ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class); defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage()); } }
"contextLoader.properties"文件就在ContextLoader.class的相同目录中,
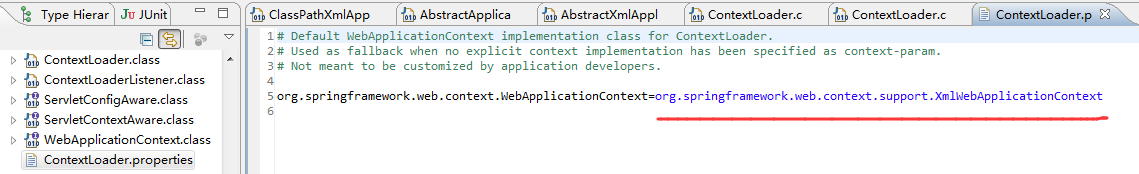
contextLoader.properties:(配置中配置的就是XmlWebApplicationContext)
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
2、上面只是将配置读取到ContextLoader中,下面看看XmlWebApplicationContext怎么初始化的,ContextLoader.initWebApplicationContext方法:
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.java
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//检查是否已经创建了Application context,如果已经存在,抛异常退出
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
//调用createWebApplicationContext,创建XmlWebApplicationContext,
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
// 如果当前的应用上下文对象是 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
//强制类型转换
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
// 如果应用上下文没有生效
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
//// 如果该上下文对象为nul
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
//加载父上下文
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
// 设置父上下文
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//将该上下文对象放入servlet上下文参数中
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
//获取当前线程的类加载器
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// 如果ContextLoader的类加载器和当前线程的类加载器一样,则应用上下文对象赋值给currentContext
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
//否则,就将ContextLoader的类加载器放入到Map中,Map的value是应用上下文对象
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
//最后返回应用上下文对象
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
在ContextLoader.createWebApplicationContext方法中
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) { //获取上下文类 Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc); //如果该上下文类没有实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口则抛出异常 if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]"); } // 返回该上下文类的实例,调用BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass),通过反射,调用XmlWebApplicationContext的无参构造函数实例化XmlWebApplicationContext对象 return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); }
----------------------------BeanUtils.instantiateClass()-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
这里插入BeanUtils.instantiateClass(),BeanUtils使用instantiateClass初始化对象注意:必须保证初始化类必须有public默认无参数构造器,注意初始化内部类时,内部类必须是静态的,否则报错!
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> clazz) throws BeanInstantiationException { Assert.notNull(clazz, "Class must not be null"); if (clazz.isInterface()) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface"); } try { return instantiateClass(clazz.getDeclaredConstructor()); } catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) { throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex); } } public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException { Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null"); try { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor); return ctor.newInstance(args); } //... } @CallerSensitive public T newInstance(Object ... initargs) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException { if (!override) { if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) { Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); checkAccess(caller, clazz, null, modifiers); } } if ((clazz.getModifiers() & Modifier.ENUM) != 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot reflectively create enum objects"); ConstructorAccessor ca = constructorAccessor; // read volatile if (ca == null) { ca = acquireConstructorAccessor(); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T inst = (T) ca.newInstance(initargs); return inst; }
----------------------------BeanUtils.instantiateClass()-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ContextLoader.java中的determineContextClass()方法:
/** * 返回上下文类型 */ protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) { //从servlet上下文中获取初始化配置参数contextClass的值 String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM); // 如果contextClassName不为null则放回配置的Class对象 if (contextClassName != null) { try { return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex); } } else { // 如果没有配置则使用XmlWebApplicationContext,这个代码就是从contextLoad.properties配置中加载进来的,配置中的就是XmlWebApplicationContext contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName()); try { return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex); } } }
在Spring web项目中XmlWebApplicationContext是如何创建的?
首先在web.xml中我们可以看到如下配置:
<context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath*:META-INF/spring/*.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
ContextLoaderListener继承Spring的ContextLoader上下文加载器类,同时实现ServletContextListener接口(Servlet上下文监听器),监听Web服务器上下文的启动和停止事件,管理Web环境中Spring的启动和销毁过程,
首先我们看看这个监听器的源码。初始化的入口是contextInitialized方法,它只是简单地将初始化功能委托为了ContextLoader进行处理。
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener.java
/** * Initialize the root web application context.初始化根WEB应用上下文 */ @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); //调用ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext() }
通过对ContextLoaderListener的源码分析,我们看到ContextLoaderListener继承ContextLoader,所以ContextLoaderListener本身也是Spring的上下文加载器。
ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener接口,当Web应用在Web服务器中被被启动和停止时,Web服务器启动和停止事件会分别触发ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized和contextDestroyed方法来初始化和销毁Spring上下文。我们通过上述对ContextLoaderListener的源码分析看到真正实现Spring上下文的初始化和销毁功能的是ContextLoader类,分析ContextLoader初始化和销毁Spring Web上下文的过程见上面。
ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext()的源码见上面的分析。
在springmvc中,如何实例化XmlWebApplicationContext的?
1、springmvc加载配置文件
<servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet是通过这个servlet,加载配置文件
FrameworkServlet中有一个属性
public static final Class<?> DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = XmlWebApplicationContext.class;
接着看FrameworkServlet的initWebApplicationContext()方法:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { ..... if (wac == null) { // No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } }
方法中有一个FrameworkServlet.createWebApplicationContext(rootContext)方法
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { //这个方法就是创建XmlWebApplicationContext实例的Class Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass(); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" + contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]"); }
//如果该上下文类没有实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口则抛出异常 if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext"); }
//调用BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass),通过反射,调用XmlWebApplicationContext的无参构造函数实例化XmlWebApplicationContext对象 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); wac.setParent(parent); wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation()); configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac); return wac; }
接口看getContextClass()方法:
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();这个方法就是创建XmlWebApplicationContext实例的Class
public Class<?> getContextClass() { return this.contextClass; }
this.contextClass就是前面FrameworkServlet定义的全局变量。
至此,实例化XmlWebApplicationContext的步骤基本相同:
1、通过读取配置文件方式,读取到org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext的类型为“org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext”;
2、检查上下文类没有实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口则抛出异常;
3、调用BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass),通过反射,调用XmlWebApplicationContext的无参构造函数实例化XmlWebApplicationContext对象;
二、XmlWebApplicationContext源码
ContextLoader初始化Spring Web上下文的determineContextClass方法中,我们知道Spring首先通过Servlet上下文从web.xml文件中获取用户自定义配置的contextClass参数值,如果没有获取到,则默认使用Spring的XmlWebApplicationContext作为Spring Web应用的IoC容器,XmlWebApplicationContext是WebApplicationContext的实现类ConfigurableWebApplicationContext的子类
public class XmlWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext { //Web应用中Spring配置文件的默认位置和名称,如果没有特别指定,则Spring会根据 //此位置定义Spring Bean定义资源 public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION = "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml"; //Spring Bean定义资源默认前缀 public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX = "/WEB-INF/"; //Spring Bean定义资源默认后置 public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX = ".xml"; //在分析Spring IoC初始化过程中我们已经分析过,加载Spring Bean定义资源的方法, //通过Spring容器刷新的refresh()方法触发 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { //为Spring容器创建XML Bean定义读取器,加载Spring Bean定义资源 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // resource loading environment. beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); //设置Bean定义读取器,因为XmlWebApplicationContext是DefaultResourceLoader的子类,所以使用默认资源加载器来定义Bean定义资源 beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); //为Bean定义读取器设置SAX实体解析器 beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); //在加载Bean定义之前,调用子类提供的一些用户自定义初始化Bean定义读取器的方法 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); //使用Bean定义读取器加载Bean定义资源 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); } //用户自定义初始化Bean定义读取器的方法 protected void initBeanDefinitionReader(XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader) { } //加载Bean定义资源 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws IOException { //获取定位的Bean定义资源路径 String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { //遍历加载所有定义的Bean定义资源 for (String configLocation : configLocations) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation); } } } //获取默认Bean定义资源 protected String[] getDefaultConfigLocations() { //获取web.xml中的命名空间,如命名空间不为null,则返回 “/WEB-INF/命名空间.xml” if (getNamespace() != null) { return new String[] {DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX + getNamespace() + DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX}; } //如果命名空间为null,则返回"/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml" else { return new String[] {DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION}; } } }
XmlWebApplicationContext将Web应用中配置的Spring Bean定义资源文件载入到Spring IoC容器中后,接下来的Spring IoC容器初始化和依赖注入的过程后面再分析。