一、Spring 容器高层视图
Spring 启动时读取应用程序提供的Bean配置信息,并在Spring容器中生成一份相应的Bean配置注册表,然后根据这张注册表实例化Bean,装配号Bean之间的依赖关系,为上层应用提供准备就绪的运行环境。
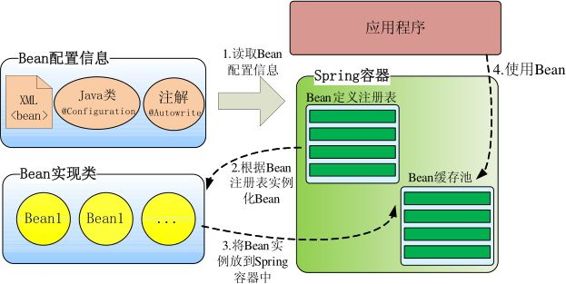
二、内部工作机制
该图描述了Spring容器从加载配置文件到创建出一个完整Bean的作业流程:
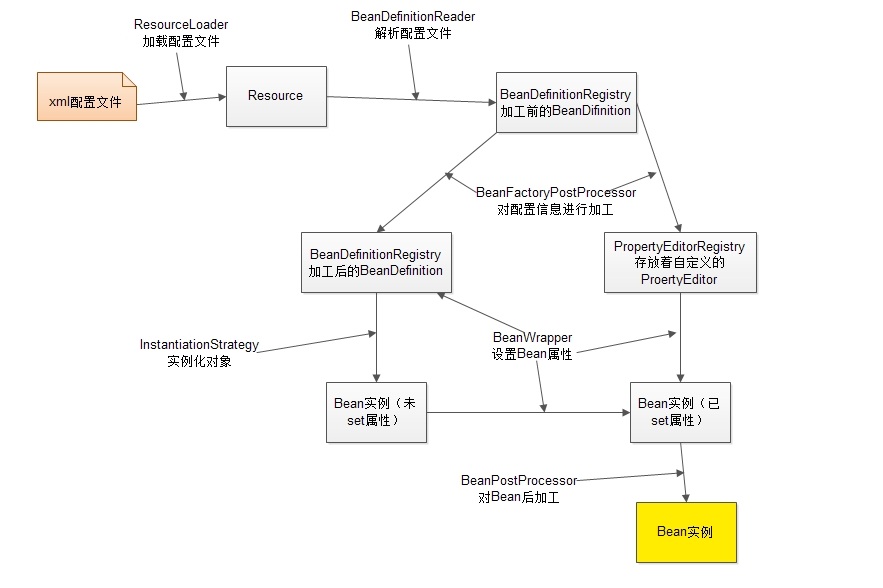
1、ResourceLoader从存储介质中加载Spring配置信息,并使用Resource表示这个配置文件的资源;
2、BeanDefinitionReader读取Resource所指向的配置文件资源,然后解析配置文件。配置文件中每一个<bean>解析成一个BeanDefinition对象,并保存到BeanDefinitionRegistry中;
3、容器扫描BeanDefinitionRegistry中的BeanDefinition,使用Java的反射机制自动识别出Bean工厂后处理后器(实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口)的Bean,然后调用这些Bean工厂后处理器对BeanDefinitionRegistry中的BeanDefinition进行加工处理。主要完成以下两项工作:
1)对使用到占位符的<bean>元素标签进行解析,得到最终的配置值,这意味对一些半成品式的BeanDefinition对象进行加工处理并得到成品的BeanDefinition对象;
2)对BeanDefinitionRegistry中的BeanDefinition进行扫描,通过Java反射机制找出所有属性编辑器的Bean(实现java.beans.PropertyEditor接口的Bean),并自动将它们注册到Spring容器的属性编辑器注册表中(PropertyEditorRegistry);
4.Spring容器从BeanDefinitionRegistry中取出加工后的BeanDefinition,并调用InstantiationStrategy着手进行Bean实例化的工作;
5.在实例化Bean时,Spring容器使用BeanWrapper对Bean进行封装,BeanWrapper提供了很多以Java反射机制操作Bean的方法,它将结合该Bean的BeanDefinition以及容器中属性编辑器,完成Bean属性的设置工作;
6.利用容器中注册的Bean后处理器(实现BeanPostProcessor接口的Bean)对已经完成属性设置工作的Bean进行后续加工,直接装配出一个准备就绪的Bean。
Spring容器确实堪称一部设计精密的机器,其内部拥有众多的组件和装置。Spring的高明之处在于,它使用众多接口描绘出了所有装置的蓝图,构建好Spring的骨架,继而通过继承体系层层推演,不断丰富,最终让Spring成为有血有肉的完整的框架。所以查看Spring框架的源码时,有两条清晰可见的脉络:
1)接口层描述了容器的重要组件及组件间的协作关系;
2)继承体系逐步实现组件的各项功能。
接口层清晰地勾勒出Spring框架的高层功能,框架脉络呼之欲出。有了接口层抽象的描述后,不但Spring自己可以提供具体的实现,任何第三方组织也可以提供不同实现, 可以说Spring完善的接口层使框架的扩展性得到了很好的保证。纵向继承体系的逐步扩展,分步骤地实现框架的功能,这种实现方案保证了框架功能不会堆积在某些类的身上,造成过重的代码逻辑负载,框架的复杂度被完美地分解开了。
Spring组件按其所承担的角色可以划分为两类:
1)物料组件:Resource、BeanDefinition、PropertyEditor以及最终的Bean等,它们是加工流程中被加工、被消费的组件,就像流水线上被加工的物料;
2)加工设备组件:ResourceLoader、BeanDefinitionReader、BeanFactoryPostProcessor、InstantiationStrategy以及BeanWrapper等组件像是流水线上不同环节的加工设备,对物料组件进行加工处理。
三、Spring容器-ApplicationContext的启动过程
ApplicationContext内部封装了一个BeanFactory对象,来实现对容器的操作,初始化完成之后,BeanFactory封装了bean的信息,而ApplicationContext通过访问这个对象获取bean的对象信息(BeanDefinition/Bean对象,都是由BeanFactory实际创建并管理的),为了实现接口的统一,ApplicationContext也实现了一系列的BeanFactory接口(可以说ApplicationContext对BeanFactory对象实现一种代理)。ApplicationContext建立在BeanFactory的基础之上,对配置对象的管理最终还是交于一个DefaultListableBeanFactory来完成(装配地址/访问等),而ApplicationContext在应用这个DefaultListableBeanFactory对象的基础上,不仅实现了BeanFactory接口提供的功能方法,并且黏合了一些面向应用的功能,如资源/国际化支持/框架事件支持等,并且将一些原先需要手动设置到BeanFactory的属性通过配置文件中配置的形式代替(如工厂后处理器BeanPostProcessor/InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor)
同样,因为对于BeanDefinition和bean对象的管理是由上下文持有的beanfactory对象完成的,用户不需要拥有这样的接口,因此,ApplicationContext的接口体系中并没有BeanDefinitionRegistry,SingletonBeanRegistry以及AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口(ApplicationContext可以访问一些接口方法在上述接口中也定义,但这些方法提供者为BeanFactory体系中的其他接口,BeanFactory接口体系中的接口之间有重复定义方法的)。
内部工作机制(Spring容器ApplicationContext的初始化)
(一) 首先来看创建ApplicationContext ,以ClassPathXmlApplicationContext为例:
ApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
源码如下:
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext { public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException { this(new String[] {configLocation}); } public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, (ApplicationContext) null); } //。。。。。。省略几个重载的构造函数 public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); this.configLocations = configLocations; //IoC容器的初始化过程,其初始化过程的大致步骤由AbstractApplicationContext来定义 refresh(); }
关键之处在于refresh方法,此方法继承于ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的间接父类:
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean {
Spring的AbstractApplicationContext是ApplicationContext抽象实现类,该抽象类的refresh()方法定义了Spring容器在加载配置文件后的各项处理过程,这些处理过程清晰刻画了Spring容器启动时所执行的各项操作(创建Spring容器如ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)。下面,我们来看一下refresh()内部定义了哪些执行逻辑:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();--------(1) // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);-------------------------------------(2) // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);---------------------------------------------(3) // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource();-------------------------------------------------------------------------(4) // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster();-----------------------------------------------------------(5) // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh();------------------------------------------------------------------------------------(6) // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners();----------------------------------------------------------------------------(7) // Instantiate singletons this late to allow them to access the message source. beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();--------------------------------------------------(8) // Last step: publish corresponding event. publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));---------------------------------------(9) } catch (BeansException ex) { // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. beanFactory.destroySingletons(); throw ex; } } } protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { refreshBeanFactory(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); return beanFactory; } protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException; public abstract ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
1.初始化BeanFactory:根据配置文件实例化BeanFactory,getBeanFactory()方法由具体子类实现。在这一步里,Spring将配置文件的信息解析成为一个个的BeanDefinition对象并装入到容器的Bean定义注册表(BeanDefinitionRegistry)中,但此时Bean还未初始化;obtainFreshBeanFactory()会调用自身的refreshBeanFactory(),而refreshBeanFactory()方法由子类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext实现,该方法返回了一个创建的DefaultListableBeanFactory对象,这个对象就是由ApplicationContext管理的BeanFactory容器对象。
这一步的操作相当于,如果我们在自己的应用代码中不用ApplicationContext而直接用BeanFactory时创建BeanFactory对象的操作
核心代码如下:
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext { } /** 该ApplicationContext管理的BeanFactory容器对象*/ private DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory; protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { // Shut down previous bean factory, if any. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory oldBeanFactory = null; synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { oldBeanFactory = this.beanFactory; } if (oldBeanFactory != null) { oldBeanFactory.destroySingletons(); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = null; } } // Initialize fresh bean factory. try { // 创建容器对象 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); // Customize the internal bean factory used by this context customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); // 装载配置文件,并传入相关联的BeanFactory对象,作为BeanDefinition的容器 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "I/O error parsing XML document for application context [" + getDisplayName() + "]", ex); } } // 创建Spring默认的容器对象 protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() { return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory()); } // 该方法为一个钩子方法,子类可以覆盖它对当前上下文管理的BeanFactory提供客户化操作,也可以忽略 protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { } // 装载配置文件的方法,需要子类实现 protected abstract void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws IOException, BeansException;
对于上面装载配置文件的方法,由其子类扩展实现:
public abstract class AbstractXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext {} protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws IOException { // 使用XMLBeanDefinitionReader来载入bean定义信息的XML文件,传入关联的BeanFactory XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // 这里配置reader的环境,其中ResourceLoader是我们用来定位bean定义信息资源位置的 // 因为上下文本身实现了ResourceLoader接口,所以可以直接把上下文作为ResourceLoader传递入 beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); // 这里转到定义好的XmlBeanDefinitionReader中对载入bean信息进行处理 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); } protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } } reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);涉及到XmlBeanDefinitionReader 工具类的使用(以后整理)
2.调用工厂后处理器:根据反射机制从BeanDefinitionRegistry中找出所有BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的Bean,并调用其postProcessBeanFactory()接口方法;
经过第一步加载配置文件,已经把配置文件中定义的所有bean装载到BeanDefinitionRegistry这个Beanfactory中,对于ApplicationContext应用来说这个BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的BeanFactory就是Spring默认的DefaultListableBeanFactory
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry
在这些被装载的bean中,若有类型为BeanFactoryPostProcessor的bean(配置文件中配置的),则将对应的BeanDefinition生成BeanFactoryPostProcessor对象
容器扫描BeanDefinitionRegistry中的BeanDefinition,使用java反射自动识别出Bean工厂后处理器(实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口)的bean,然后调用这些bean工厂后处理器对BeanDefinitionRegistry中的BeanDefinition进行加工处理,可以完成以下两项工作(当然也可以有其他的操作,用户自己定义):
1 对使用到占位符的<bean>元素标签进行解析,得到最终的配置值,这意味着对一些半成品式的BeanDefinition对象进行加工处理并取得成品的BeanDefinition对象。2 对BeanDefinitionRegistry中的BeanDefinition进行扫描,通过Java反射机制找出所有属性编辑器的Bean(实现java.beans.PropertyEditor接口的Bean),并自动将它们注册到Spring容器的属性编辑器注册表中(PropertyEditorRegistry),这个Spring提供了实现:CustomEditorConfigurer,它实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,用它来在此注册自定义属性编辑器;
AbstractApplicationContext中的代码如下:
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance. for (Iterator it = getBeanFactoryPostProcessors().iterator(); it.hasNext();) { BeanFactoryPostProcessor factoryProcessor = (BeanFactoryPostProcessor) it.next(); factoryProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // 通过ApplicatinContext管理的beanfactory获取已经注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的bean的名字 String[] factoryProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement the Ordered // interface and those that do not. List orderedFactoryProcessors = new ArrayList(); List nonOrderedFactoryProcessorNames = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < factoryProcessorNames.length; i++) { if (isTypeMatch(factoryProcessorNames[i], Ordered.class)) { // 调用beanfactory的getBean取得所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor对象 orderedFactoryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(factoryProcessorNames[i])); } else { nonOrderedFactoryProcessorNames.add(factoryProcessorNames[i]); } } // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. Collections.sort(orderedFactoryProcessors, new OrderComparator()); for (Iterator it = orderedFactoryProcessors.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { BeanFactoryPostProcessor factoryProcessor = (BeanFactoryPostProcessor) it.next(); // 执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法,传入当前持有的beanfactory对象,以获取要操作的 // BeanDefinition factoryProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); } // Second, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors, one by one. for (Iterator it = nonOrderedFactoryProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { String factoryProcessorName = (String) it.next(); ((BeanFactoryPostProcessor) getBean(factoryProcessorName)). postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); } }
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口代码如下,实际的操作由用户扩展并配置--扩展点
参考:spring扩展点之一:BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor
3.注册Bean后处理器:根据反射机制从BeanDefinitionRegistry中找出所有BeanPostProcessor类型的Bean,并将它们注册到容器Bean后处理器的注册表中;
AbstractApplicatinContext中对应代码如下:
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { String[] processorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + processorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); List orderedProcessors = new ArrayList(); List nonOrderedProcessorNames = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < processorNames.length; i++) { if (isTypeMatch(processorNames[i], Ordered.class)) { orderedProcessors.add(getBean(processorNames[i])); } else { nonOrderedProcessorNames.add(processorNames[i]); } } // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. Collections.sort(orderedProcessors, new OrderComparator()); for (Iterator it = orderedProcessors.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { // 注册bean后处理器,该方法定义于ConfigurableBeanFactory接口 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor((BeanPostProcessor) it.next()); } // Second, register all other BeanPostProcessors, one by one. for (Iterator it = nonOrderedProcessorNames.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { String processorName = (String) it.next(); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor((BeanPostProcessor) getBean(processorName)); } }
整段代码类似于第三步的调用工厂后处理器,区别之处在于,工厂后处理器在获取后立即调用,而Bean后处理器在获取后注册到上下文持有的beanfactory中,供以后操作调用(在用户获取bean的过程中,对已经完成属性设置工作的Bean进行后续加工,他加工的是bean,而工厂后处理器加工的是BeanDefinition)
BeanPostProcessor 接口代码如下,实际的操作由用户扩展并配置--扩展点
参考:spring扩展点之一:BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor
4.初始化消息源:初始化容器的国际化信息资源;
源代码如下:
protected void initMessageSource() {
// 补充
}
5.初始化应用上下文事件广播器;(观察者模式中的具体主题角色,持有观察者角色的集合,称为注册表)
AbstractApplciationContext拥有一个applicationEventMulticaster 成员变量,applicationEventMulticaster 提供了容器监听器的注册表,成其为事件广播器。在第七步中将会将事件监听器装入其中
AbstractApplicationContext中的代码如下:
private ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster; protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() { // "applicationEventMulticaster",先看配置文件中有无配置该类型类(用户扩展 扩展点,如何扩展) if (containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { this.applicationEventMulticaster = (ApplicationEventMulticaster) getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class); } else { // 若没有,则应用Spring框架提供的事件广播器实例 this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(); } } public boolean containsLocalBean(String name) { return getBeanFactory().containsLocalBean(name); } public Object getBean(String name, Class requiredType) throws BeansException { return getBeanFactory().getBean(name, requiredType); }
Spring初始化事件广播器,用户可以在配置文件中为容器定义一个自定义的事件广播器(bean的名称要为"applicationEventMulticaster"),只要实现ApplicationEventMulticaster就可以了,Spring在此会根据beanfactory自动获取。如果没有找到外部配置的事件广播器,Spring使用SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster作为事件广播器。
6.初始化其他特殊的Bean:这是一个钩子方法,子类可以借助这个钩子方法执行一些特殊的操作:如AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext就使用该钩子方法执行初始化ThemeSource的操作;
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {//--扩展点 package org.springframework.context; // For subclasses: do nothing by default. }
7.注册事件监听器;(观察者模式中的观察者角色)
Spring根据上下文持有的beanfactory对象,从它的BeanDefinitionRegistry中找出所有实现org.springfamework.context.ApplicationListener的bean,将BeanDefinition对象生成bean,注册为容器的事件监听器,实际的操作就是将其添加到事件广播器所提供的监听器注册表中
AbstractApplicationContext中的代码如下:
/** Statically specified listeners */ private List applicationListeners = new ArrayList(); public List getApplicationListeners() { return this.applicationListeners; } protected void registerListeners() { // Register statically specified listeners first. for (Iterator it = getApplicationListeners().iterator(); it.hasNext();) { addListener((ApplicationListener) it.next()); } // 获取ApplicationListener类型的所有bean,即事件监听器 // uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! Collection listenerBeans = getBeansOfType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false).values(); for (Iterator it = listenerBeans.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { // 将事件监听器装入第五步初始化的事件广播器 addListener((ApplicationListener) it.next()); } } public Map getBeansOfType(Class type, boolean includePrototypes, boolean allowEagerInit) throws BeansException { return getBeanFactory().getBeansOfType(type, includePrototypes, allowEagerInit); } protected void addListener(ApplicationListener listener) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); }
ApplicationListener 的源代码如下:
package org.springframework.context; import java.util.EventListener; /** * Interface to be implemented by application event listeners. * @see org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster */ public interface ApplicationListener extends EventListener { void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event); }
--扩展点 参考:spring扩展点之三:Spring 的监听事件 ApplicationListener 和 ApplicationEvent 用法,在spring启动后做些事情
8.初始化singleton的Bean:实例化所有singleton的Bean,并将它们放入Spring容器的缓存中;这就是和直接在应用中使用BeanFactory的区别之处,在创建ApplicationContext对象时,不仅创建了一个BeanFactory对象,并且还应用它实例化所有单实例的bean。
AbstractApplicationContext中的代码如下:
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
关于BeanFactory体系的代码参照。。。。。。
9.发布上下文刷新事件:在此处时容器已经启动完成,发布容器refresh事件(ContextRefreshedEvent)
创建上下文刷新事件,事件广播器负责将些事件广播到每个注册的事件监听器中。
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)); public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null"); // 在此获取事件广播器,并调用其方法发布事件:调用所有注册的监听器的方法 getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(event); if (this.parent != null) { this.parent.publishEvent(event); } }
至此,ApplicationContext对象就完成了初始化工作:创建BeanFactory来装配BeanDefiniton,加工处理BeanDefiniton,注册了bean后处理器,初始化了消息资源,初始化了应用上下文事件广播器,注册了事件监听器,初始化了所有singleton的bean,最后发布上下文刷新事件