*digital exam (DE)*, *multiple choice*
Lecture content:
- slides02 - uninformed search;
- slides03 - informed search;
- slides04 - Non-determinism and partial observability
- slides05 -
What is a search problem?
Informally: Given an initial state, a goal state (or set of goal states) and a set of available actions. Find a sequence of actions that take you from the initial state to the goal state.

Tree search VS graph search:
Tree search can visit a state multiple times. And as such it will explore the "sub tree" found after this state several times, which can be expensive. Graph search fixes this by keeping track of all visited states in a closed list. If a newly found successor to next is already known, it won't be inserted into the open list

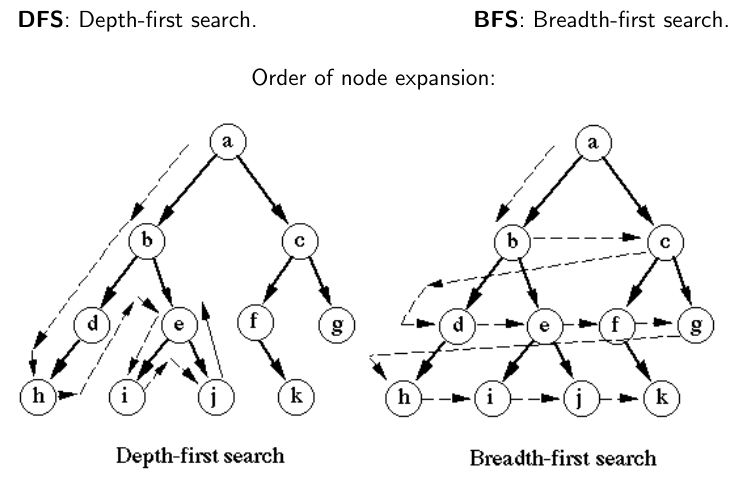
The search has two types of nodes:
• Expanded nodes: Nodes for which all children have been generated.
• Frontier: Nodes that have been generated, but for which we haven’t yet computed the children.


Informed search
Best-first search strategies with Graph-Search
Best-first search:
• Frontier is a priority queue where the key of a node n is denoted f (n).
• choose a node n from frontier : extract minimal node from priority queue, that is, a node n with minimal f (n).
• add child m to frontier: insert node into priority queue.

A* search:
The most widely known form of best-first search is called A∗ search (pronounced “A-star search”). It evaluates nodes by combining g(n), the cost to reach the node, and h(n), the cost to get from the node to the goal:
f(n)=g(n)+h(n).
A∗search is both complete and optimal.
Conditions for optimality: Admissibility and consistency


Non-determinism and partial observability
• Deterministic. Every action has a unique outcome.
• Fully observable. The full state description is accessible to the agent.
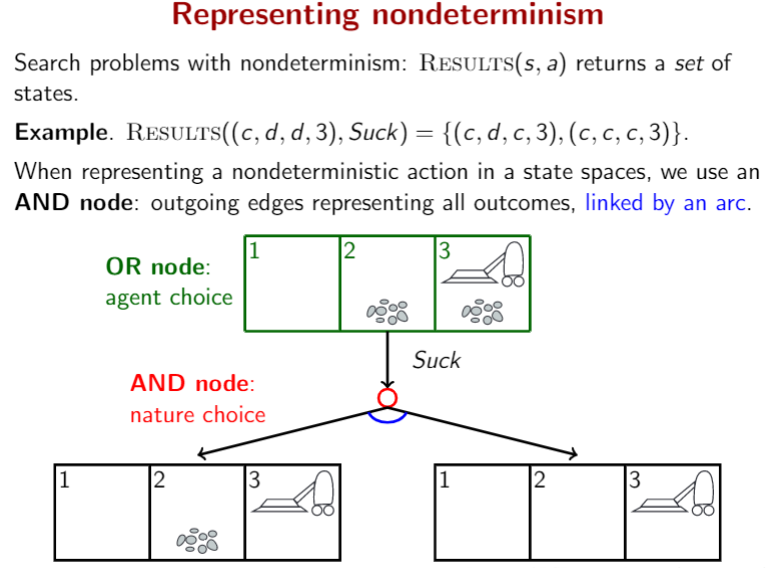
Deterministic search problems: Solution is a path in state space, can be turned into a sequence of Actions (sequential plan).
Nondeterministic search problems: Solution is a subtree of state space, can be turned into a conditional plan (contingency plan). every leaf of T` is a goal state.
Partial observability means that the full state might not be observable. E.g. vacuum cleaning robot not knowing which squares are clean.
Null observability: Partial observability where nothing can be observed about the current state. Search problems under null observability are called conformant problems or sensorless problems.
Belief state: A set of (physical) states. Contains the states considered possible by an agent in a given state.
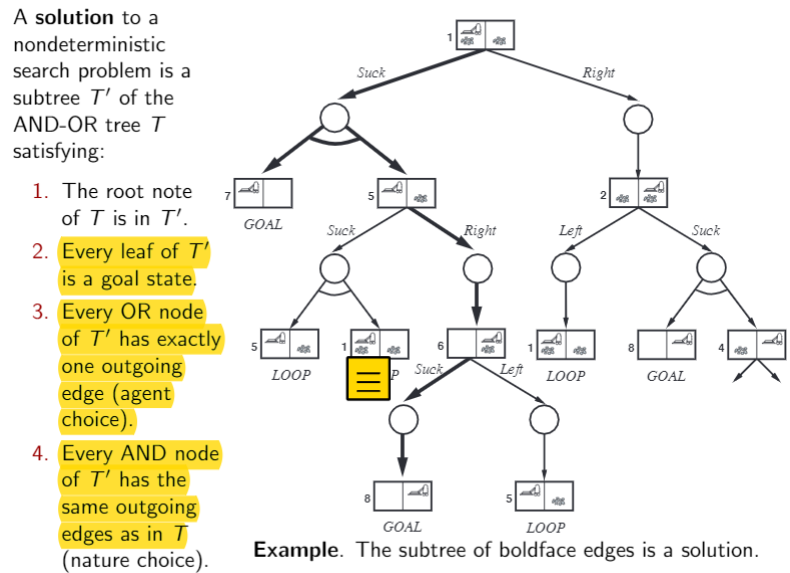
subtree: 到达OR node (action)的时候,只选一条边,到达AND node(possible states)的时候所有的子节点要包含进去。 包含起始节点;所有叶子节点都得是goal state.