先介绍一下TensorFlow自带的数据格式:
TensorFlow自带一种数据格式叫做tfrecords。 你可以把你的输入转成专属与TensorFlow的tfrecords格式并保存在本地。
-关于输入碎碎念:输入比如图片,可以有各种格式呀首先你从网上下载到的一般是png或者jpg格式的吧, 你可以把它存成一个矩阵的形式(numpy ndarray),如果不用TensorFlow自带的tfrecords,你其实也可以存成python独有的pickle文件哈。
那么要怎样把数据存成tfrecords呢?
当然是用TensorFlow api库啦,就是下面这个Class:
tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter
__init__(self, path, options=None)
Opens file `path` and creates a `TFRecordWriter` writing to it.
Args:
path: The path to the TFRecords file.
options: (optional) A TFRecordOptions object.
在参数列表里指明你想要存放的路径。
tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter('SVHN/train.tfrecords')
虽然有一点没逻辑,但是我还是要介绍一下在处理图片数据输入需要用到的一个TensorFlow Class:
class GFile(tensorflow.python.lib.io.file_io.FileIO)
这是一个用来处理文件IO的类,它包含一个类似正则的查找匹配的函数我们可以用它来找到我们想要的文件->tf.gfile.Glob
它返回一个包含所有满足条件元素的列表。
初始化一个TFRecordWriter完成后,就等于知道了tfrecords的存放路径,接下来就要往这个文件中存数据呀!这里用到了这个类的write函数。
tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter
write(self, record)
Write a string record to the file.
Args:
record: str
当要读取tfrecords中的数据时,要做以下的事情:
首先呢需要一个pipeline,然后需要将tfrecords的存放路径作为一个str放入到一个queue中。string_input_producer这个函数负责完成这件事。
string_input_producer(string_tensor, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True, seed=None, capacity=32, shared_name=None, name=None, cancel_op=None)
Output strings (e.g. filenames) to a queue for an input pipeline.
这个函数需要传入一个文件名list,系统会自动将它转为一个文件名队列。
tf.train.string_input_producer还有两个重要的参数,一个是num_epochs,它就epoch数。另外一个就是shuffle,shuffle是指在一个epoch内文件的顺序是否被打乱。
在tensorflow中,内存队列不需要我们自己建立,我们只需要使用reader对象从文件名队列中读取数据就可以了。
类似的TensorFlow有相对应的TFRecordReader类来读取。
class TFRecordReader(ReaderBase)
A Reader that outputs the records from a TFRecords file
__init__(self, name=None, options=None)
Create a TFRecordReader.
Args:
name: A name for the operation (optional).
options: A TFRecordOptions object (optional).
初始化一个TFRecordWriter完成后,接下来就要往这个文件中读数据呀!这里用到了这个类的read函数。
read(self, queue, name=None)
Returns the next record (key, value) pair produced by a reader.
Will dequeue a work unit from queue if necessary (e.g. when the
Reader needs to start reading from a new file since it has
finished with the previous file).
Args:
queue: A Queue or a mutable string Tensor representing a handle
to a Queue, with string work items.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A tuple of Tensors (key, value).
key: A string scalar Tensor.
value: A string scalar Tensor.
当要读取整个文件的时候,也可以使用WholeFileReader这个阅读器。它是TensorFlow提供的一个类。class tf.WholeFileReader
一个阅读器,读取整个文件,返回文件名称key,以及文件中所有的内容value。
创建阅读器之后,要从文件名队列中读取文件。
read(queue, name=None) method of tensorflow.python.ops.io_ops.WholeFileReader instance
Returns the next record (key, value) pair produced by a reader.返回下一个文件名称key和文件中所有内容的value。
Will dequeue a work unit from queue if necessary (e.g. when the
Reader needs to start reading from a new file since it has
finished with the previous file).
如果需要,会从队列中出队一个单元。读取器在完成上一个文件后,继续读取下一个文件。
Args:
queue: A Queue or a mutable string Tensor representing a handle
to a Queue, with string work items.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A tuple of Tensors (key, value).
key: A string scalar Tensor.
value: A string scalar Tensor.
关于TensorFlow的读取机制:
转载于https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27238630
什么是数据读取?假设我们的硬盘中有一个图片数据集0001.jpg,0002.jpg,0003.jpg……我们只需要把它们读取到内存中,然后提供给GPU或是CPU进行计算。
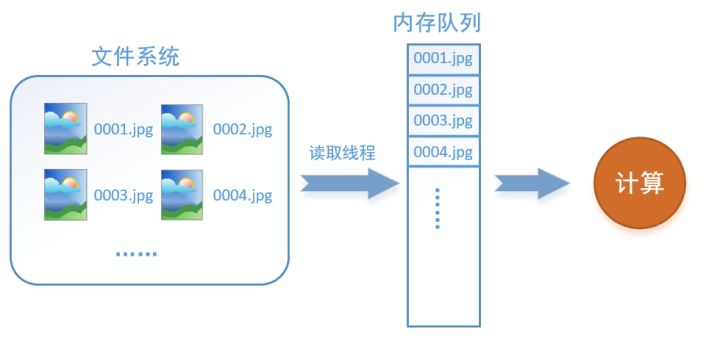
读取线程源源不断地将文件系统中的图片读入到一个内存的队列中,而负责计算的是另一个线程,计算需要数据时,直接从内存队列中取就可以了。这样就可以解决GPU因为IO而空闲的问题!
而在tensorflow中,为了方便管理,在内存队列前又添加了一层所谓的“文件名队列”。
为什么要添加这一层文件名队列?我们首先得了解机器学习中的一个概念:epoch。对于一个数据集来讲,运行一个epoch就是将这个数据集中的图片全部计算一遍。
