题意:一个细胞自动机包含 n 个格子,每个格子取值是 0 ~ m-1,给定距离,则每次操作后每个格子的值将变成到它距离不超过 d 的所有格子在操作之前的值之和取模 m 后的值,其中 i 和 j 的距离为 min{|i-1|, n-|i-j|}。给定 n,m,d,k 和自动机每个格子的初始值,求 k 次操作后的各个格子的值。
析:由于能够直接能推出公式,而且 k 比较大,很容易想到是矩阵快速幂,并且也能够写出矩阵方程。假设 d = 1
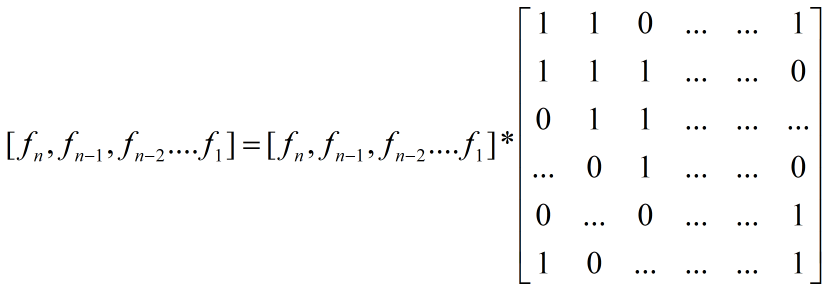
很容易得到这个矩阵,然后使用矩阵快速幂,但是复杂度是 O(n^3*logk),而且还有多组数据,会TLE的,然后考虑优化,从这个矩阵可以看出这是一个循环矩阵,也就是第 i 列可以由第 i-1 列通过向下移动一个得到,而且还有结论,那就是两个循环矩阵相乘得到的矩阵依然是循环矩阵,既然的话,我们就可以只保留第一列就可以了,因为其他列都可以由于第一列得到,由于只要算一次,那么在矩阵相乘的时候,时间复杂度就不是O(n^3) 了,而是O(n^2),然后再加上快速幂,总时间复杂度就是O(n^2*logk),可以解决这个问题。
代码如下:
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cctype>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <sstream>
#include <list>
#include <assert.h>
#include <bitset>
#include <numeric>
#define debug() puts("++++")
#define gcd(a, b) __gcd(a, b)
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sqr(x) ((x)*(x))
#define ms(a,b) memset(a, b, sizeof a)
#define sz size()
#define pu push_up
#define pd push_down
#define cl clear()
#define lowbit(x) -x&x
//#define all 1,n,1
#define FOR(i,n,x) for(int i = (x); i < (n); ++i)
#define freopenr freopen("in.in", "r", stdin)
#define freopenw freopen("out.out", "w", stdout)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<int, int> P;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LNF = 1e17;
const double inf = 1e20;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int maxn = 500 + 5;
const int maxm = 1e6 + 2;
const LL mod = 1000000007;
const int dr[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, -1, -1};
const int dc[] = {0, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 1, -1};
const char *de[] = {"0000", "0001", "0010", "0011", "0100", "0101", "0110", "0111", "1000", "1001", "1010", "1011", "1100", "1101", "1110", "1111"};
int n, m;
const int mon[] = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
const int monn[] = {0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
inline bool is_in(int r, int c) {
return r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m;
}
struct Matrix{
int a[maxn], n;
void init(){ ms(a, 0); }
void toOne(){ a[0] = 1; }
Matrix operator * (const Matrix &rhs){
Matrix res; res.n = n; res.init();
FOR(i, n, 0) FOR(j, n, 0) res.a[i] = (res.a[i] + (LL)a[(i-j+n)%n] * rhs.a[j]) % m;
return res;
}
};
Matrix fast_pow(Matrix x, int n){
Matrix res; res.n = x.n; res.init(); res.toOne();
while(n){
if(n&1) res = res * x;
x = x * x;
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
int d, k;
while(scanf("%d %d %d %d", &n, &m, &d, &k) == 4){
Matrix x, y; x.init(); y.init();
x.n = y.n = n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) scanf("%d", &x.a[i]);
y.a[0] = 1;
int cnt = 1;
while(cnt <= d) y.a[cnt] = 1, ++cnt;
cnt = 1;
while(cnt <= d) y.a[n-cnt] = 1, ++cnt;
Matrix ans = x * fast_pow(y, k);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf("%d%c", ans.a[i], "
"[i+1==n]);
}
return 0;
}