1.numpy.random.uniform(low,high,size)
例如:numpy.random.uniform(-0.25,0.25,300) 随机的产生大小在[-0.25,0.25)之间维度为300的nparray 随机初始化词向量有论文说-0.25,0.25之间较好
2.Python内置的range()和Numpy中的arange()函数的区别
Range(5)只有一个参数则默认从0开始步长为1输出0,1,2,3,4
Range(1,5)此时从1开始步长为1输出1,2,3,4
Range(1,5,2)此时从1开始步长为2输出1,3.注意写为range(5,2)并不会代表从0开始到5步长为2,这是不对的,此外对于步长也不可设置为小数
arange()函数具备以上特性但是其步长可以设置为小数。同时它返回的是一个ndarray()所以具备reshape()属性
当arange与浮点参数一起使用时,由于浮点数的精度是有限的,通常不可能预测获得的元素数量。出于这个原因,通常最好使用函数linspace,它接收我们想要的元素数量而不是步长作为参数:
np.linspace( 0, 2, 9 )# 9 numbers from 0 to 2
3.python中字典的items()
items函数,将一个字典以列表的形式返回,因为字典是无序的,所以返回的列表也是无序的。items()方法把字典中每对key和value组成一个元组,并把这些元组放在列表中返回。
4.字典的get函数
_dict.get(key,value) #若字典中不存在相应的key,则默认的key对应为value
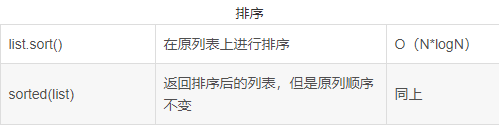
5.argsort()函数和sort、sorted函数以及lambda创建匿名函数的用法
sort 是应用在 list 上的方法,sorted 可以对所有可迭代的对象进行排序操作。list的sort方法返回的是对已经存在的列表进行操作,而内建函数 sorted 方法返回的是一个新的 list,而不是在原来的基础上进行的操作。
例如:对List进行排序只需_list.sort()
Sorted的语法:
sorted(iterable[, cmp[, key[, reverse]]])
参数说明:
iterable -- 可迭代对象。
cmp -- 比较的函数,这个具有两个参数,参数的值都是从可迭代对象中取出,此函数必须遵守的规则为,大于则返回1,小于则返回-1,等于则返回0。
key -- 主要是用来进行比较的元素,只有一个参数,具体的函数的参数就是取自于可迭代对象中,指定可迭代对象中的一个元素来进行排序。
reverse -- 排序规则,reverse = True 降序 , reverse = False 升序(默认)。
返回值:返回重新排序的列表
例如通过sorted对字典进行排序
import operator _dict={'a':1,'b':3} sorted_dict=sorted(_dict.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True)
返回的sorted_dict是排序好的列表[('b', 3), ('a', 1)]
或者:
_dict = {'a': 1, 'b': 3}
sorted_dict = sorted(_dict.items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
argsort()函数
import numpy as np
x=np.array([1,4,3,-1,6,9])
y=x.argsort()
我们发现argsort()函数是将x中的元素从小到大排列,提取其对应的index(索引),然后输出
print(y) 则为[3,0,2,1,4,5]
6.遍历多个序列zip()的使用
同时遍历两个或更多的序列,使用zip()函数可以成对读取元素。
questions = ['name','quest','color'] answers = ['lancelot','holy','blue','blue'] for q, a in zip(questions, answers): print(q,a)
输出:
name lancelot
quest holy
color blue
注意:以短列表为遍历的结束标准
若a_list=['flower','flow','flight']
想对a_list中的每个元素遍历
for i in zip(*a_list):
print(i)
输出为:
('f', 'f', 'f')
('l', 'l', 'l')
('o', 'o', 'i')
('w', 'w', 'g')
注意:以a_list中最短的元素为结束标准,zip的外层也可以加enumerate
7.numpy中的np.dot, np.multiply, *
以下说的矩阵和数组都是数据类型
np.multiply对于数组和矩阵而言都是对应的元素相乘,其中一个是矩阵一个是数组也是对应的元素相乘
*对于数组而言对应的是元素相乘,*对于矩阵而言是运行矩阵相乘(注意一个乘数是矩阵一个是数组也是矩阵相乘)
dot()不管对于两个矩阵、两个数组、还是一个矩阵一个数组而言都是运行的矩阵相乘
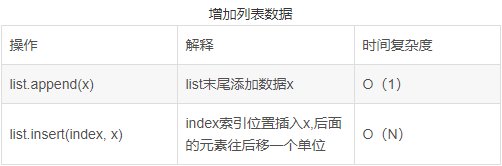
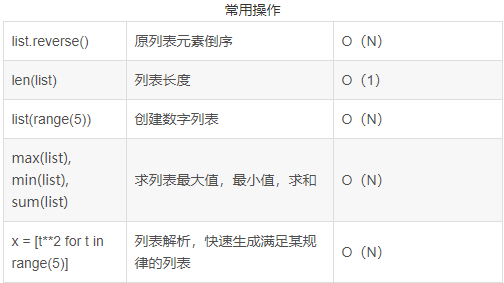
8.列表常用操作的时间复杂度
用的最多的切片,其时间复杂度为0(n)



9.通过分层采样对数据集进行划分
train_con0,dev_con0,train_con1,dev_con1,train_label1,dev_label1=train_test_split(con_0,con_1,label,test_size=0.1,random_state=4,stratify=label)
进行分层采样:保证测试集和训练集的分布比例相同。
数据不均衡时采用此方法
10.数据打乱
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
train_df=shuffle(train_df)
11.TensorFlow设置最多保留几个检测点
saver=tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=5) #最多保留5个,默认就是保留5个
12.欧氏距离与余弦相似度计算相似度的区别
https://www.cnblogs.com/HuZihu/p/10178165.html
13.tf.name_scope与tf.variable_scope用法区别
具体参考:https://blog.csdn.net/daizongxue/article/details/84284007
总结:
1.`tf.variable_scope`和`tf.get_variable`必须要搭配使用(全局scope除外),为参数共享提供支持。
with tf.variable_scope('scp', reuse=True) as scp: a = tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) print(a.name)
报错,因为reuse=True是,get_variable会强制共享,如果不存在,报错
with tf.variable_scope('scp', reuse=False) as scp: a = tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) a = tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) print(a.name)
报错,因为reuse=False时,会强制创造,如果已经存在,也会报错。
如果想实现“有则共享,无则新建”的方式,可以:
with tf.variable_scope('scp', reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE) as scp: a = tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) print(a.name) a = tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) print(a.name)
输出为:
scp/a:0
scp/a:0
2.`tf.Variable`可以单独使用,也可以搭配`tf.name_scope`使用,给变量分类命名,模块化,这样。
3. `tf.Variable`和`tf.variable_scope`搭配使用不伦不类,不是设计者的初衷。
对于使用tf.Variable来说,tf.name_scope和tf.variable_scope功能一样,都是给变量加前缀,相当于分类管理,模块化。
4.对于tf.get_variable来说,tf.name_scope对其无效,也就是说tf认为当你使用tf.get_variable时,你只归属于tf.variable_scope来管理共享与否
with tf.name_scope('scp') as scp: a=tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) print(a.name)
输出:a:0
5.tf.variable_scope默认的reuse=False
with tf.variable_scope('scp') as scp: a=tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) print(a.name)
输出为:scp/a:0
6.直接使用tf.get_variable默认是直接创建,若存在则报错,必须结合tf.variable_scope共享
a=tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1))
print(a.name)
输出:a:0
a=tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) a=tf.get_variable('a',shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) print(a.name)
报错
7.tf.Variable()会自动检测有没有变量重名,如果有则会自行处理
14.collections中双向队列deque和List对比
主要是插入元素尤其是从左端不断插入元素时用双向队列更省时
因为List是连续的空间,insert的时间复杂度为O(n),双向队列是链表实现的,insert以及appendleft时间复杂度都为O(1)
# coding:utf8
import time
from collections import deque
D = deque()
L = []
def calcTime(func):
def doCalcTime():
sst = int(time.time() * 1000)
func()
eed = int(time.time() * 1000)
print(func, 'cost time:', eed - sst, 'ms')
return doCalcTime
@calcTime
def didDeque():
for i in range(0, 100000):
D.insert(0,i)
@calcTime
def didList():
for i in range(0, 100000):
L.insert(0,i)
if __name__ == '__main__':
didDeque()
print("------------")
didList()